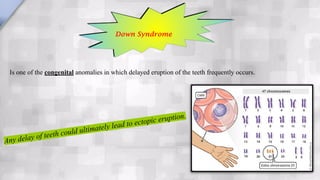
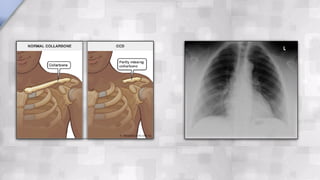
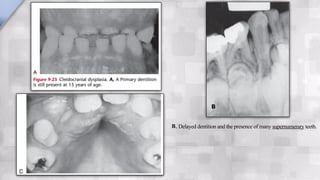
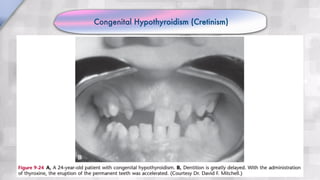
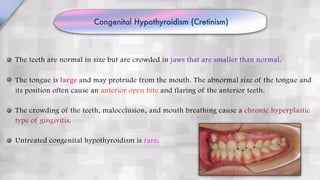
Systemic conditions such as Down syndrome, cleidocranial dysplasia, hypothyroidism, and hypopituitarism can cause delayed tooth eruption. Specifically, Down syndrome is associated with delayed eruption that can lead to ectopic eruption. Cleidocranial dysplasia is characterized by absent clavicles, delayed primary dentition, and presence of supernumerary teeth. Congenital hypothyroidism results in smaller jaws, crowded teeth, and delayed eruption of both primary and permanent teeth. Hypopituitarism causes retention of primary teeth and failure of permanent teeth to erupt.