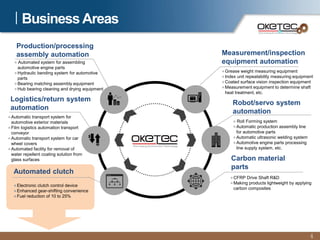
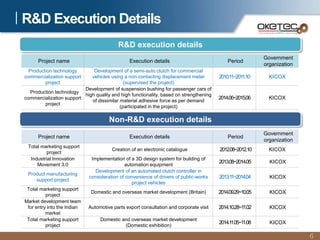
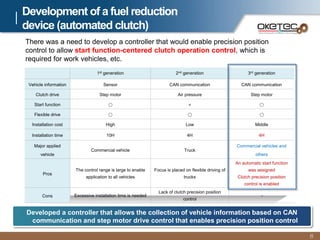
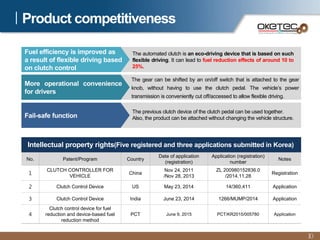
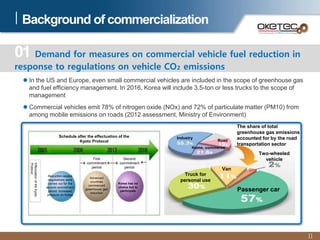
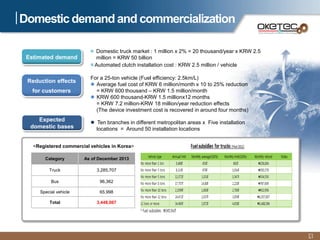
Oketec Co. is a South Korean company established in 2000 that specializes in automation equipment. The document provides an overview of Oketec's history and certifications, main business areas of production automation, key R&D projects participated in or led relating to automated clutches, and the commercialization potential for its fuel-efficient automated clutch technology, particularly in the Chinese market. The automated clutch allows for precision clutch control and flexible driving to reduce fuel consumption by 10-25% for commercial vehicles.