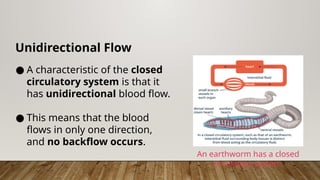
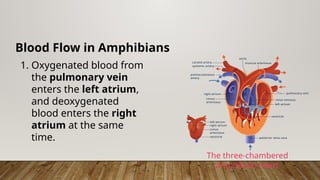
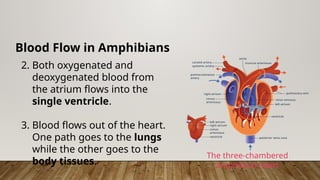
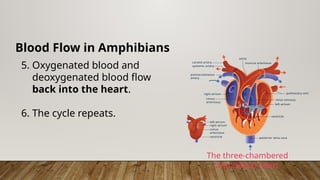
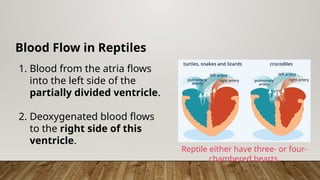
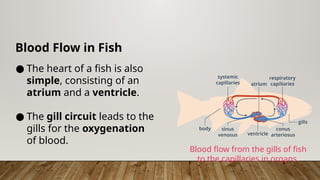
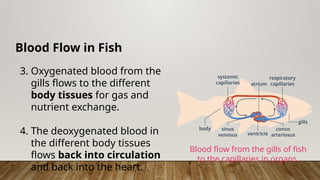
The closed circulatory system consists of a heart, blood, and blood vessels, allowing for unidirectional blood flow. This system is present in all vertebrates as well as some invertebrates, with variations like single and double circulation observed in different species. Specific adaptations in blood flow are seen in amphibians, reptiles, and fish, each employing unique cardiac structures for effective circulation.