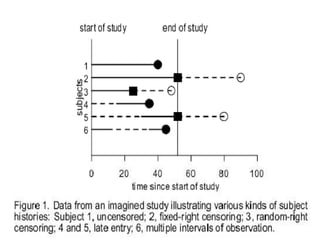
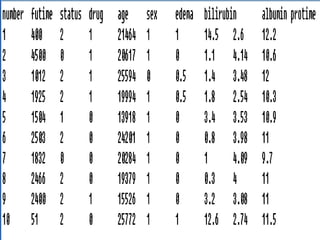
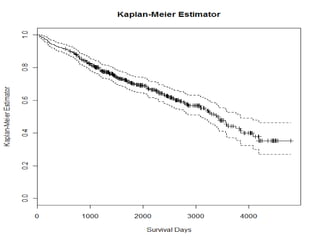
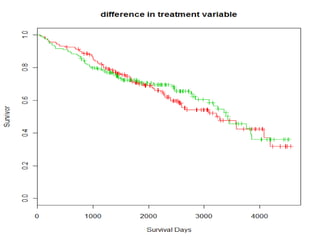
- Survival analysis models time to event data and accounts for censoring. It can compare groups and examine covariate effects.
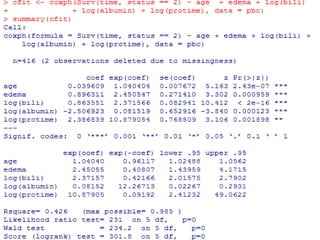
- The document demonstrates survival analysis in R using the PBC dataset. Key methods include the Kaplan-Meier estimator, Mantel-Haenzel test, and Cox regression model.
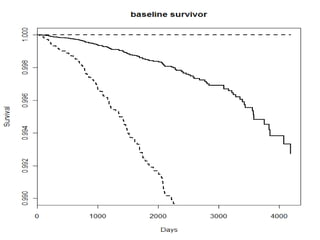
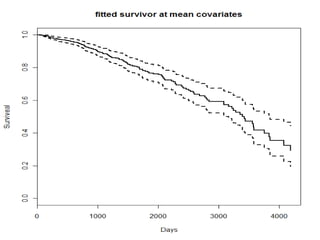
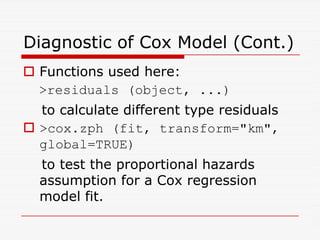
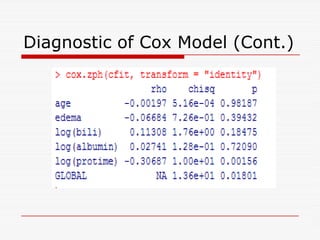
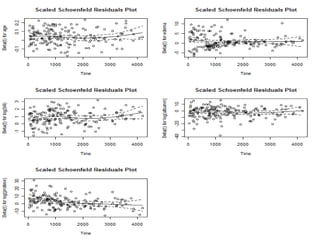
- Functions like survfit(), survdiff(), and coxph() are used to generate Kaplan-Meier curves, perform log-rank tests, and fit Cox models respectively. Diagnostics assess the proportional hazards assumption.