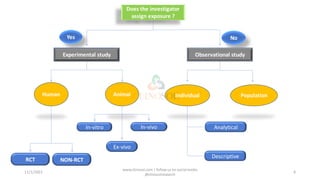
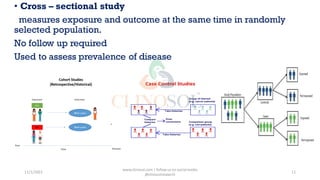
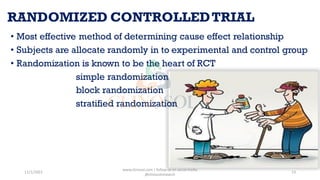
This document discusses study designs in clinical trials. It defines a study design as a specific plan or protocol for conducting a study. There are two main types of study designs: observational studies and experimental studies. Observational studies observe subjects and have no active intervention, while experimental studies manipulate variables under controlled conditions. Some fundamental study designs discussed include randomized controlled trials, cohort studies, case-control studies, case reports, and case series. The conclusion is that a study design should be a highly specific plan to be followed without deviation to achieve the research purpose.