This document discusses Prof. Martin Christen's experience using JupyterHub for teaching Python courses. Some key points:
- JupyterHub was used to teach several Python courses at the University of Applied Sciences and Arts Northwestern Switzerland, including introductory, intermediate, and advanced courses.
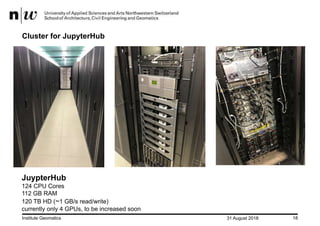
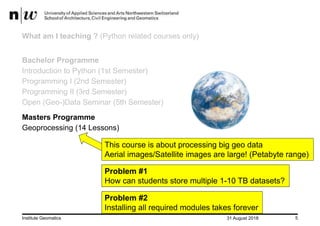
- JupyterHub solved problems with students installing modules and storing large datasets (up to 10TB) on their own computers by providing a shared computing environment.
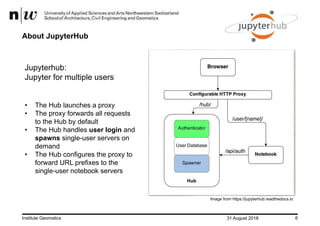
- The installation and configuration of JupyterHub allowed students to access tutorials, exercises, and datasets through a web interface without extensive local setup.
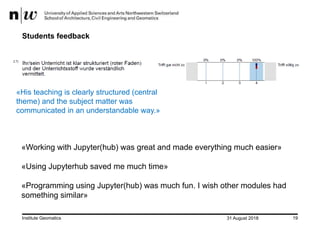
- Students provided positive feedback on using JupyterHub, finding it made the coursework easier and more enjoyable compared






![31 August 2018Institute Geomatics 10
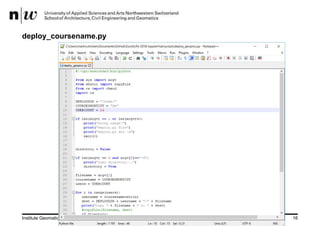
Configuration
/opt/anaconda3/bin/jupyterhub_config.py
# Custom Logo
c.JupyterHub.logo_file = "/path/to/logo.png"
# for Jupyter Lab
c.Spawner.cmd = ["jupyter-labhub"]
c.Spawner.default_url = '/lab‘
c.Spawner.environment = {'JUPYTER_ENABLE_LAB': 'yes' }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentation-180831074007/85/Teaching-with-JupyterHub-lessons-learned-10-320.jpg)