The document discusses several topics related to cybersecurity including:
1. Current issues in cyberspace including usage growth, criminal/terrorist elements, and need for national/global cooperation and efforts that have been made.
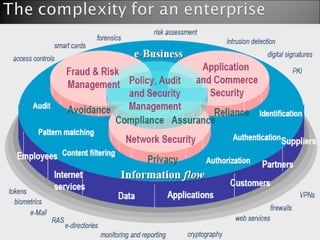
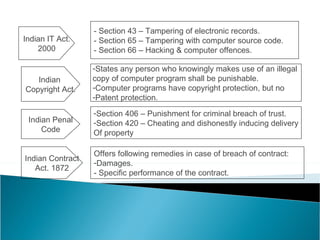
2. The Indian scenario regarding cybersecurity laws and critical infrastructure protection.
3. Statistics on internet and mobile phone users globally and in countries like India, China, Japan, and South Korea.
4. Types of cyber threats like malware, data theft, denial of service attacks, and regulations/laws in place in India regarding cybersecurity.








![[email_address] [email_address]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/subimalbhattarchajee-101221055717-phpapp01/85/Subimal-bhattarchajee-11-320.jpg)