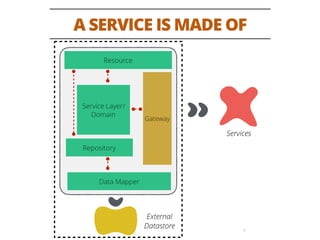
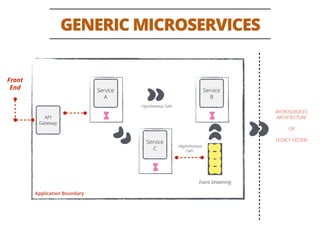
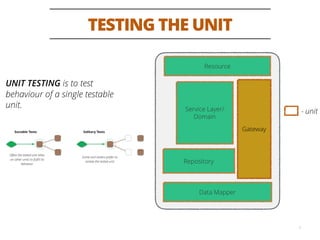
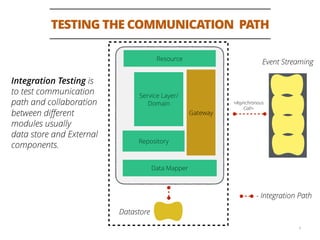
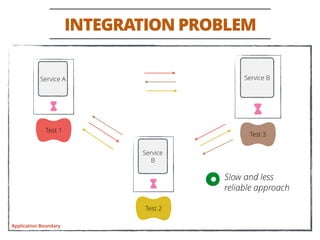
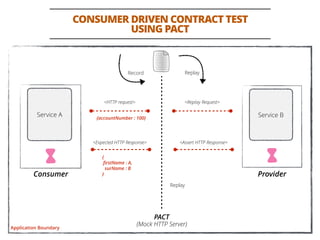
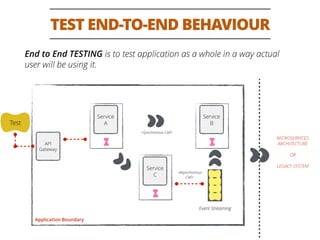
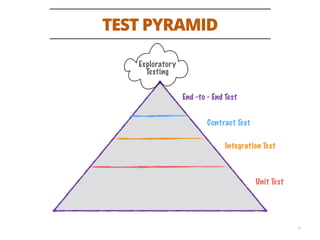
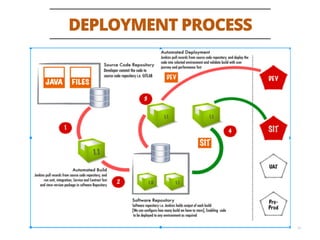
The document discusses testing methodologies for microservices architecture, emphasizing unit, integration, and end-to-end testing. Key learnings include ensuring correct status codes, testing through flaky endpoints, and meaningful log generation. It also highlights the importance of incorporating tests into the build pipeline for quicker feedback and overall agility in the deployment process.