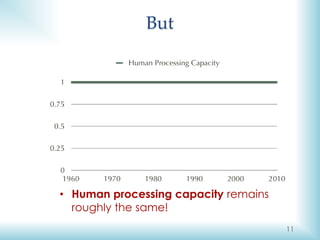
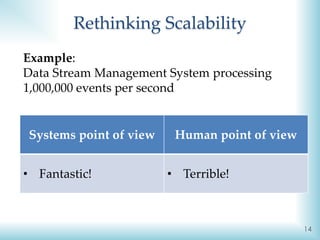
The document discusses the challenges and definitions of big data, highlighting its importance in today's technological landscape. It introduces the 'big data – same humans problem' where human processing capacity does not keep pace with the rapid increase in data volume, velocity, and variety. The document also references Moore's and Bezos’ laws in relation to computing power and storage capacity, emphasizing the need for effective data management strategies.





![8
Enter Moore’s Law
[ Wikipedia Image ]
Moore's law is the observation that, over the
history of computing hardware, the number of
transistors in a dense integrated circuit doubles
approximately every two years. The law is
named after Gordon E. Moore, co-founder of
Intel Corporation, who described the trend in
his 1965 paper.
Source: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Moore's_law](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cidr15-150612033459-lva1-app6892/85/The-Big-Data-Same-Humans-Problem-CIDR-2015-8-320.jpg)

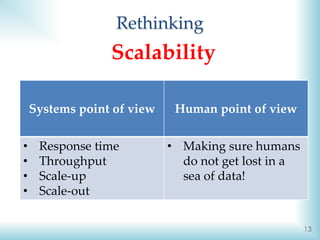
![10
Storage capacity increase
0
1000
2000
3000
4000
5000
6000
7000
HDD Capacity (GB)
[ Wikipedia Data ]
Insert other exponentially increasing graphs here
(e.g., data generation rates, world-wide smartphone access rates,
Internet of Things, …)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cidr15-150612033459-lva1-app6892/85/The-Big-Data-Same-Humans-Problem-CIDR-2015-10-320.jpg)