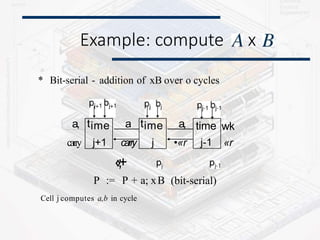
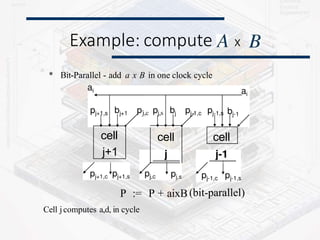
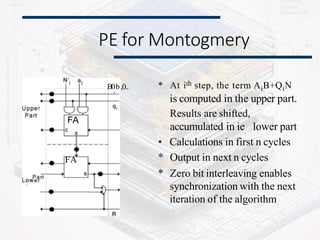
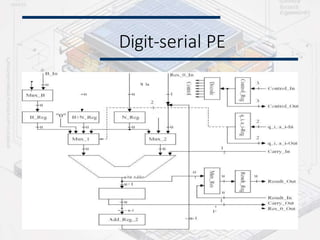
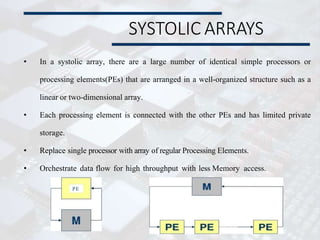
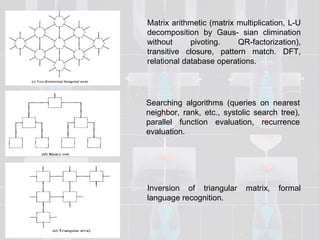
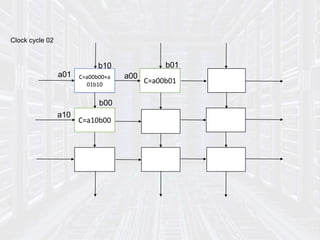
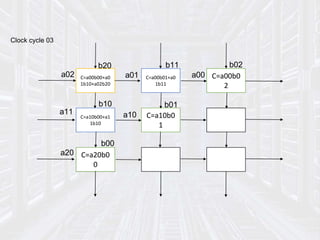
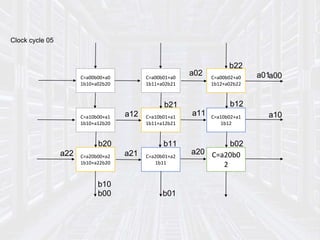
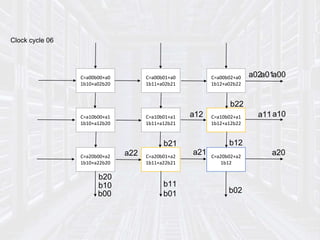
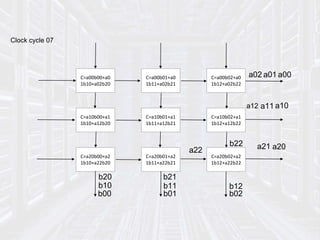
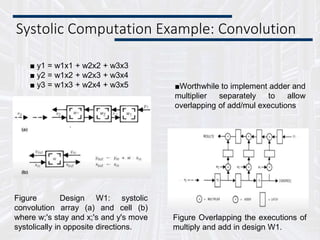
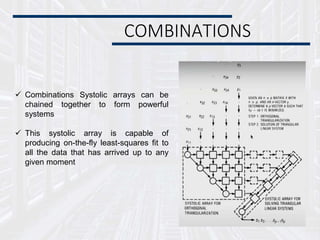
Systolic arrays are parallel processing architectures that leverage a rhythmic data flow to perform computations efficiently using a network of identical processing elements with local connections. This architecture is particularly suited for applications requiring high data throughput and minimizing memory access, distinguishing itself from von Neumann architectures by relying on synchronous data transfers and providing significant parallelism. Modern implementations of systolic arrays can be found in Google's Tensor Processing Unit, NVIDIA's tensor cores, and MIT's Eyeriss architecture, all designed to accelerate machine learning and AI workloads.









![RL 1
LR;
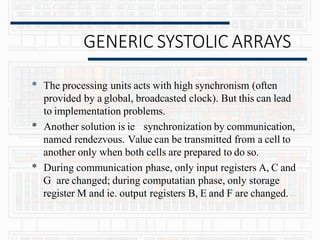
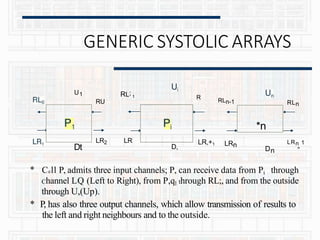
GENERIC SYSTOLIC ARRAYS
B[i] C[i]
A[i]
RL,
LR„,](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/systolicarch-240422095206-3b57a895/85/SYSTOLIC-ARCH-IN-COMPUTER-OPERATING-SYSTEM-pptx-23-320.jpg)
![GENERIC SYSTOLIC ARRAYS
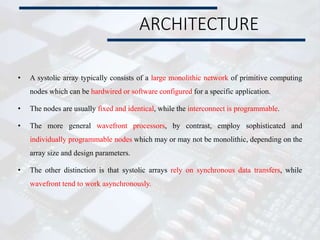
* The internal memory of cell PE contains six communica-tions
registers, denoted A[i], B[i],C[i], E[i], F[j] and G[i] .The remaining part of the
memory is denoted M[i] its size is independent from the size n of
the network.
* The program executed by every cell is a loop, whose body is
finite, partially ordered by set of statement that specify three
kinds of actions
• values (data) from some input channels,
• Performing computations within the internal memory
• Transmitting values (results) to output channels.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/systolicarch-240422095206-3b57a895/85/SYSTOLIC-ARCH-IN-COMPUTER-OPERATING-SYSTEM-pptx-24-320.jpg)