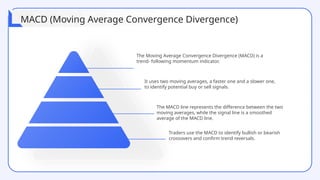
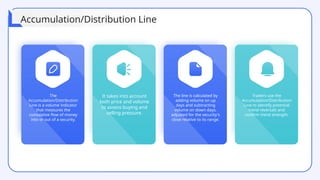
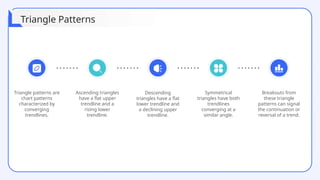
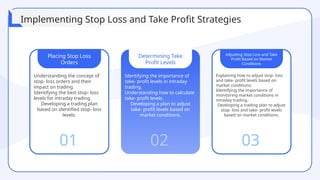
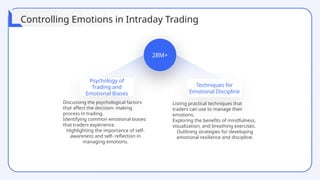
The document provides a comprehensive overview of technical analysis for intraday trading, detailing its definition, purpose, and various tools used to analyze price data, such as trend analysis, momentum indicators, and volume analysis. It emphasizes the importance of using technical indicators, support and resistance levels, and pattern recognition to make informed trading decisions while also addressing the benefits and limitations of these methods. Additionally, the document outlines how to develop a trading strategy, including risk management techniques, and includes case studies to illustrate practical applications of technical analysis in trading.