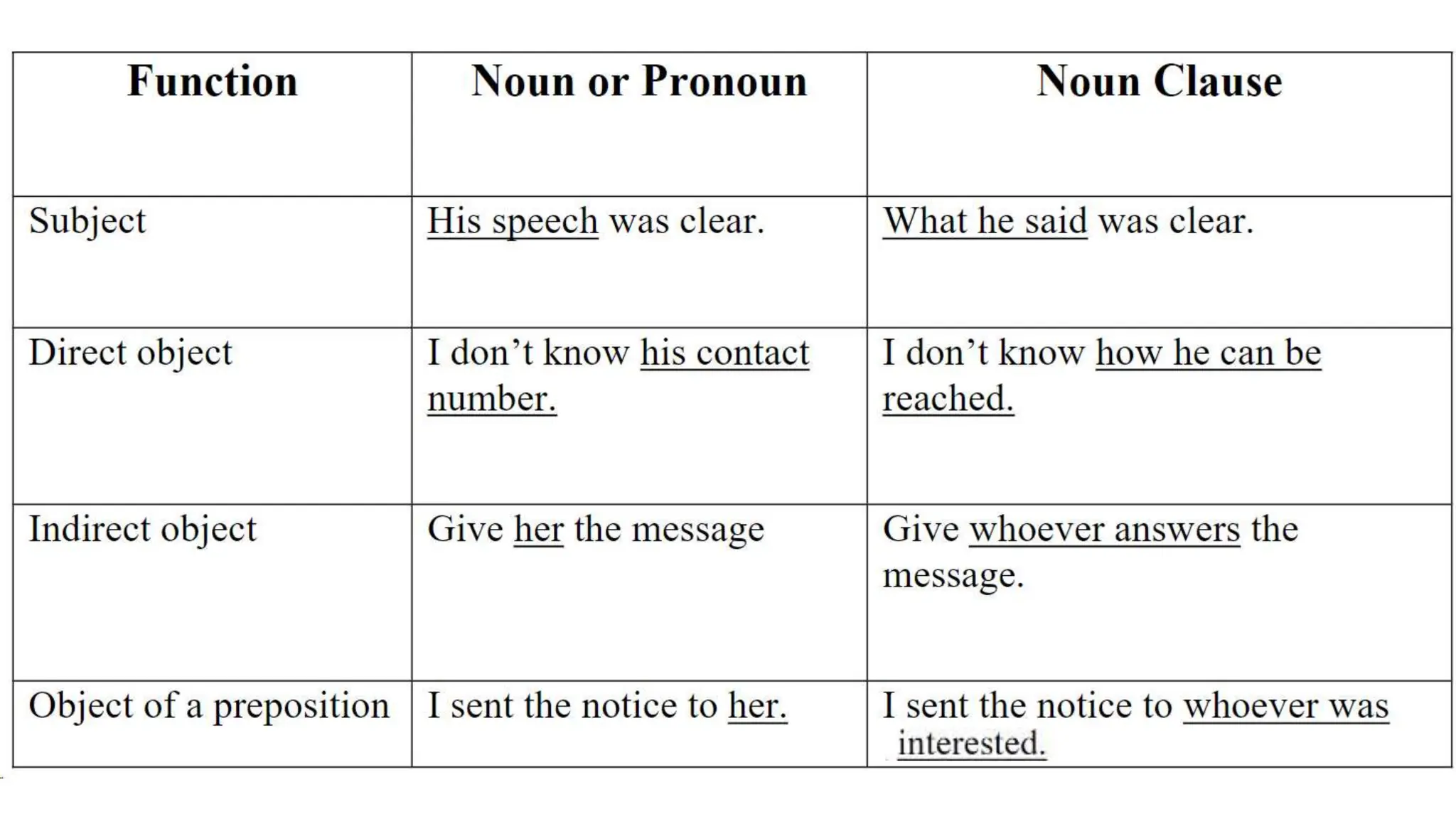
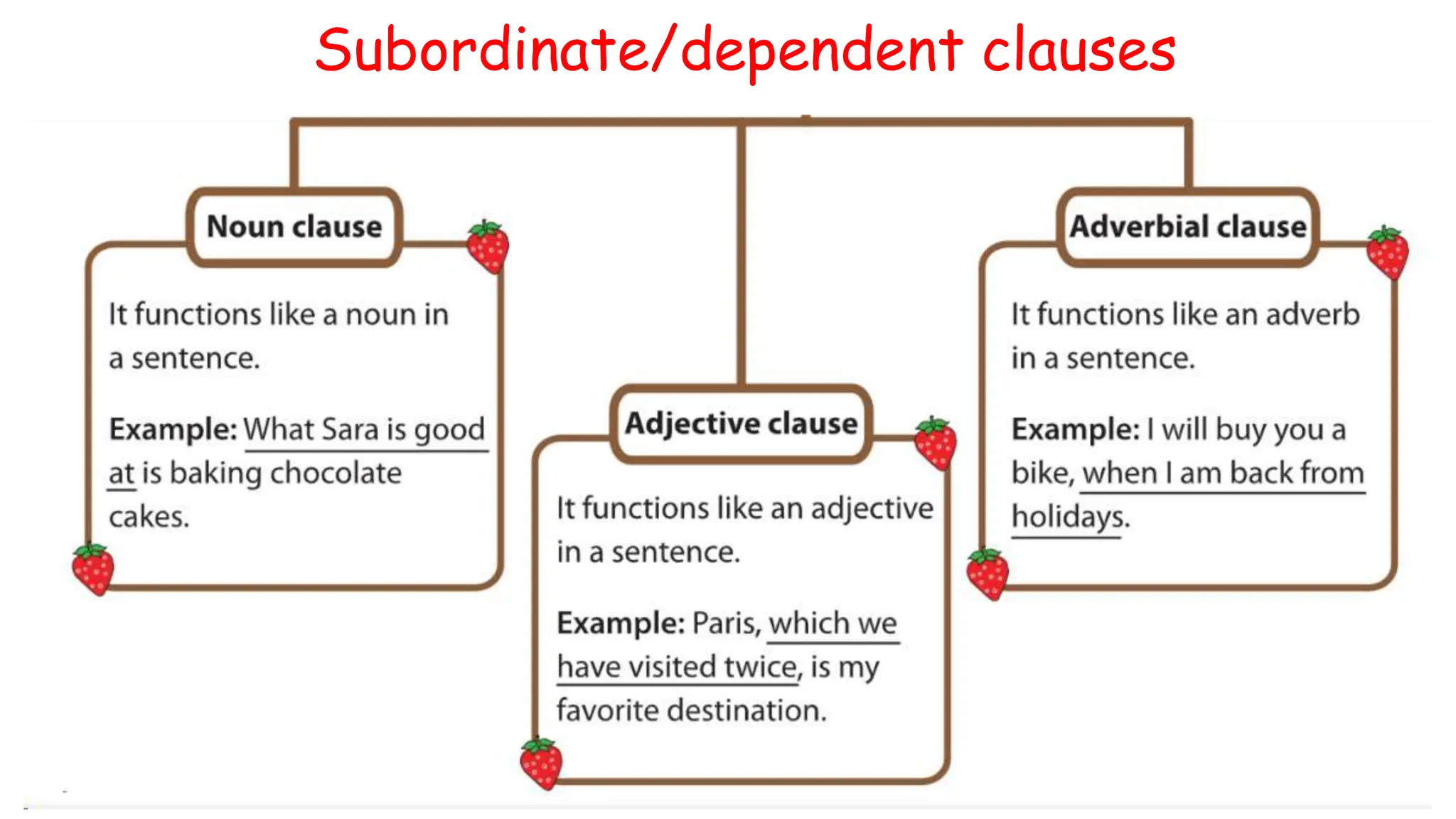
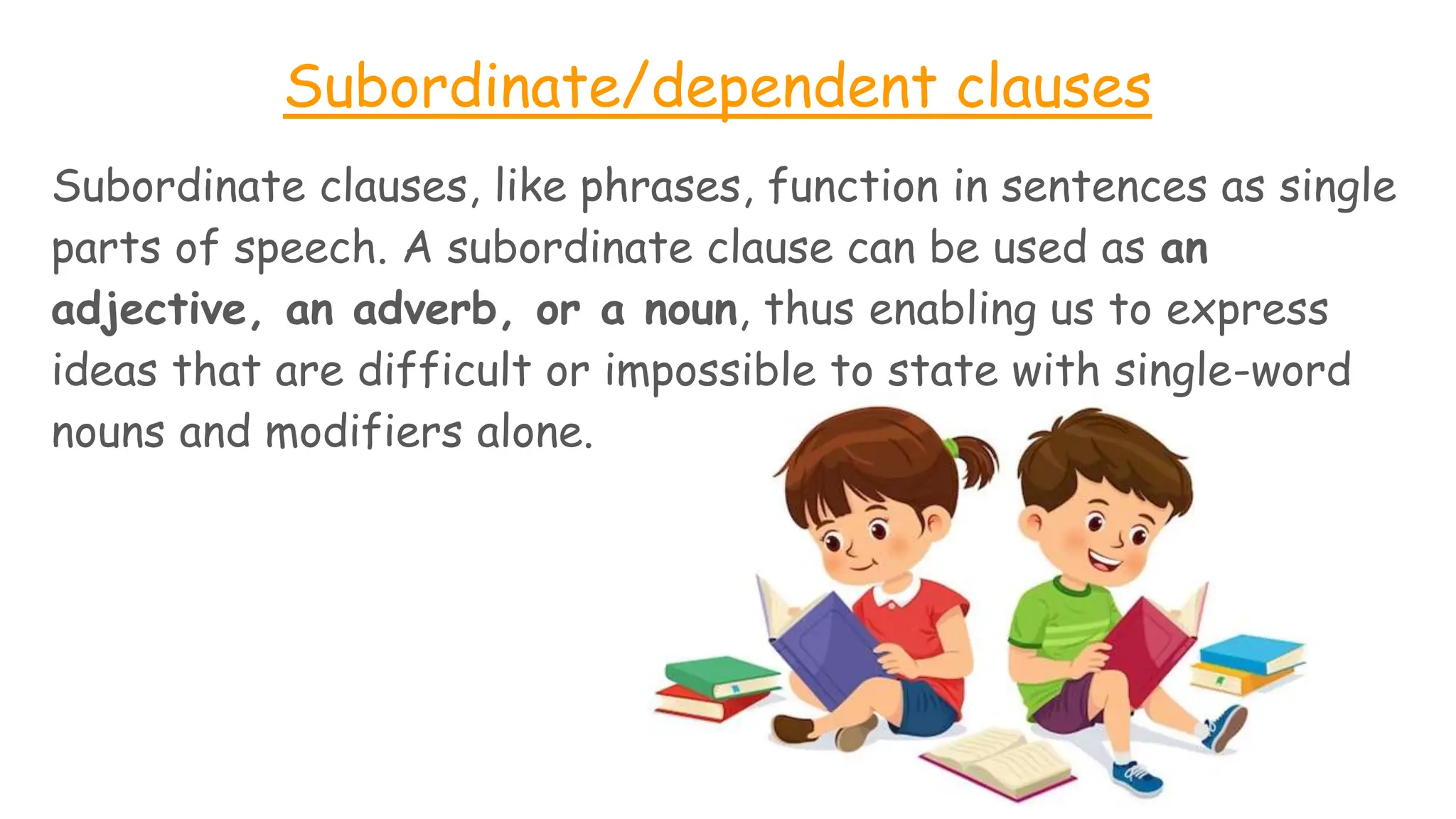
The document explains subordinate or dependent clauses, which function as single parts of speech in sentences. It details different types of clauses, such as adjective clauses (modifying nouns/pronouns), adverb clauses (modifying verbs/adjectives/adverbs), and noun clauses (acting as nouns). It also discusses the role of relative pronouns in introducing adjective clauses and the use of subordinating conjunctions for adverb clauses.


![Relative Pronouns: Examples
● Lois, who enjoys running, has decided to
enter the marathon. [The relative
pronoun who relates the adjective clause
to Lois. Who is used as the subject of
the adjective clause.]
● Donna suggested the science project
that I exhibited at the fair. [Project,
The word that the clause modifies, is the
antecedent of the relative pronoun that.
The pronoun is used as the direct object
in the adjective clause.]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/subordinateclauses-240717181527-5d29275e/75/Subordinate-clauses-for-grade-5-students-5-2048.jpg)