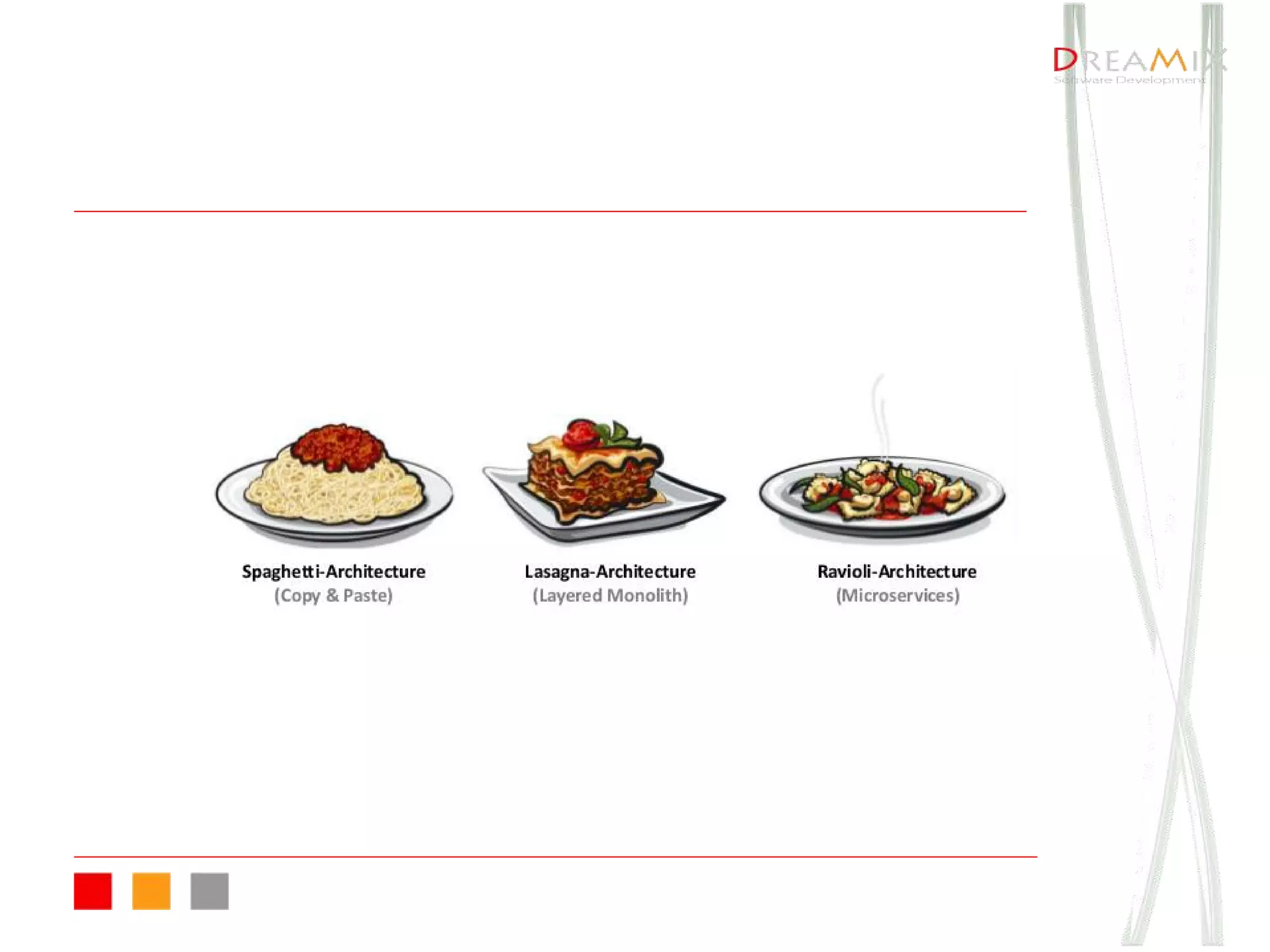
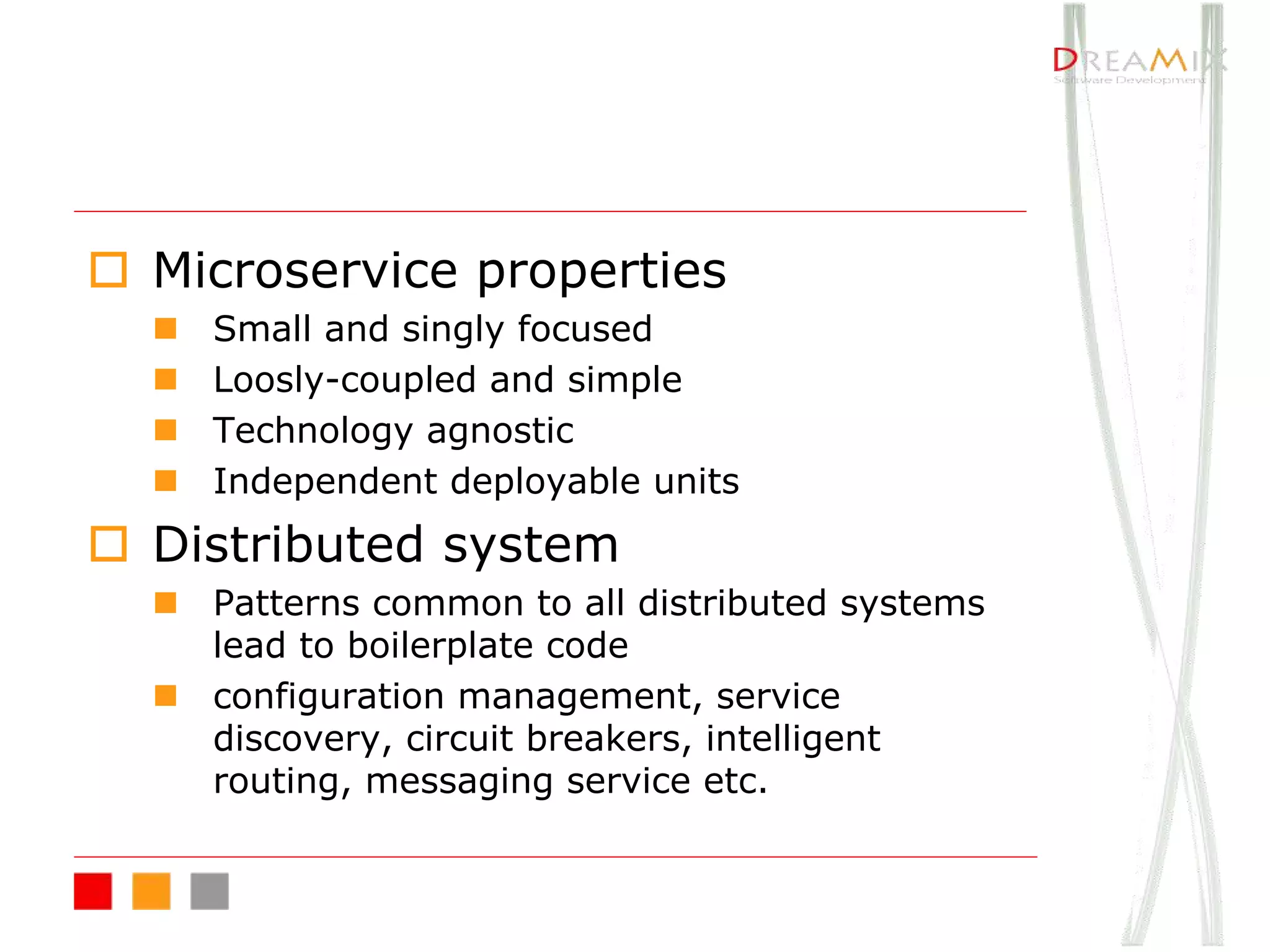
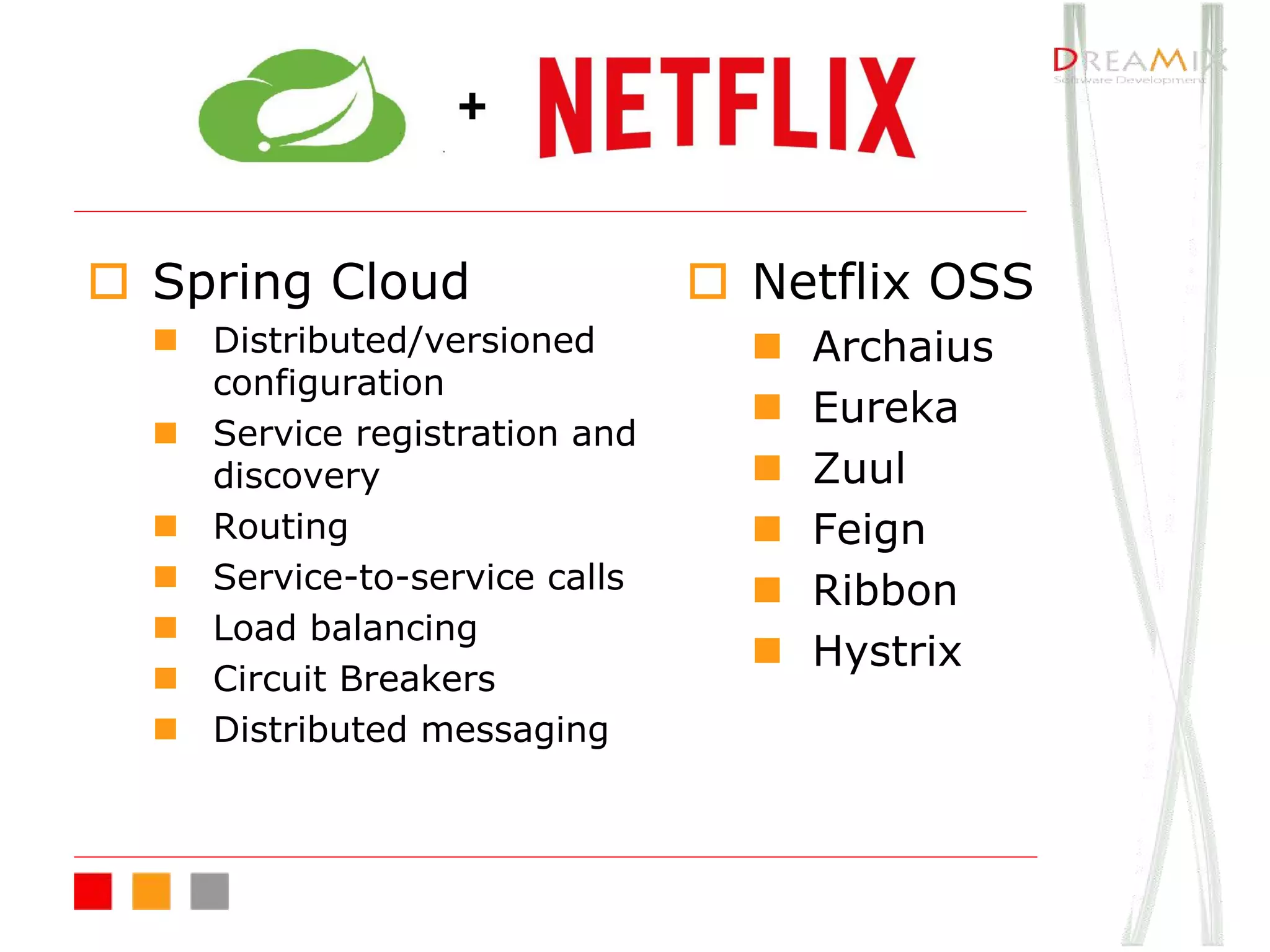
