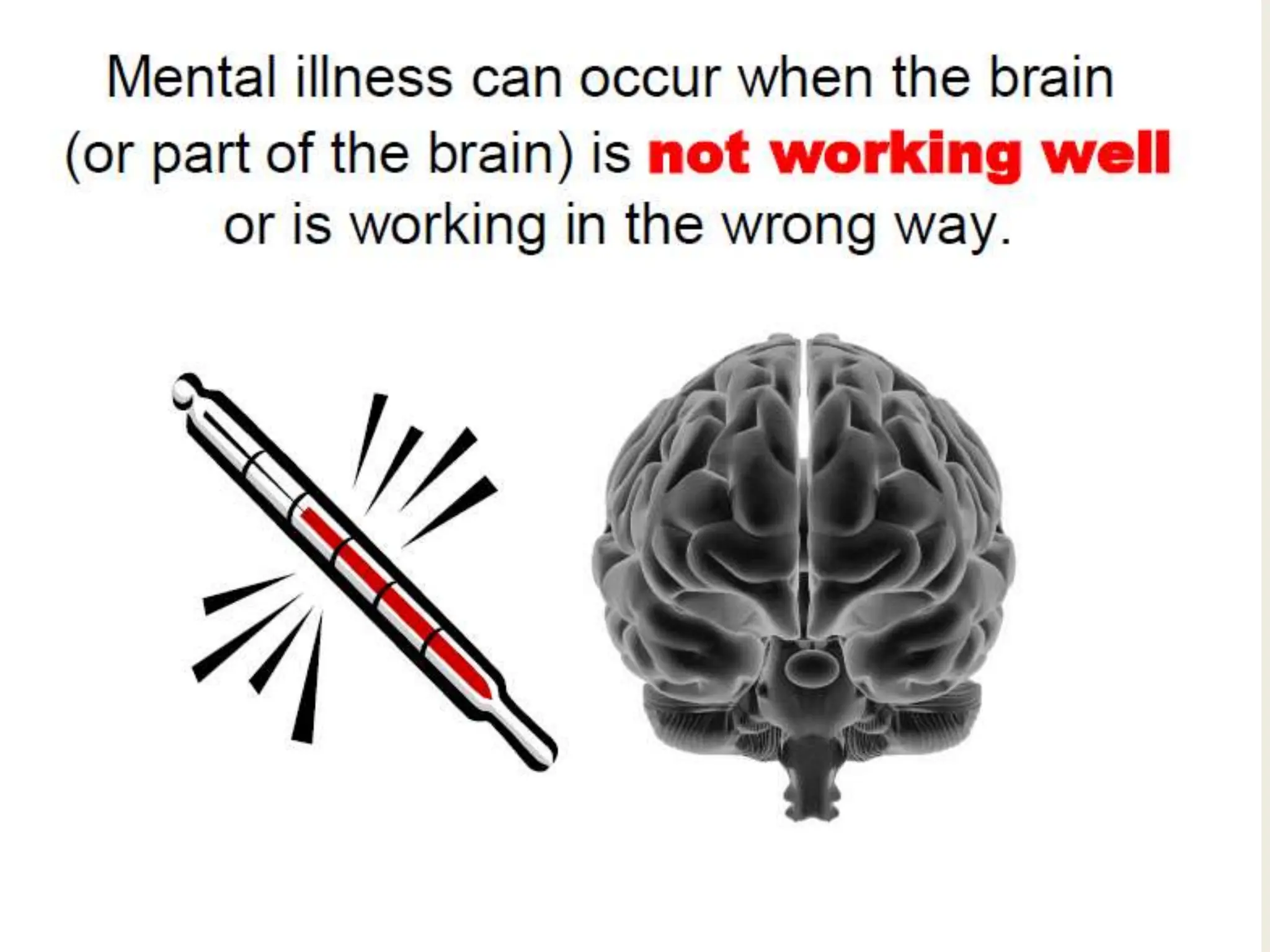
