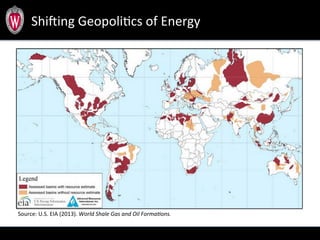
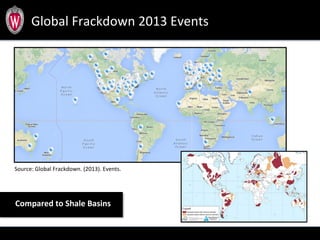
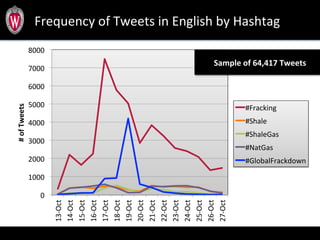
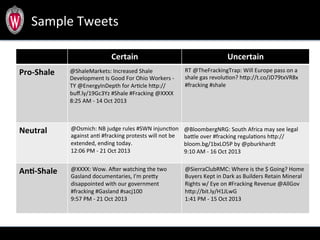
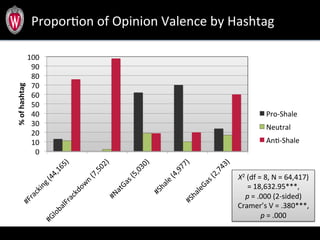
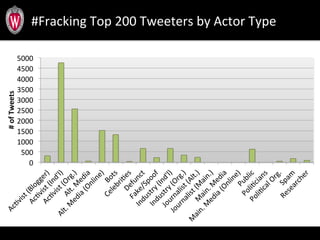
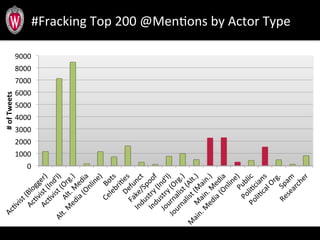
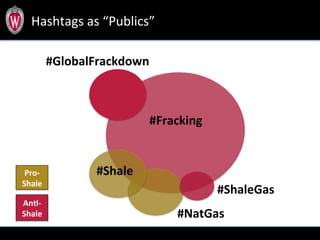
This document summarizes a study analyzing over 64,000 tweets regarding hydraulic fracturing (fracking) during Global Frackdown events in October 2013. The study used machine learning to classify tweets by hashtag (such as #fracking and #globalfrackdown), geographic origin, and opinion (pro-shale, neutral, anti-shale). It found differences in the proportions of opinions expressed between hashtags, with #fracking having more pro-shale tweets and #globalfrackdown having more anti-shale tweets. The study also analyzed the top tweeters and mentions to identify key actors in the discussions.