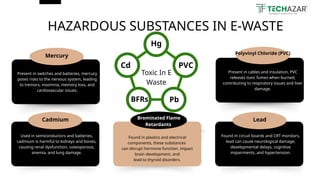
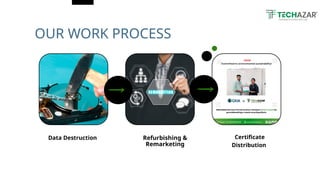
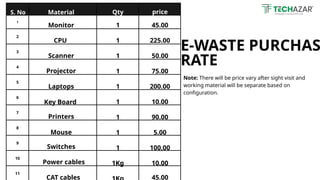
Techazar offers expert e-waste recycling solutions, responsibly handling electronic waste for safe disposal and resource recovery. E-waste is the fastest-growing waste stream, with over 50 million tons produced annually, containing harmful substances that can adversely affect health and the environment. The company promotes sustainability through refurbishing and remarketing electronics, alongside initiatives for mindful consumption and technological innovations in recycling.