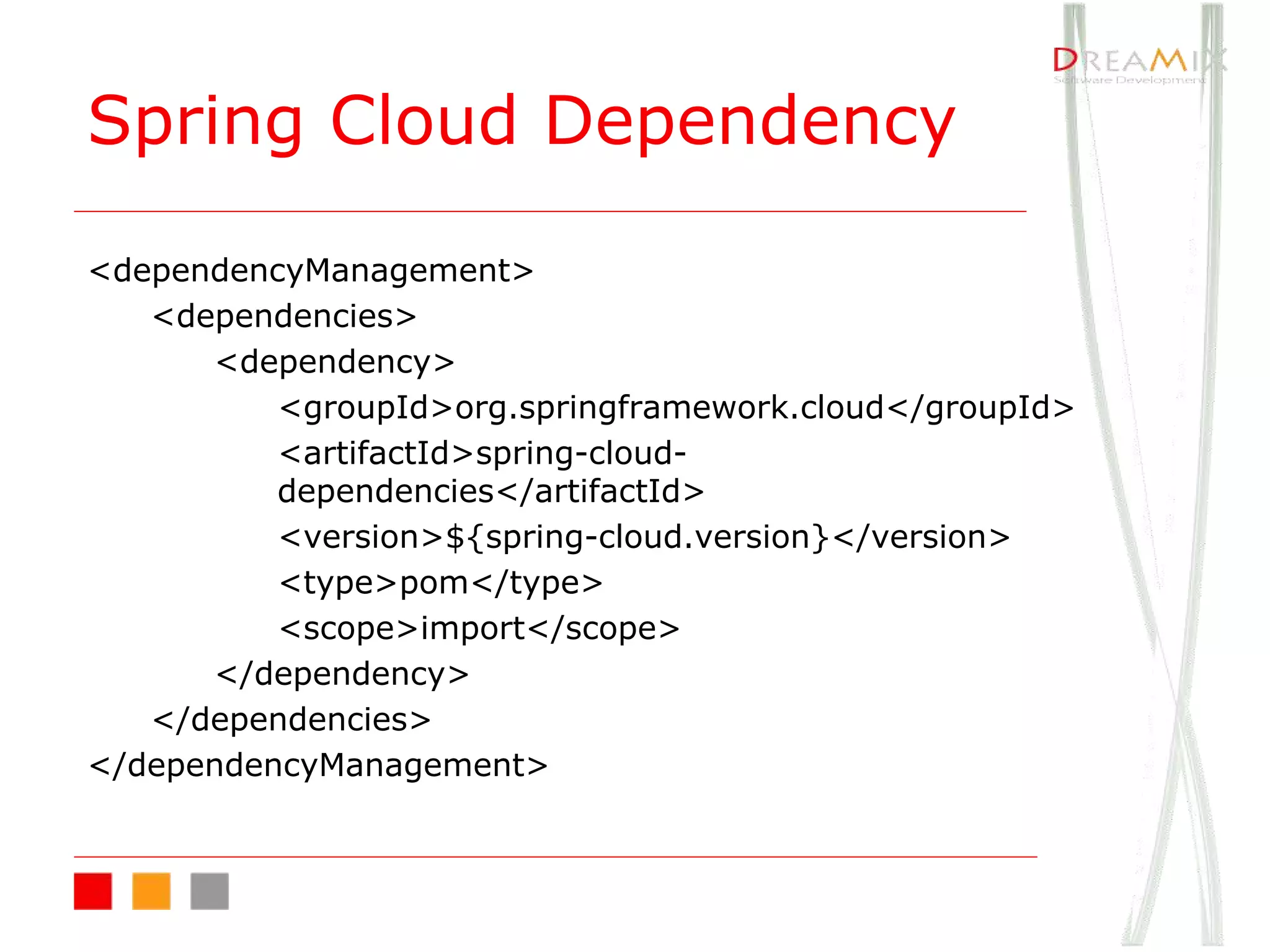
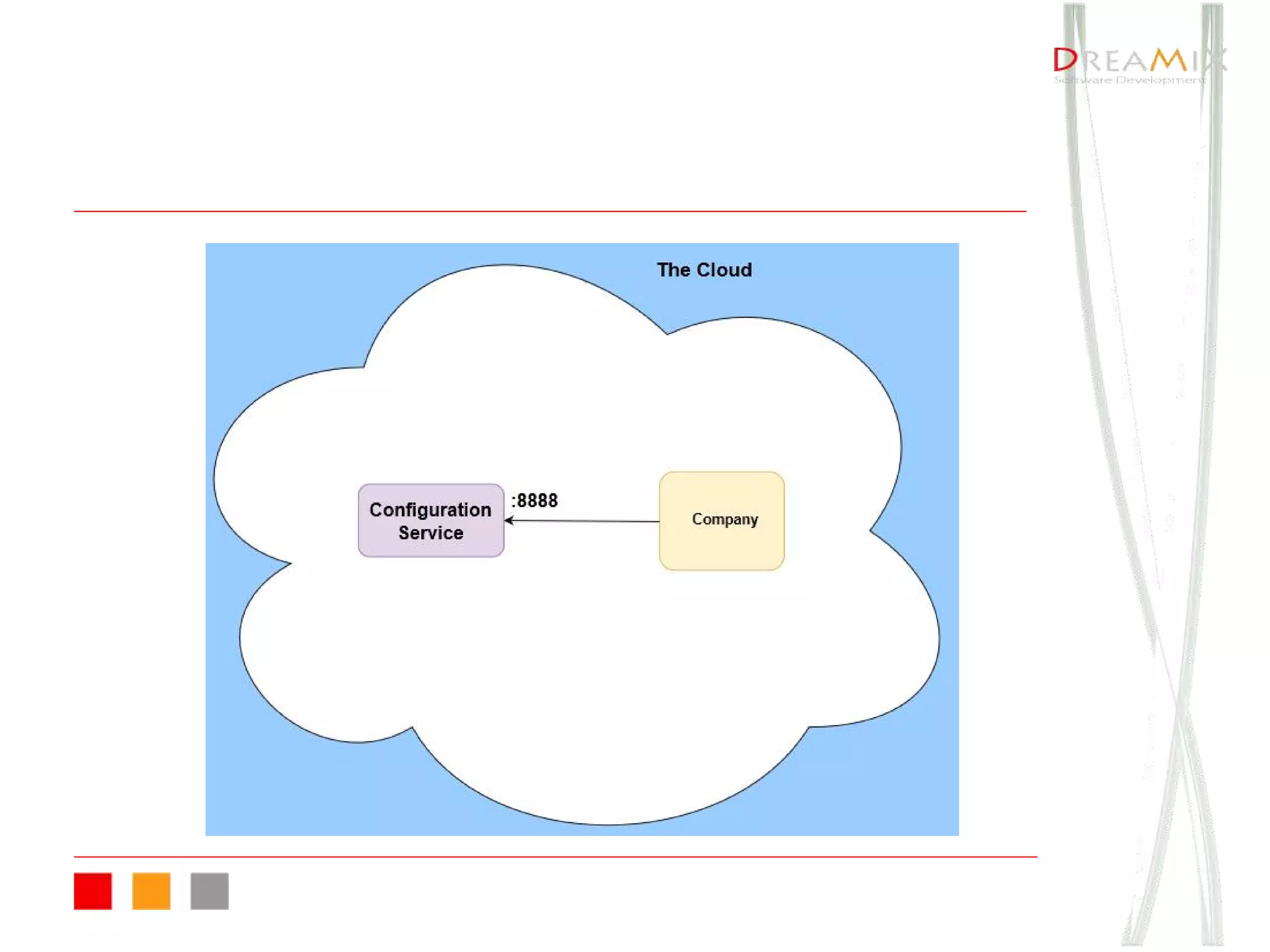
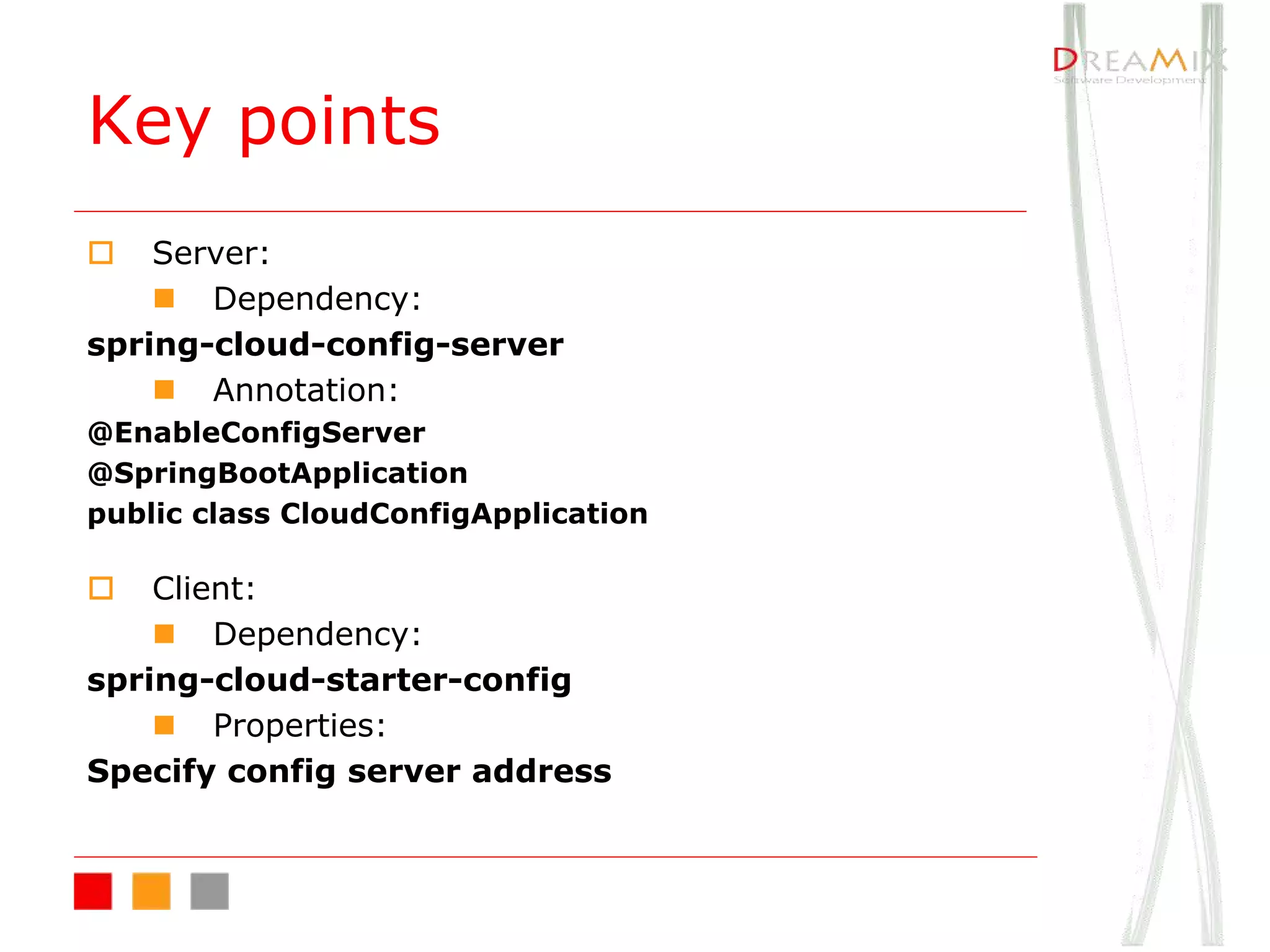
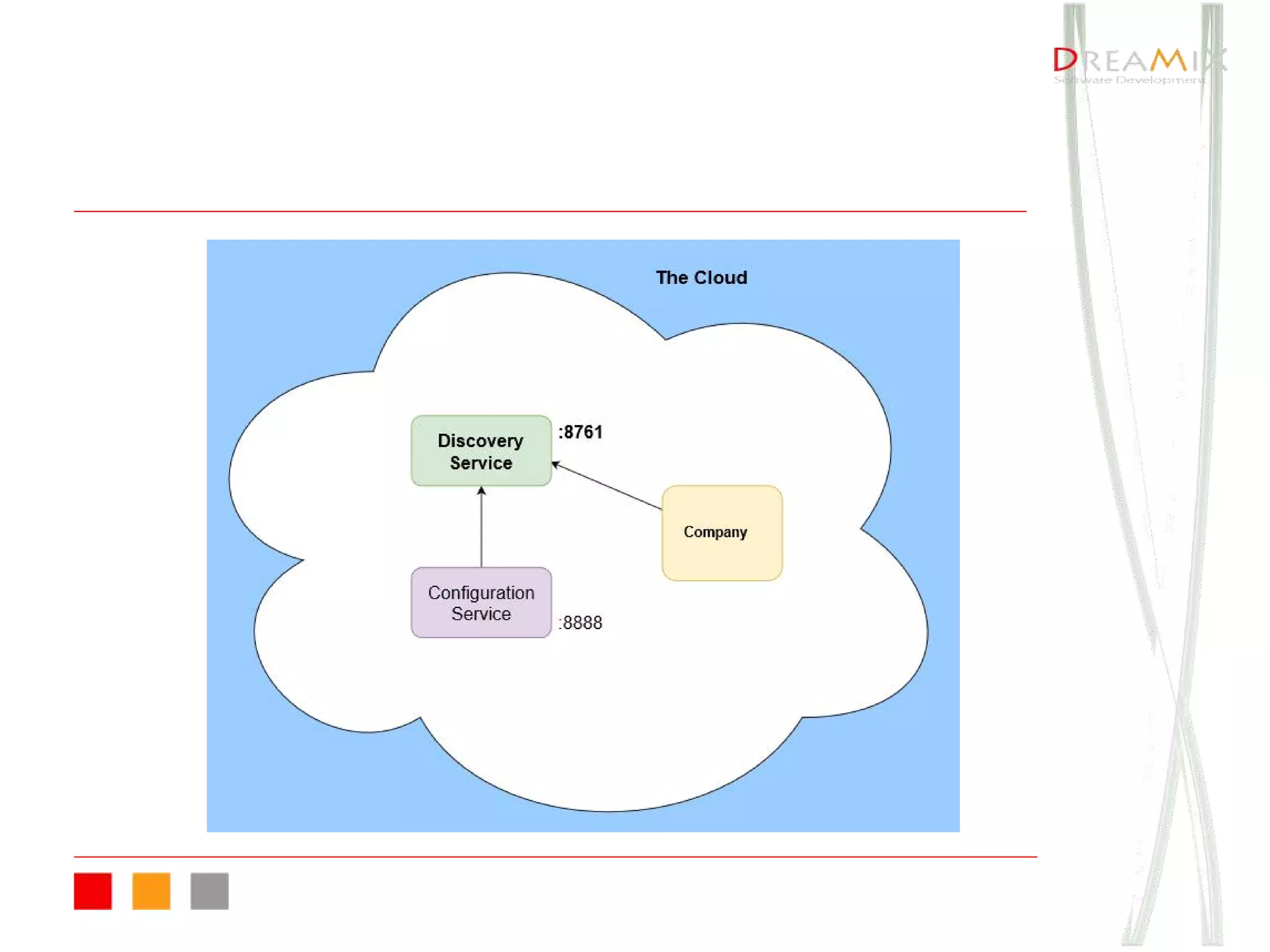
