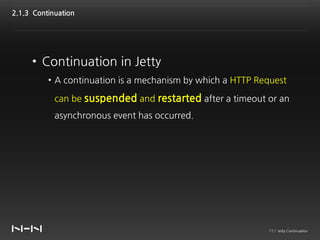
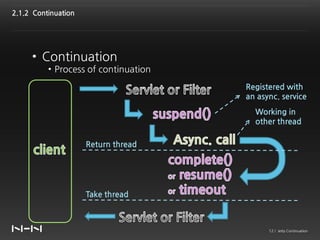
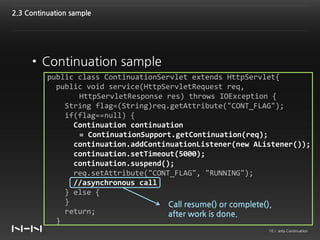
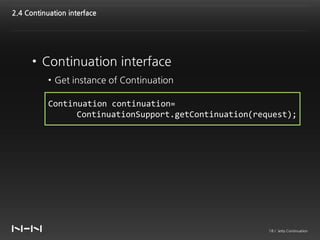
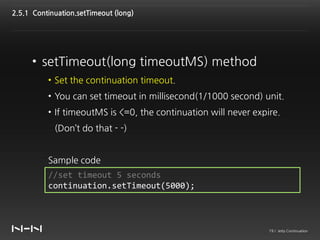
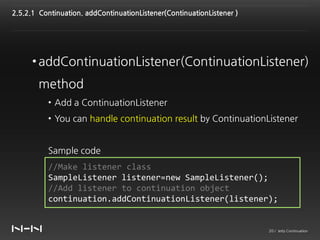
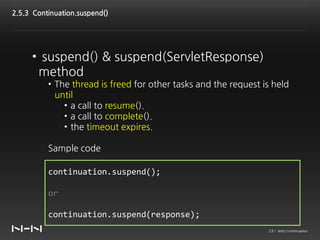
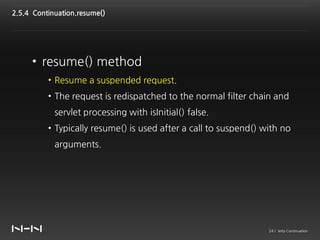
This document discusses Jetty Continuation, which allows suspending and resuming HTTP requests in Jetty. It allows one thread to handle multiple requests asynchronously. With Continuation, thread usage can be reduced by suspending requests during asynchronous operations and resuming them on completion. Listeners can be used to handle request completion or timeout. Continuations provide asynchronous servlet processing capabilities to Jetty.















![2.6 Asynchronous on Java
• Thread sample
package com.cont.sample.async;
public class ThreadSample extends Thread {
public static void main(String args[]) {
ThreadSample sample=new ThreadSample();
System.out.println("Before start sample."); Before start sample.
sample.start(); After start sample.
System.out.println("After start sample."); Run method called
}
public void run() {
System.out.println("Run method called");
}
}
28 / Jetty Continuation](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/t3s2-jettycontinuation-100713195722-phpapp02/85/Jetty-Continuation-28-320.jpg)
![2.6 Asynchronous on Java
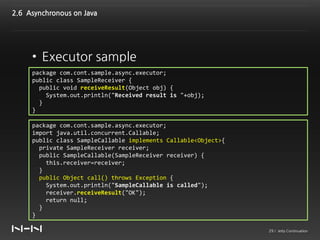
• Executor sample – execute
package com.cont.sample.async.executor;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
public class ExecutorMain {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ExecutorService service=
Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
Before submit
After submit
SampleReceiver receiver=
SampleCallable is called
new SampleReceiver();
Received result is OK
SampleCallable callable=
new SampleCallable(receiver);
System.out.println("Before submit");
service.submit(callable);
System.out.println("After submit");
}
}
30 / Jetty Continuation](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/t3s2-jettycontinuation-100713195722-phpapp02/85/Jetty-Continuation-30-320.jpg)