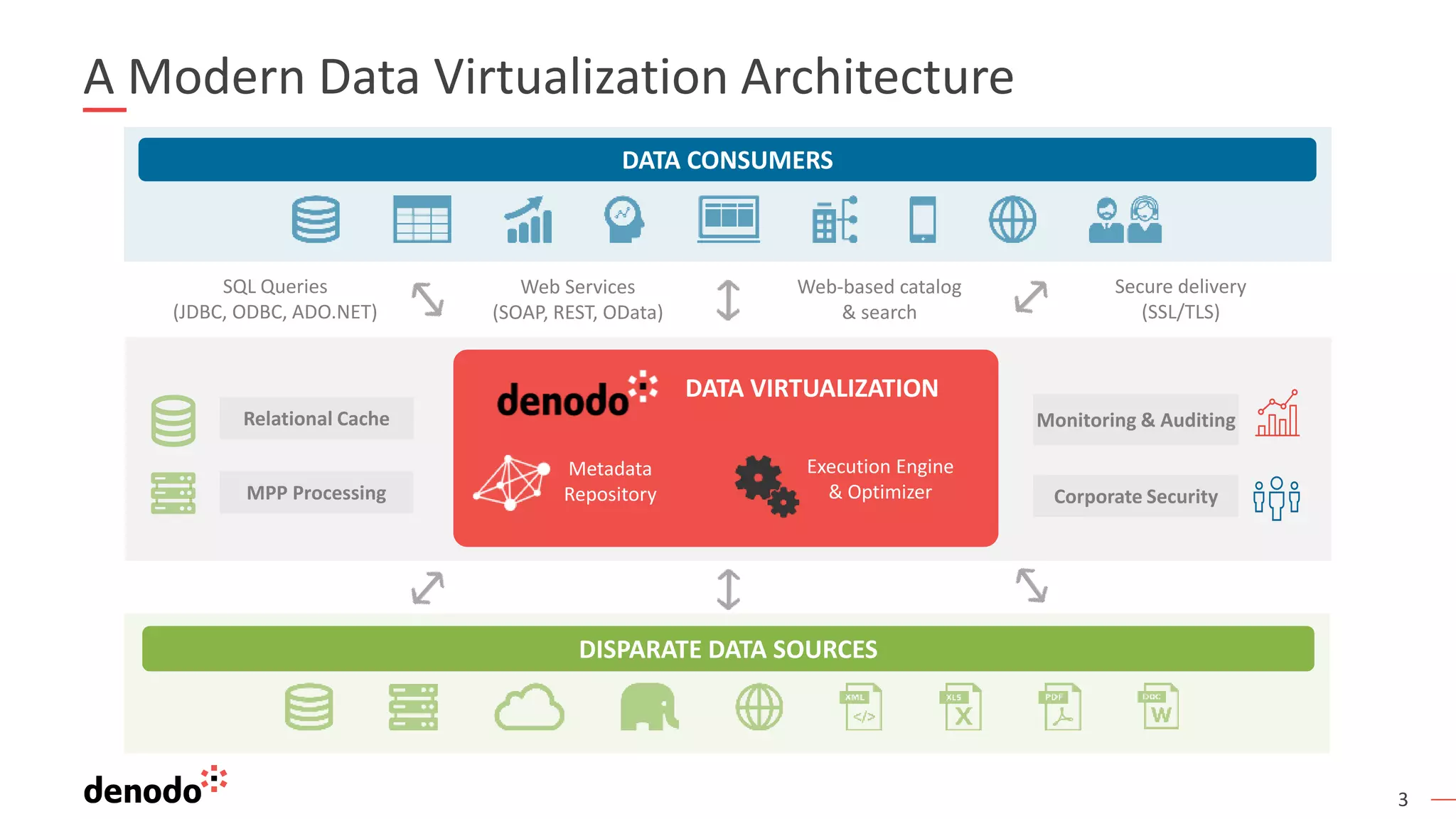
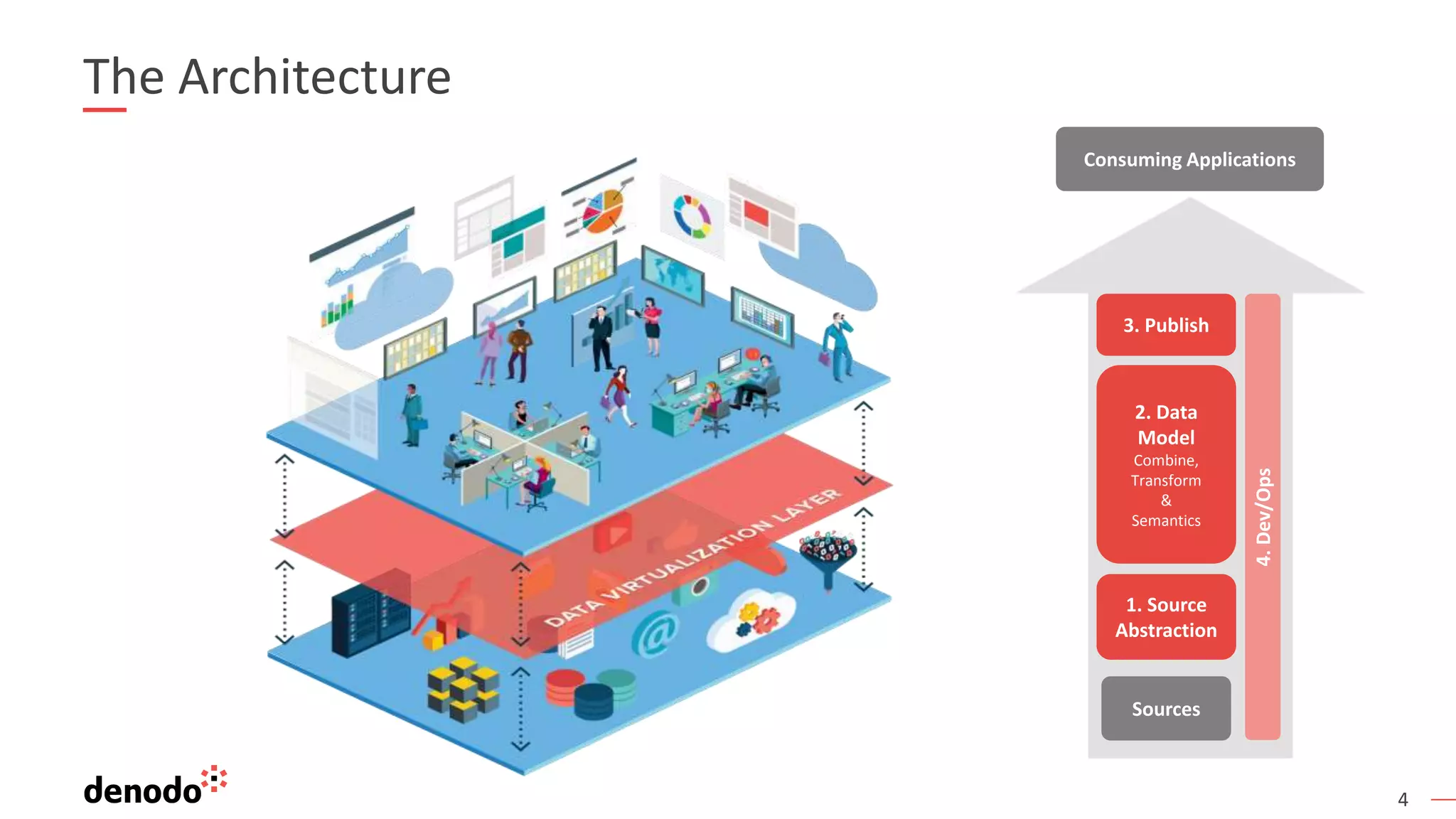
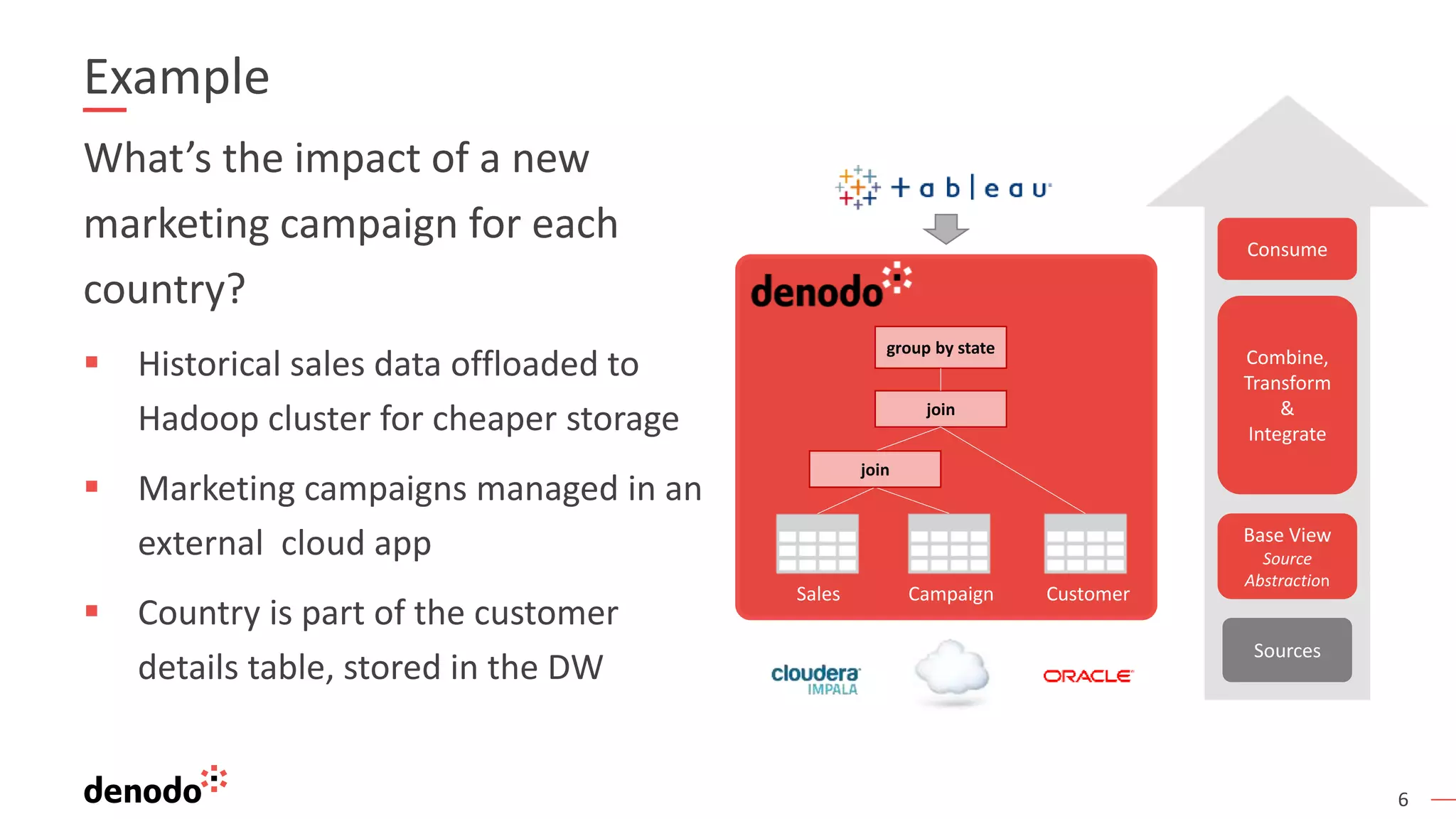
