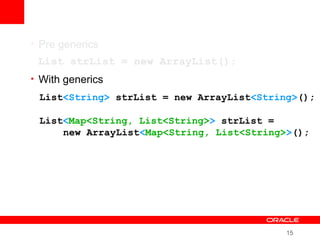
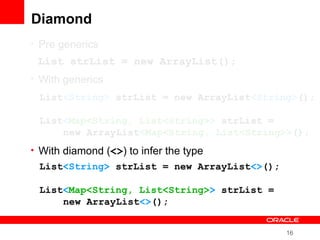
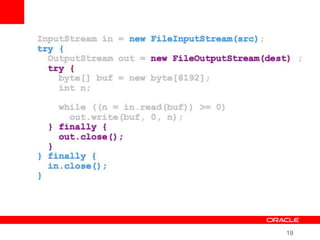
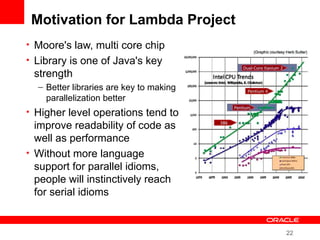
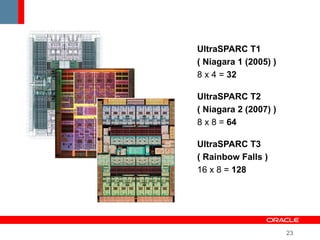
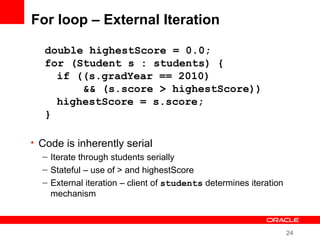
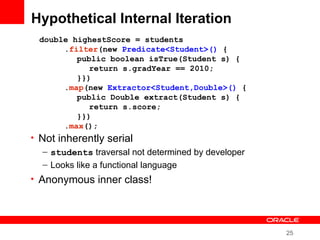
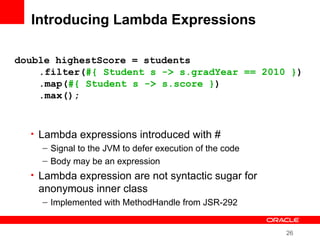
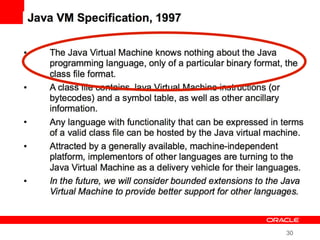
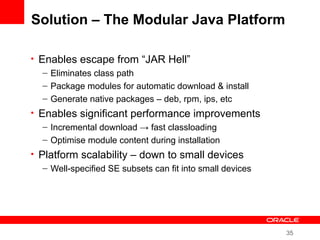
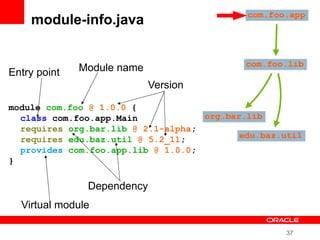
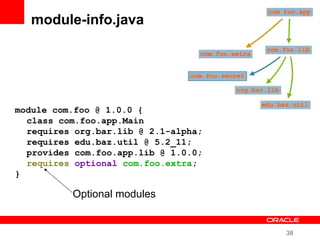
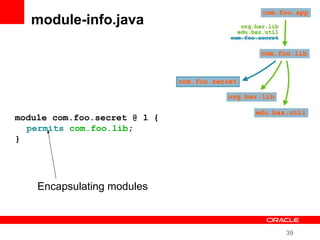
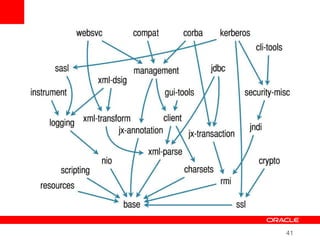
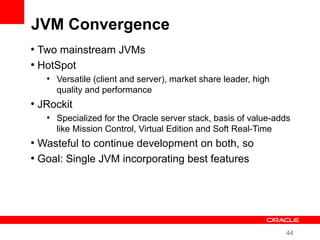
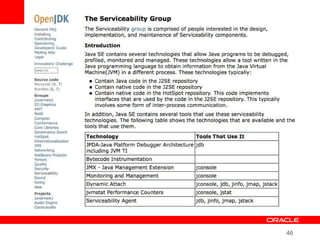
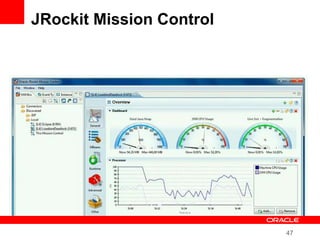
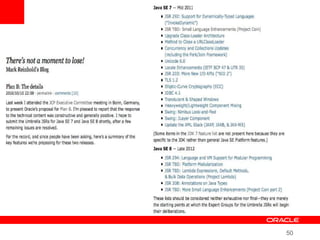
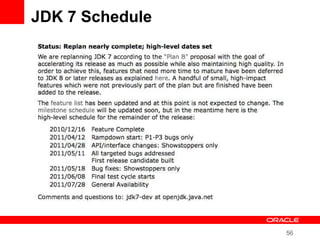
This document provides an overview of Oracle's plans and projects to evolve the Java platform. It discusses Project Coin which aims to make small language improvements, Project Lambda which adds closures and other functional programming features, Project Jigsaw which develops a modularity system, and convergence of the HotSpot and JRockit JVMs. The document also mentions other projects like Project DaVinci and performance optimizations. It emphasizes that the language will evolve cautiously to maintain simplicity and compatibility while improving developer productivity. The development schedule and roadmap are not commitments and remain at Oracle's discretion.