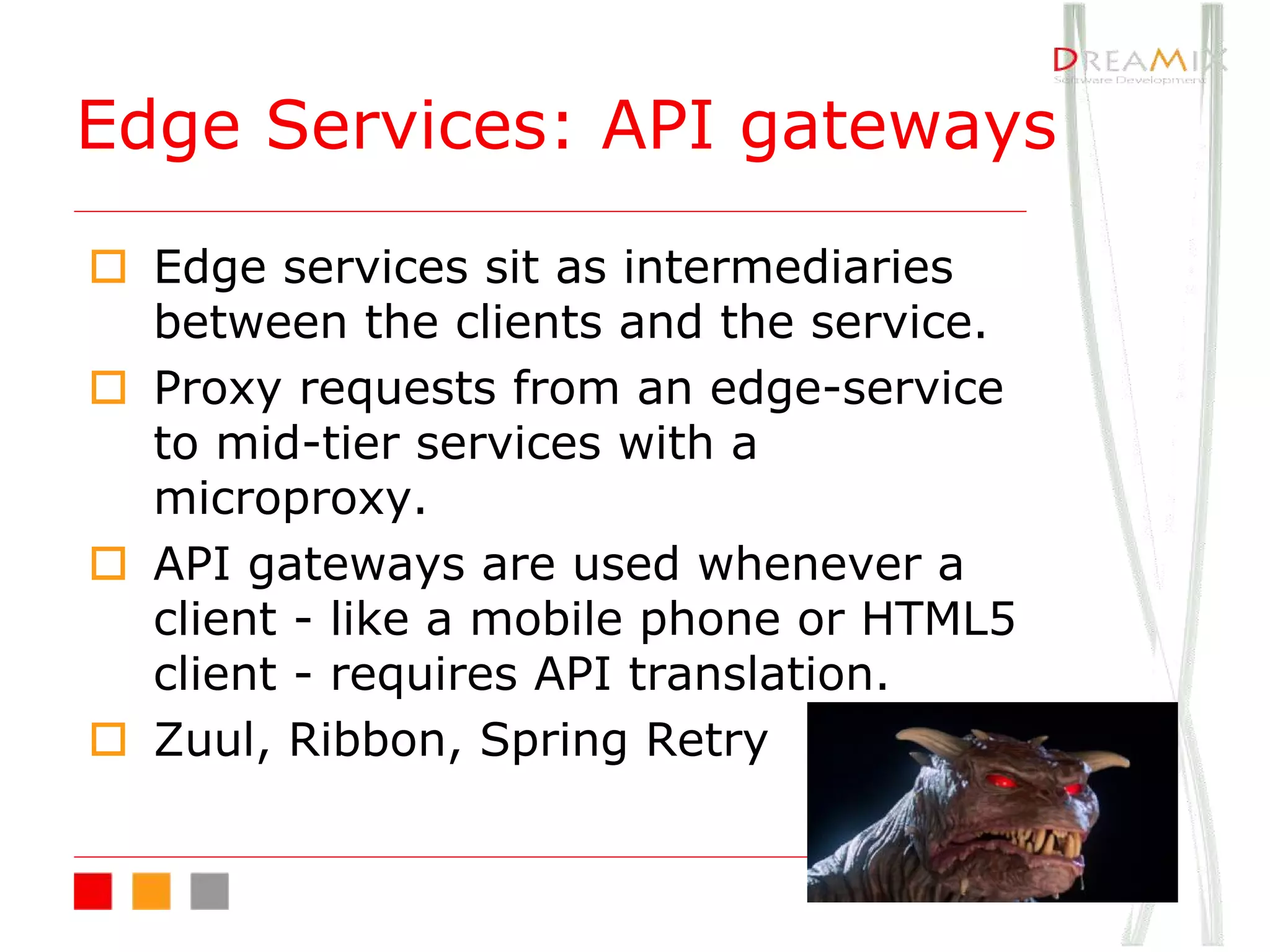
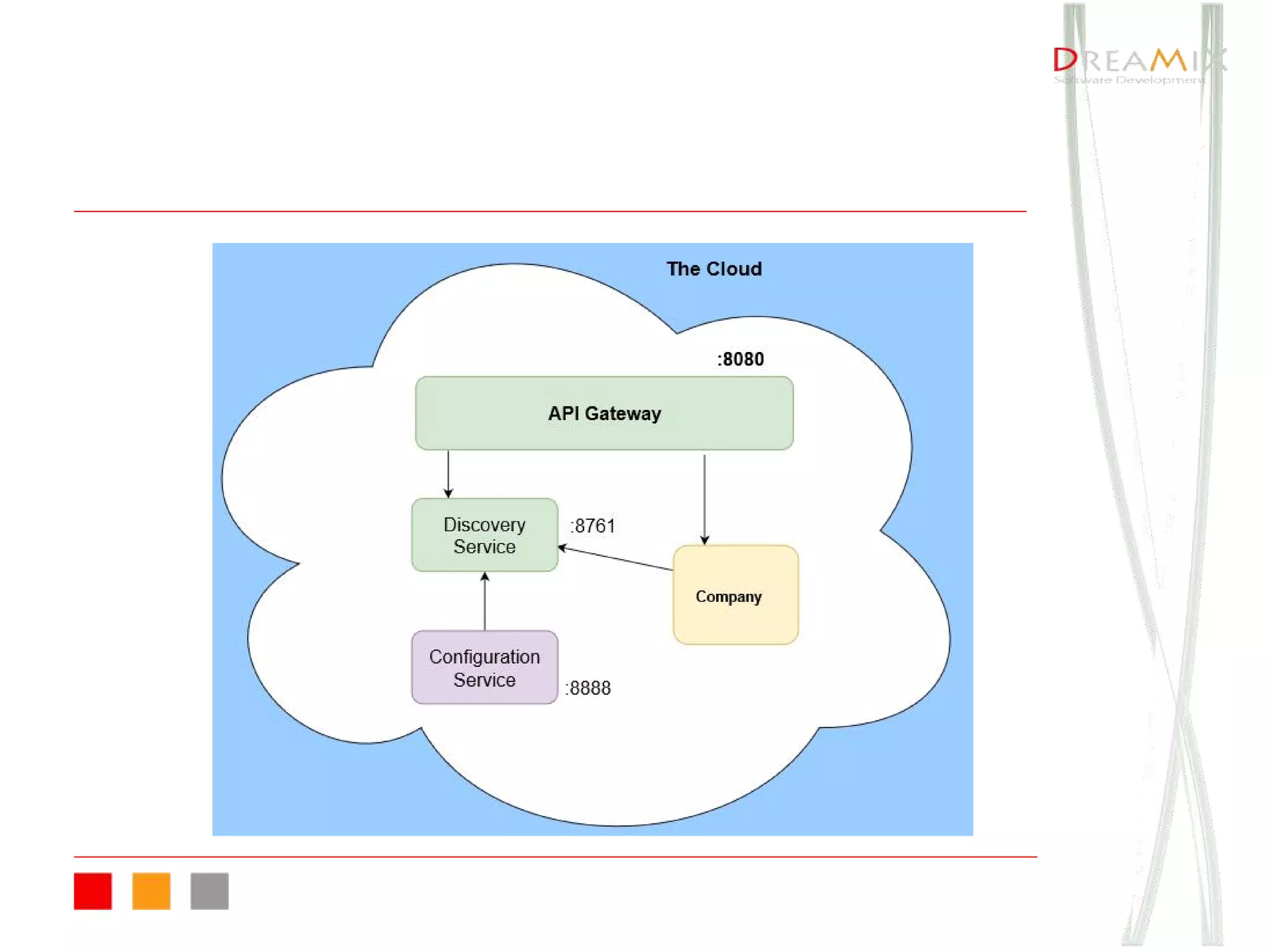
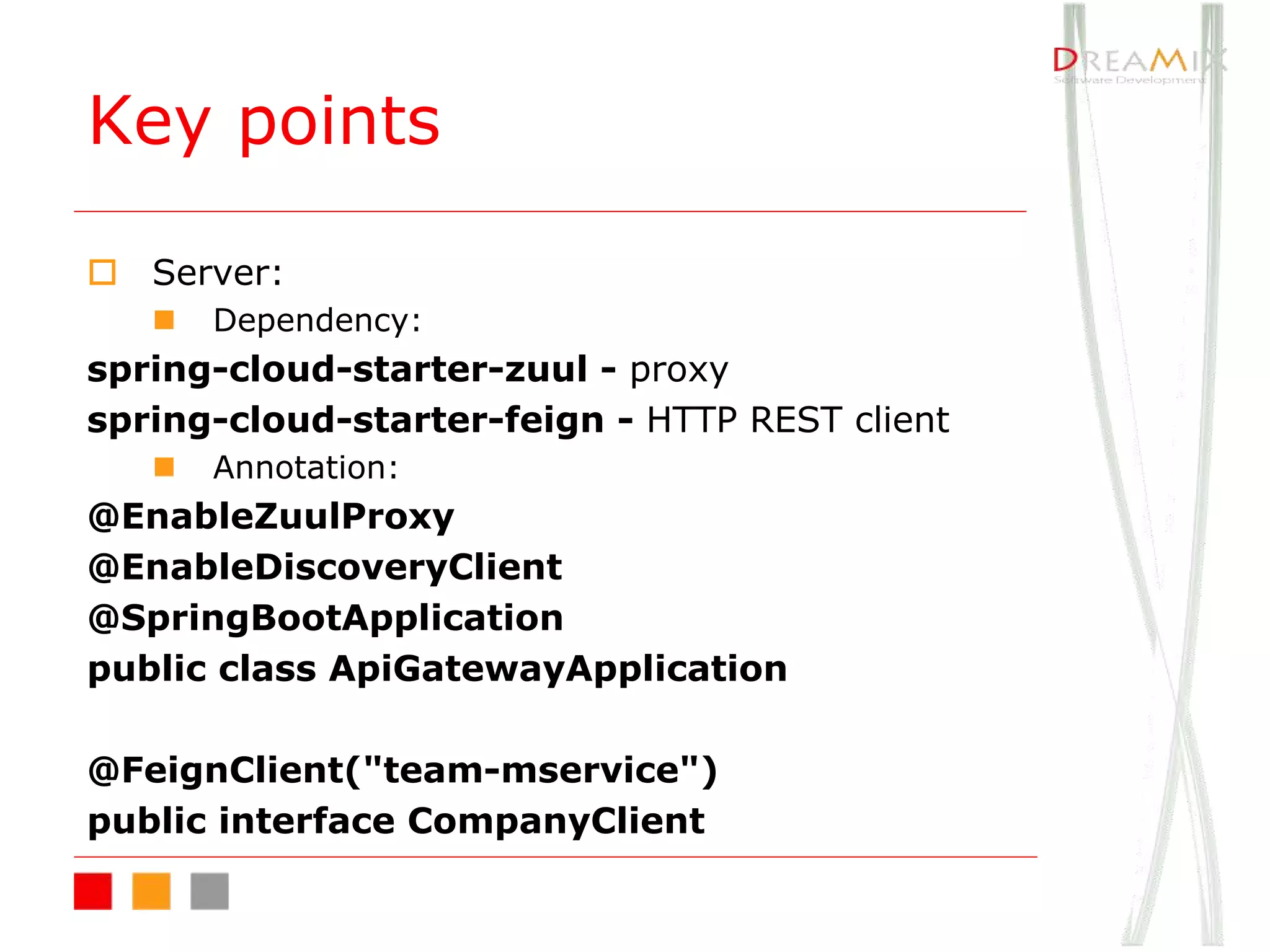