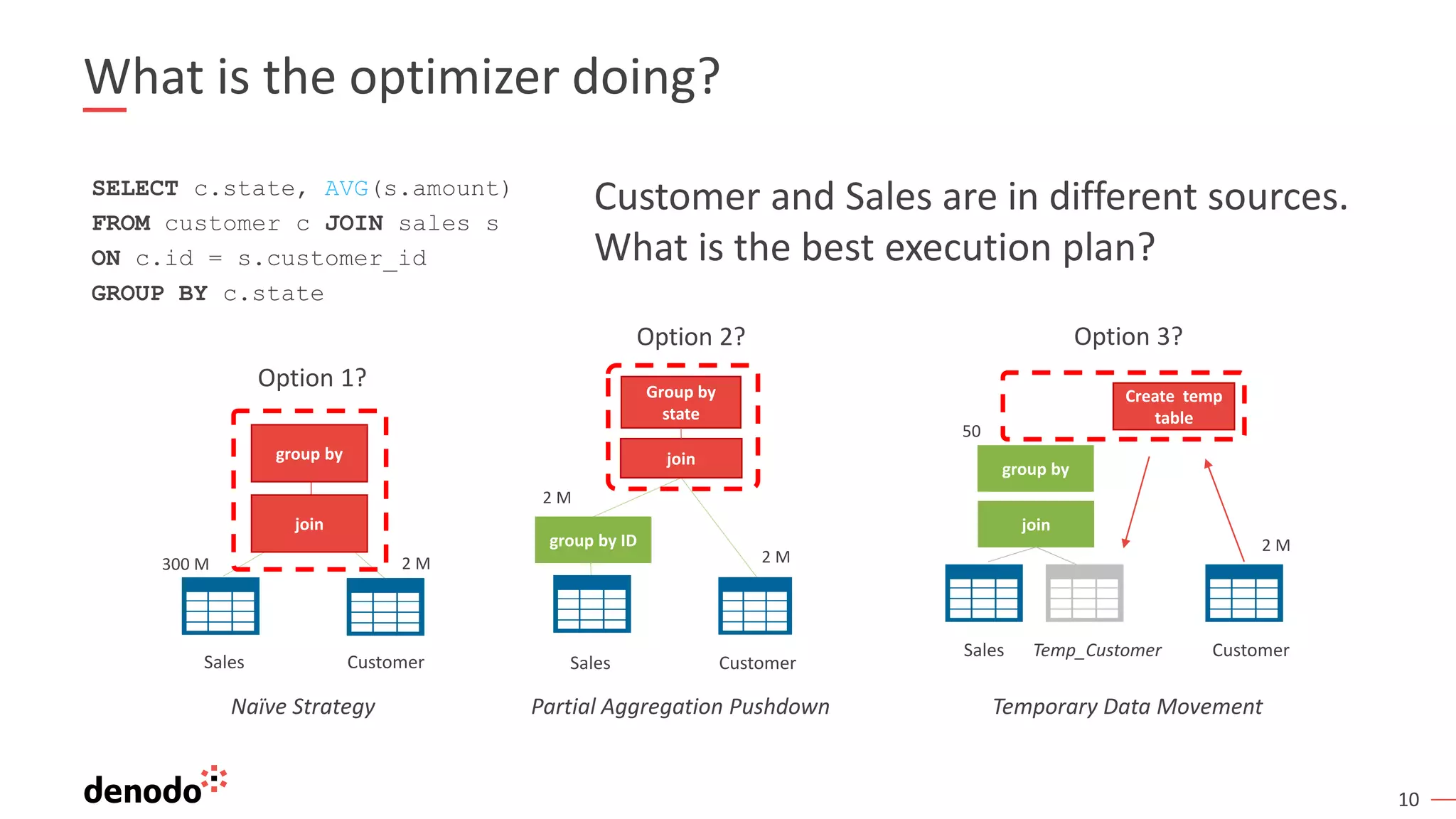
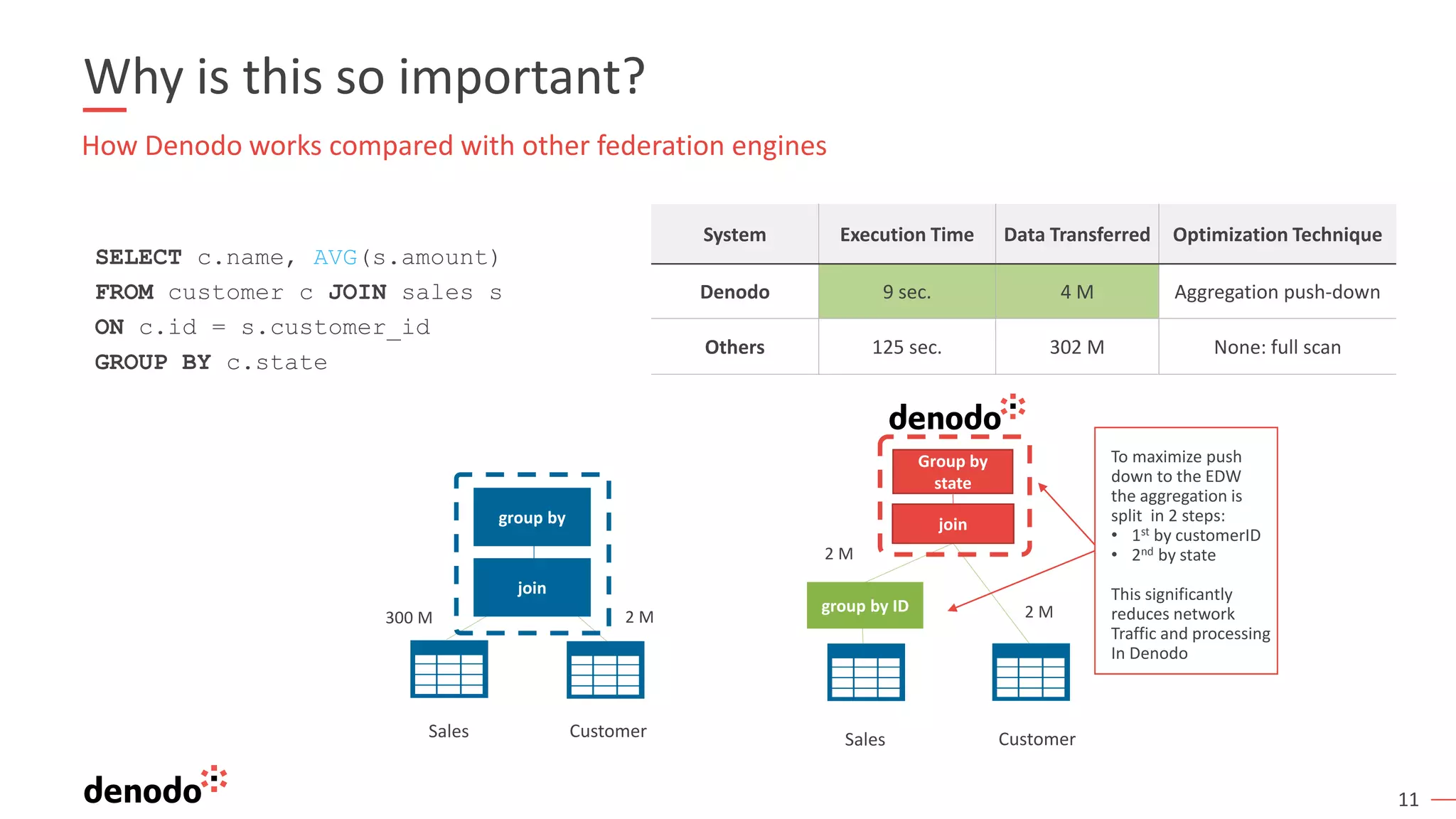
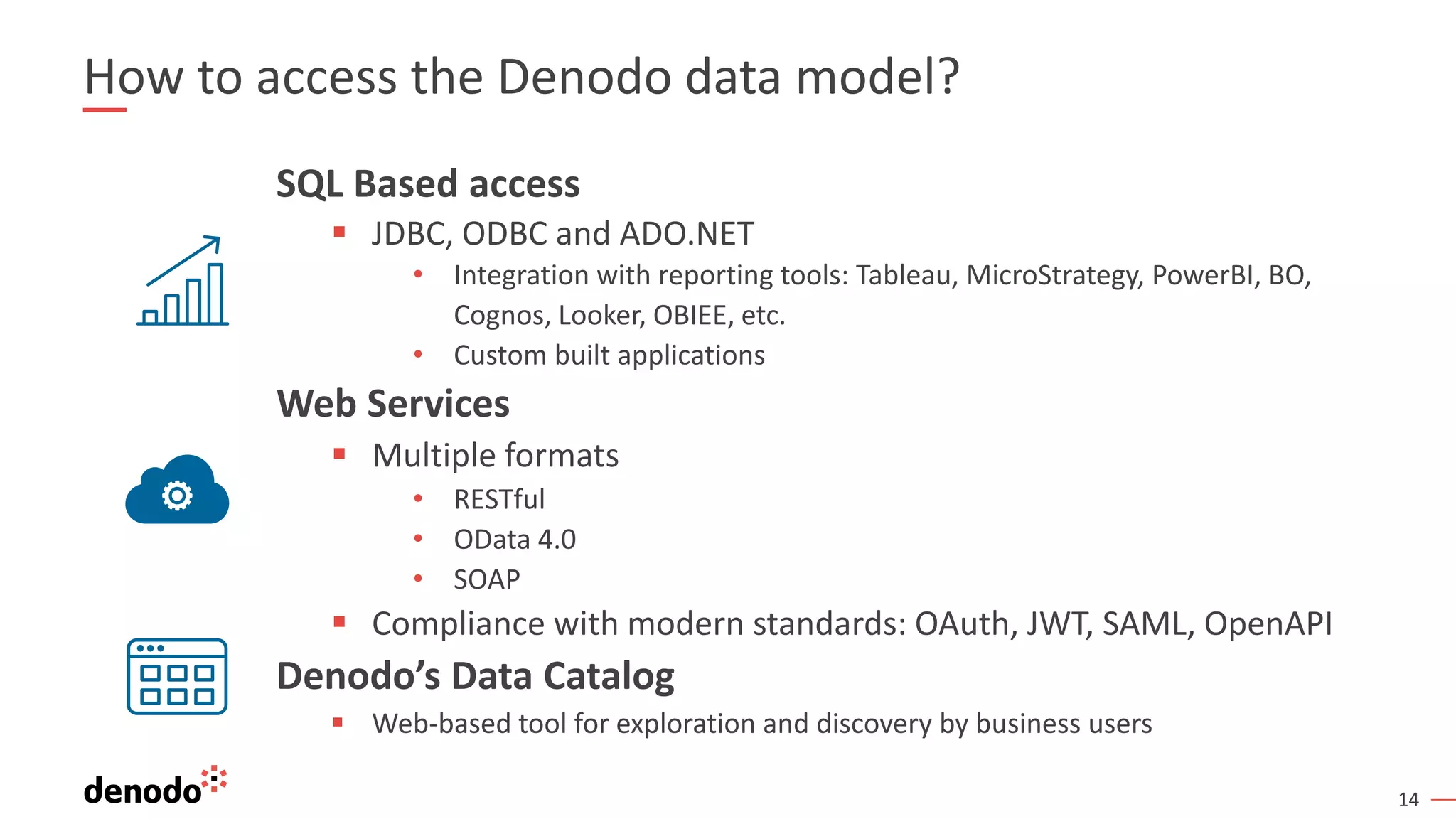
This document provides an overview, agenda, and demonstration of Denodo 7.0. It discusses Denodo's data virtualization architecture, how to set up Denodo including connectivity and modeling, how execution works by optimizing query plans, and how to access the Denodo data model through SQL, web services, and a data catalog. The demonstration shows how Denodo minimizes network traffic and processing loads through techniques like aggregation pushdown and leveraging massive parallel processing in external systems.