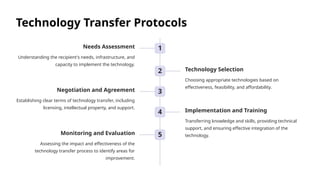
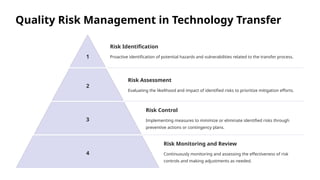
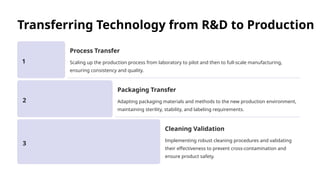
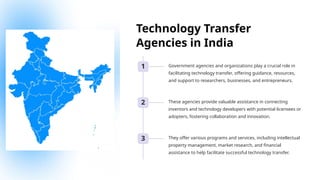
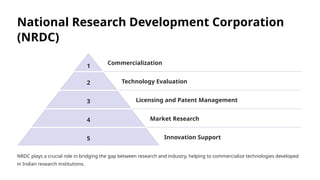
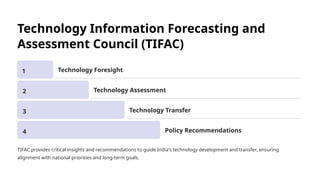
The document outlines the World Health Organization's guidelines for technology development and transfer, emphasizing the importance of equitable access to healthcare technologies and outlining key protocols for effective implementation. It discusses essential aspects such as risk management, regulatory standards, commercialization strategies, and the role of various agencies in facilitating successful technology transfer. The conclusion highlights the need for collaboration among stakeholders to leverage technology for improved health outcomes globally.