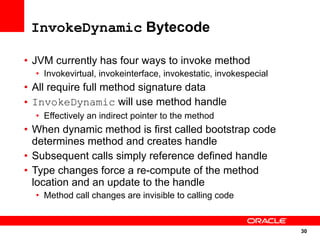
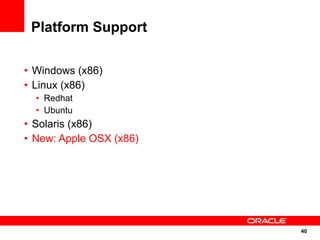
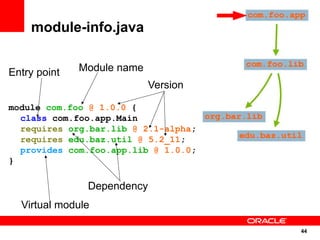
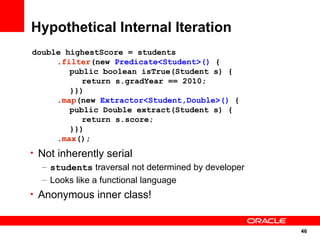
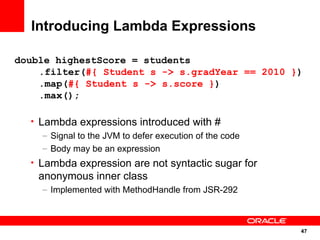
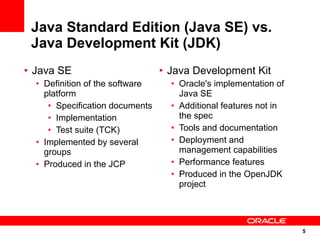
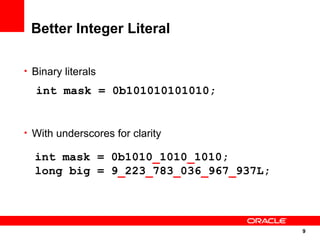
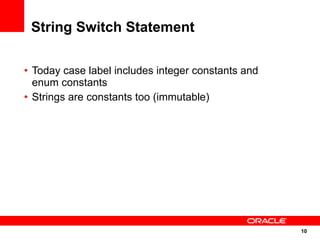
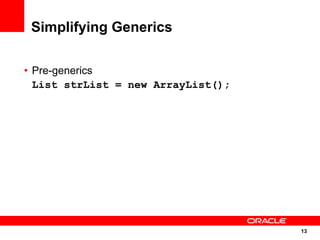
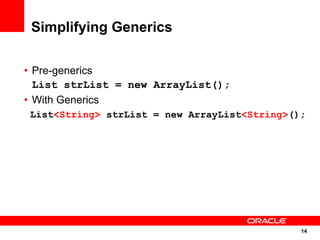
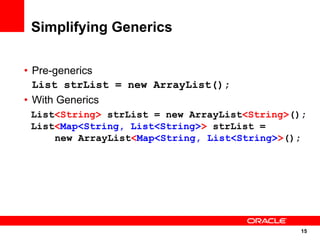
The document discusses the evolution of the Java platform, including new features in Java SE 7 and Java SE 8. Some key changes in Java SE 7 include better integer literals, string switches, simplified generics using diamond operator, and automatic resource management. Java SE 8 will focus on invokedynamic for multi-language support on the JVM and method handles. The JVM specification defines the runtime environment independently of the Java programming language.










![Simplifying Resource Use
InputStream in = new FileInputStream(src);
OutputStream out = new FileOutputStream(dest);
byte[] buf = new byte[8192];
int n;
while (n = in.read(buf)) >= 0)
out.write(buf, 0, n);
17
17](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/terencebarr-jdk78-24mai2011-110607052911-phpapp02/85/Terence-Barr-jdk7-8-24mai2011-17-320.jpg)
![Simplifying Resource Use
InputStream in = new FileInputStream(src);
OutputStream out = new FileOutputStream(dest);
try {
byte[] buf = new byte[8192];
int n;
while (n = in.read(buf)) >= 0)
out.write(buf, 0, n);
} finally {
in.close();
out.close();
}
18
18](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/terencebarr-jdk78-24mai2011-110607052911-phpapp02/85/Terence-Barr-jdk7-8-24mai2011-18-320.jpg)
![Simplifying Resource Use
InputStream in = new FileInputStream(src);
try {
OutputStream out = new FileOutputStream(dest);
try {
byte[] buf = new byte[8192];
int n;
while (n = in.read(buf)) >= 0)
out.write(buf, 0, n);
} finally {
out.close();
}
} finally {
in.close();
}
19
19](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/terencebarr-jdk78-24mai2011-110607052911-phpapp02/85/Terence-Barr-jdk7-8-24mai2011-19-320.jpg)
![Automatic Resource Management
try (InputStream in = new FileInputStream(src),
OutputStream out = new FileOutputStream(dest))
{
byte[] buf = new byte[8192];
int n;
while (n = in.read(buf)) >= 0)
out.write(buf, 0, n);
}
20
20](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/terencebarr-jdk78-24mai2011-110607052911-phpapp02/85/Terence-Barr-jdk7-8-24mai2011-20-320.jpg)