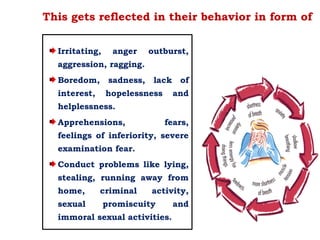
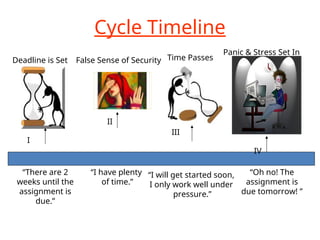
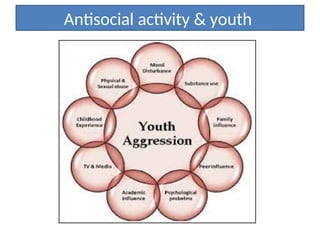
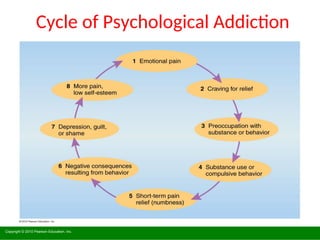
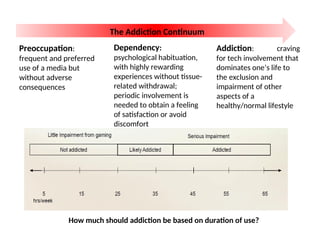
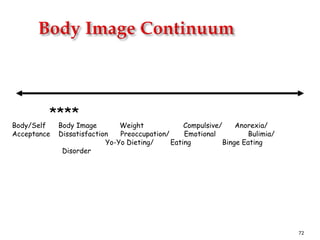
The document discusses the mental health challenges faced by students, emphasizing the impact of psychological issues on academic performance and social relationships. It highlights procrastination, exam anxiety, and substance abuse as significant factors contributing to academic dysfunction, while also providing insights into coping strategies. Additionally, it addresses broader issues such as emotional problems, addiction, and the importance of discipline and support in managing youth mental health.