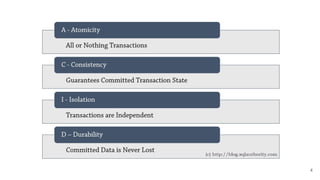
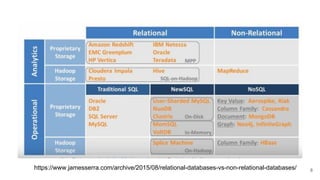
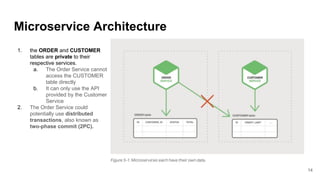
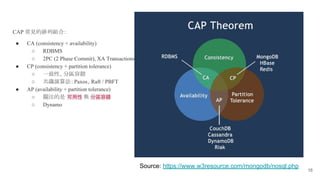
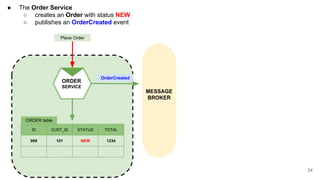
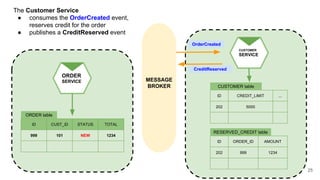
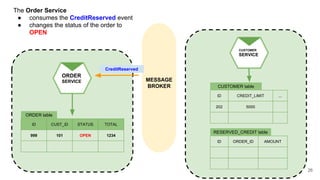
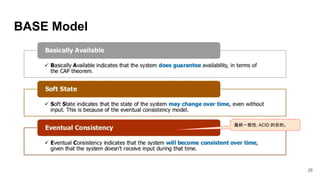
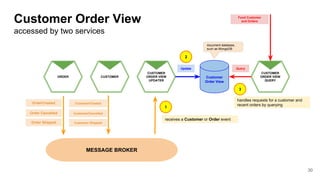
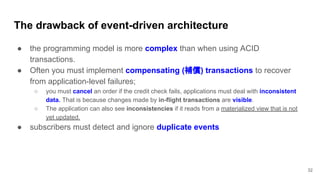
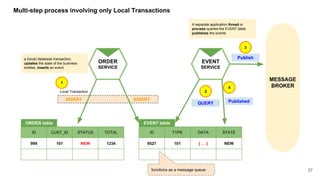
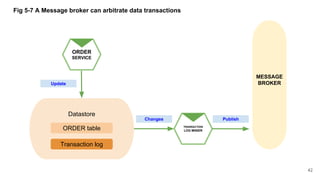
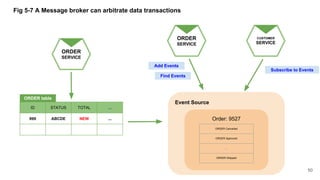
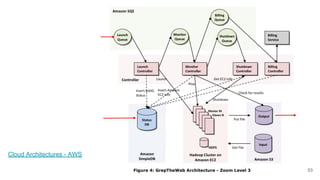
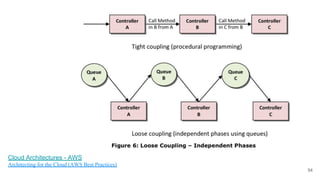
In microservices architecture, each service has its own private datastore, leading to challenges in maintaining consistency across multiple services and implementing queries. An event-driven architecture can help address these challenges by allowing services to publish and subscribe to events, though it presents its own difficulties, such as ensuring atomicity in updates and handling eventual consistency. Various methods, including using databases as message queues and event sourcing, can be used to implement this architecture effectively.