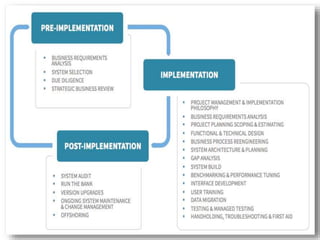
The document discusses system maintenance. It defines system maintenance as keeping software operational through preventative measures, monitoring, and fixing problems. System maintenance involves three classes: corrective maintenance fixes errors, adaptive maintenance changes functions to satisfy new user needs due to organizational changes, and perfective maintenance adds or modifies programs to enhance performance and respond to additional user needs due to internal or external changes. Post-implementation maintenance refers to maintaining the system after it has been installed and is operational.