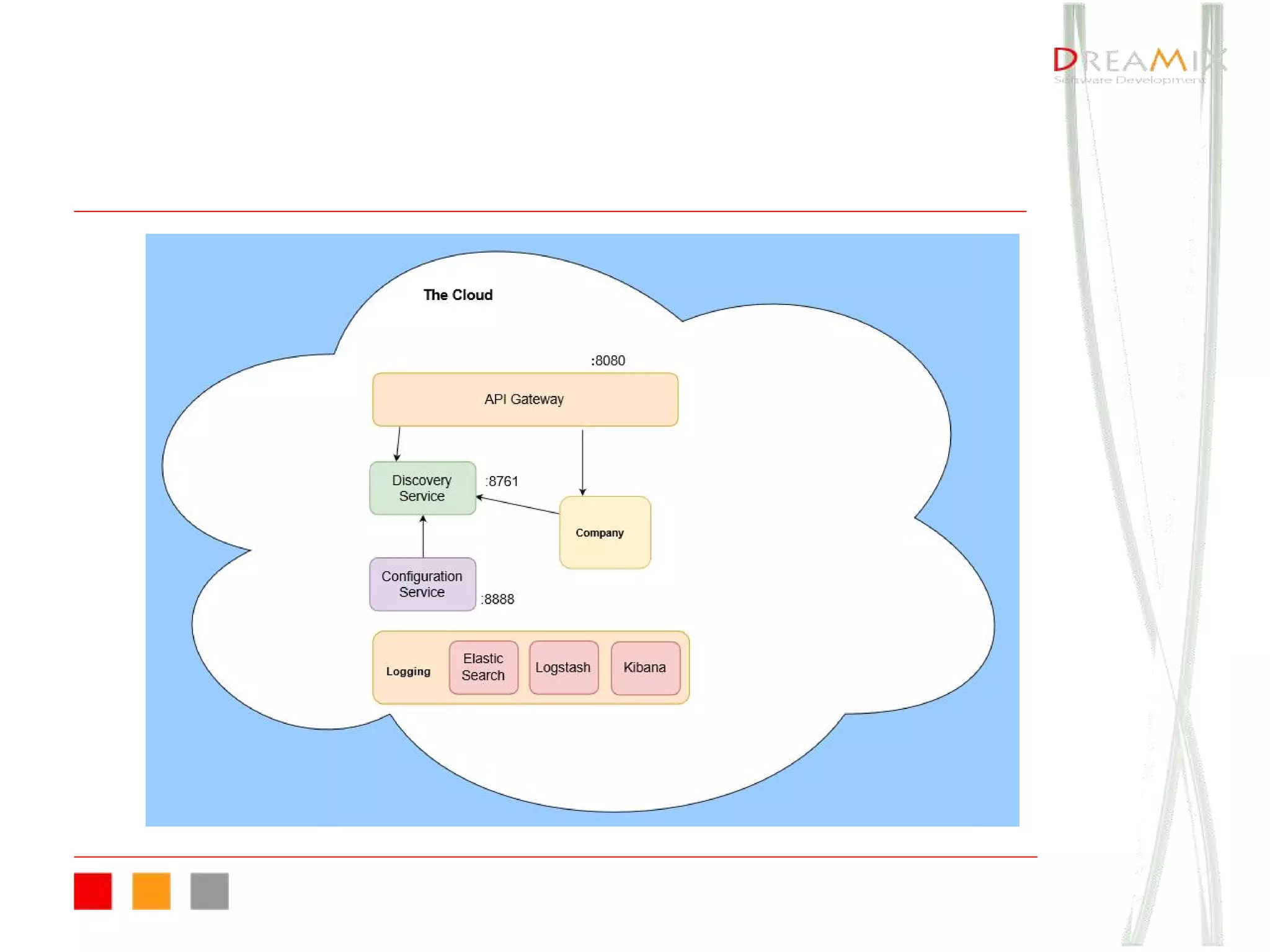
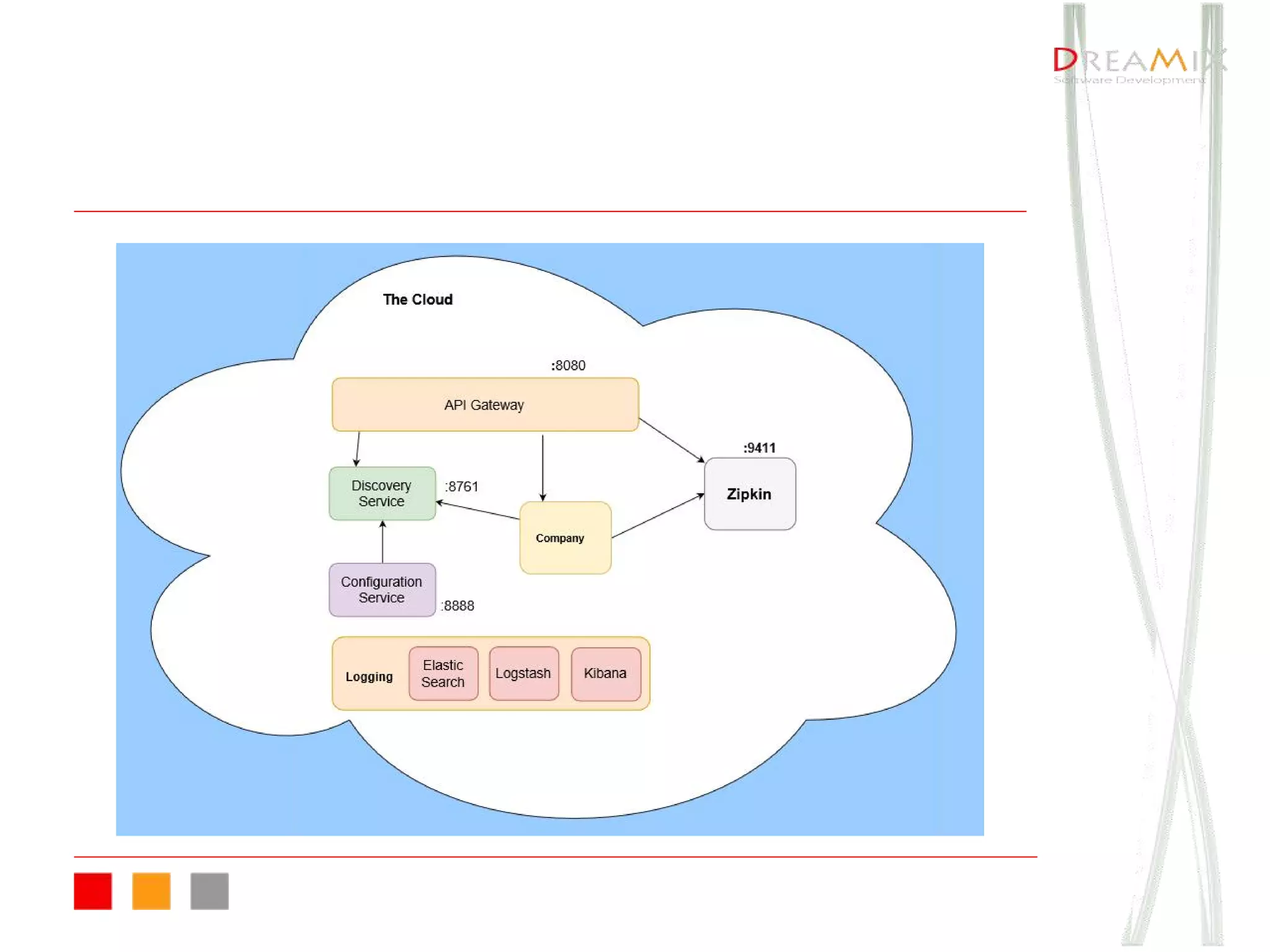
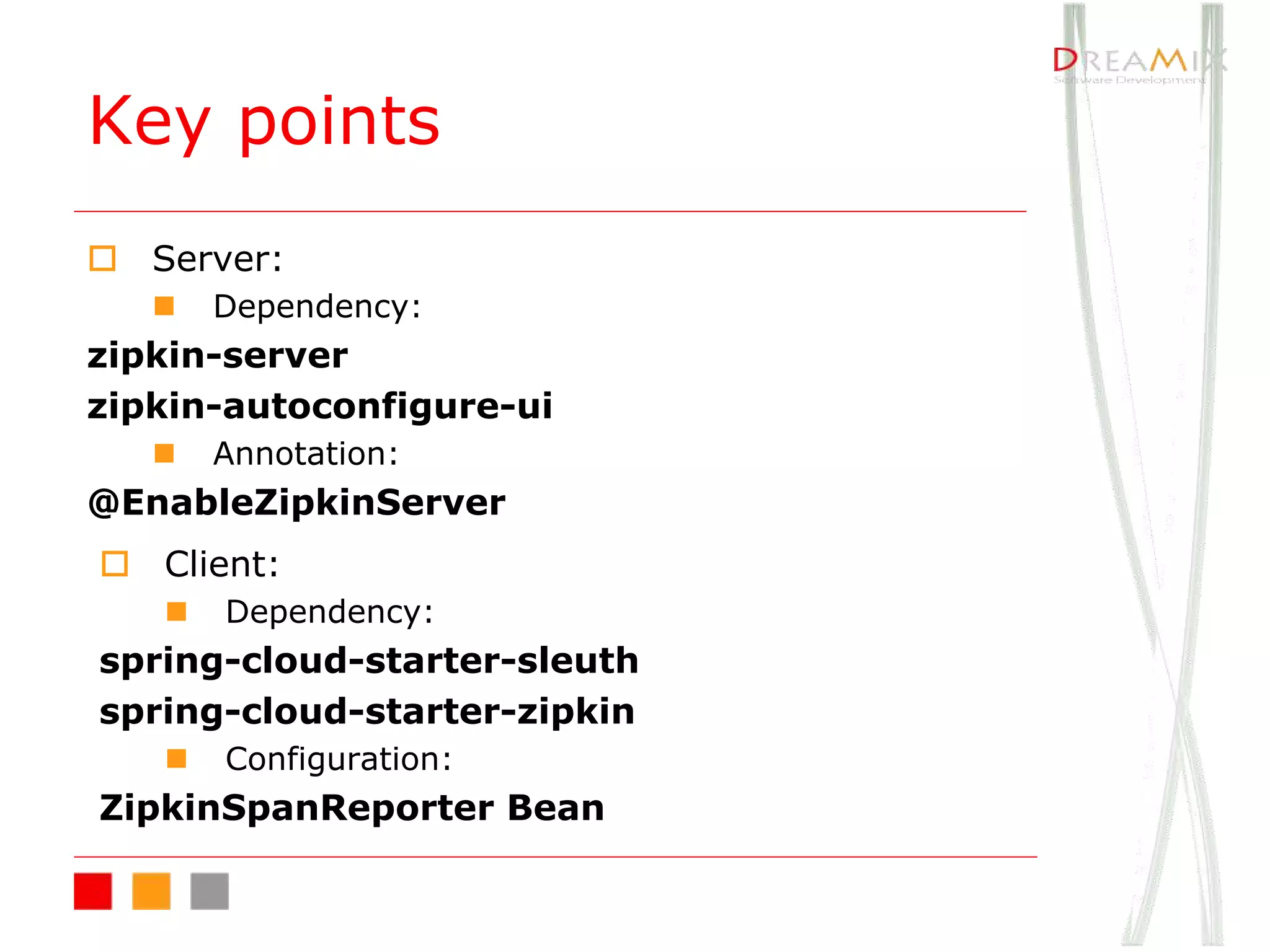
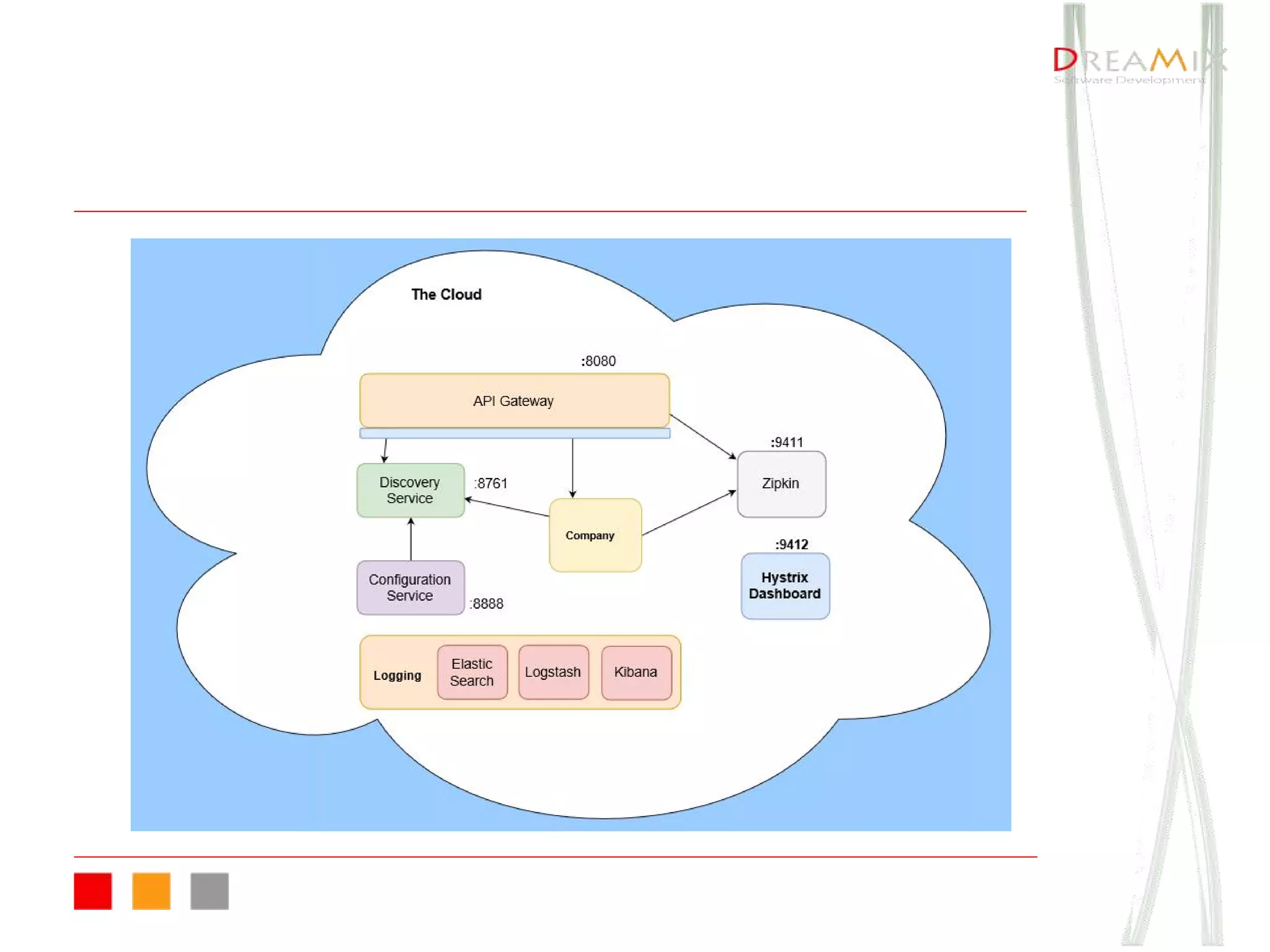
