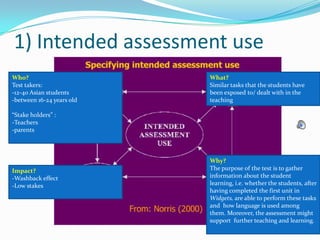
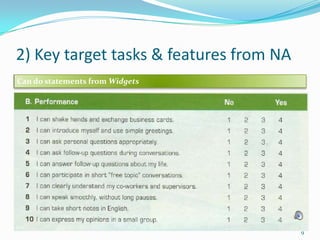
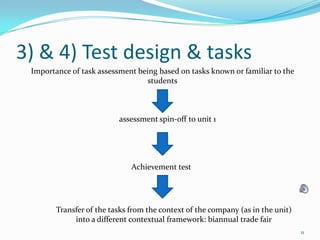
1) The document outlines a proposed task-based language test designed for students who have completed the first unit of the Widgets course. It describes the tasks, assessment criteria, and limitations of the proposed test.
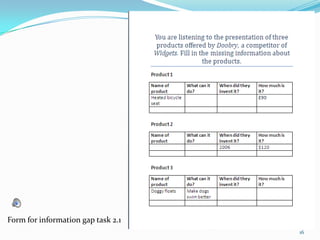
2) The test includes two speaking tasks - a role play conversation and product presentation - and a listening note-taking task on competitive products.
3) Criteria for assessing the tasks include task-dependent criteria related to content and task completion, as well as task-independent criteria such as language use.