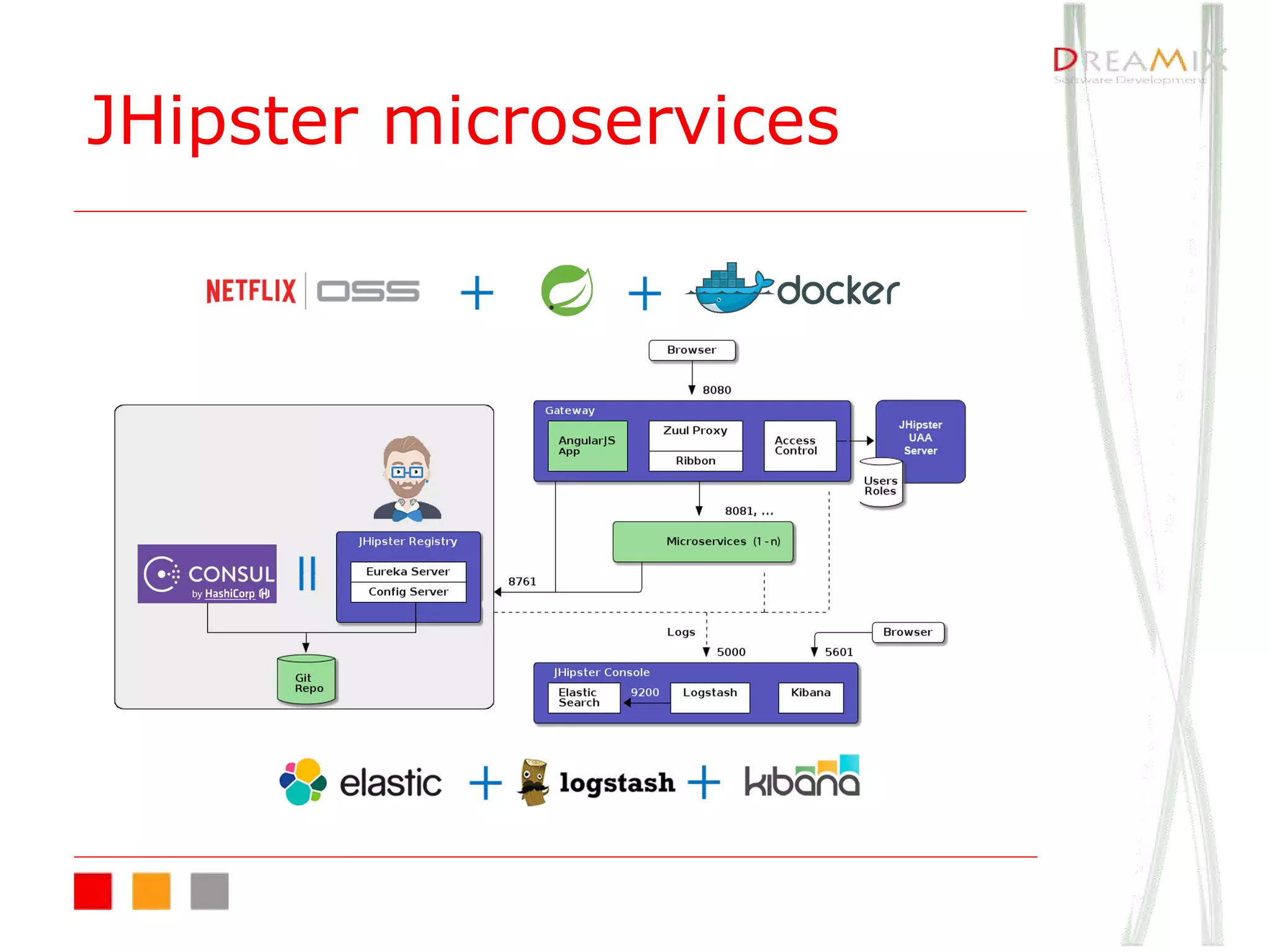
The document provides an overview of microservice architecture using Spring Cloud and Netflix OSS, highlighting critical components such as service discovery, configuration management, and logging. It discusses key technologies including Spring Boot, Eureka, and Hystrix, emphasizing concepts like distributed systems and the importance of production readiness. Additionally, it touches on best practices, including the 12-factor manifesto and tools for logging and tracing in microservice environments.