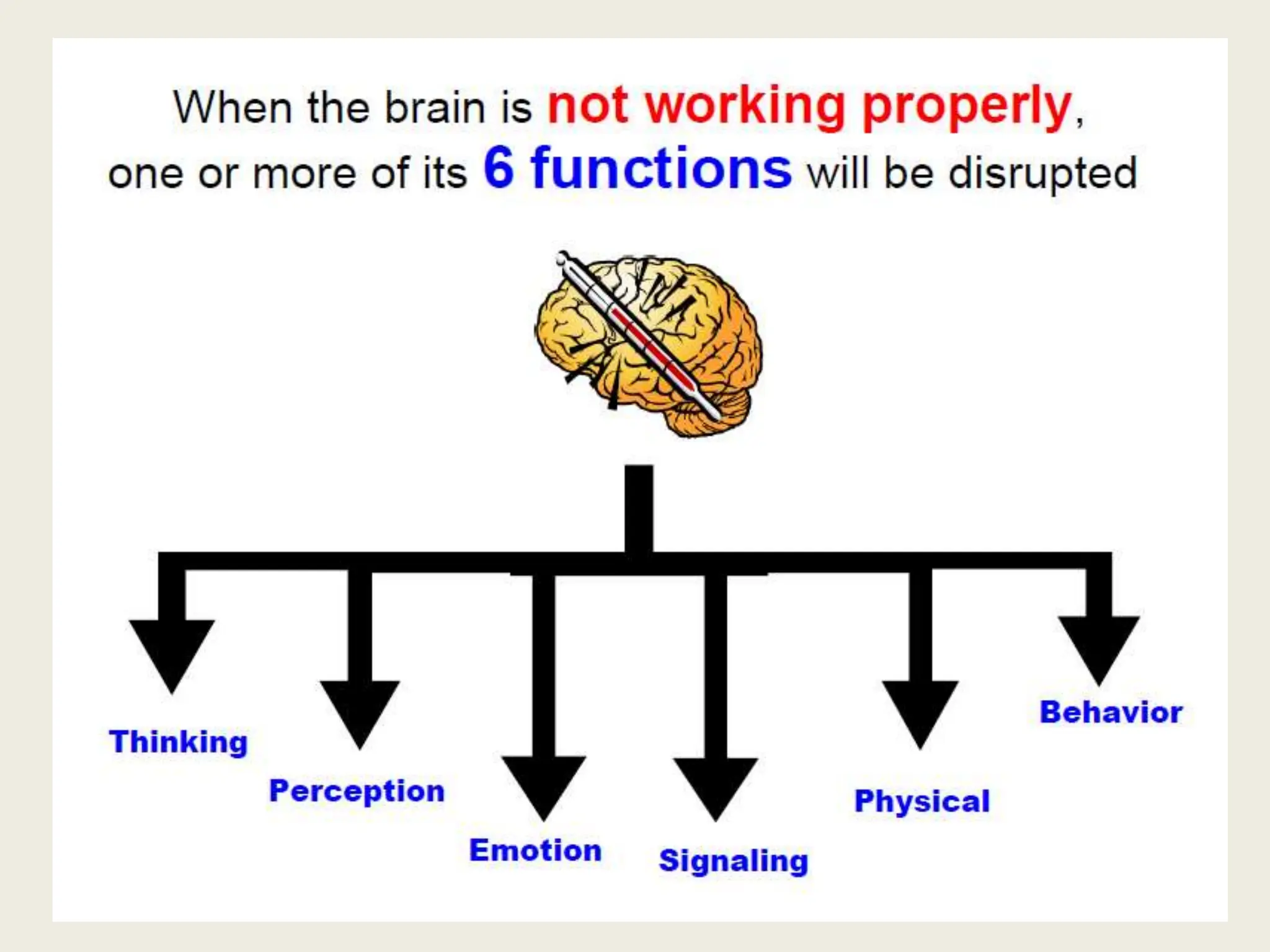
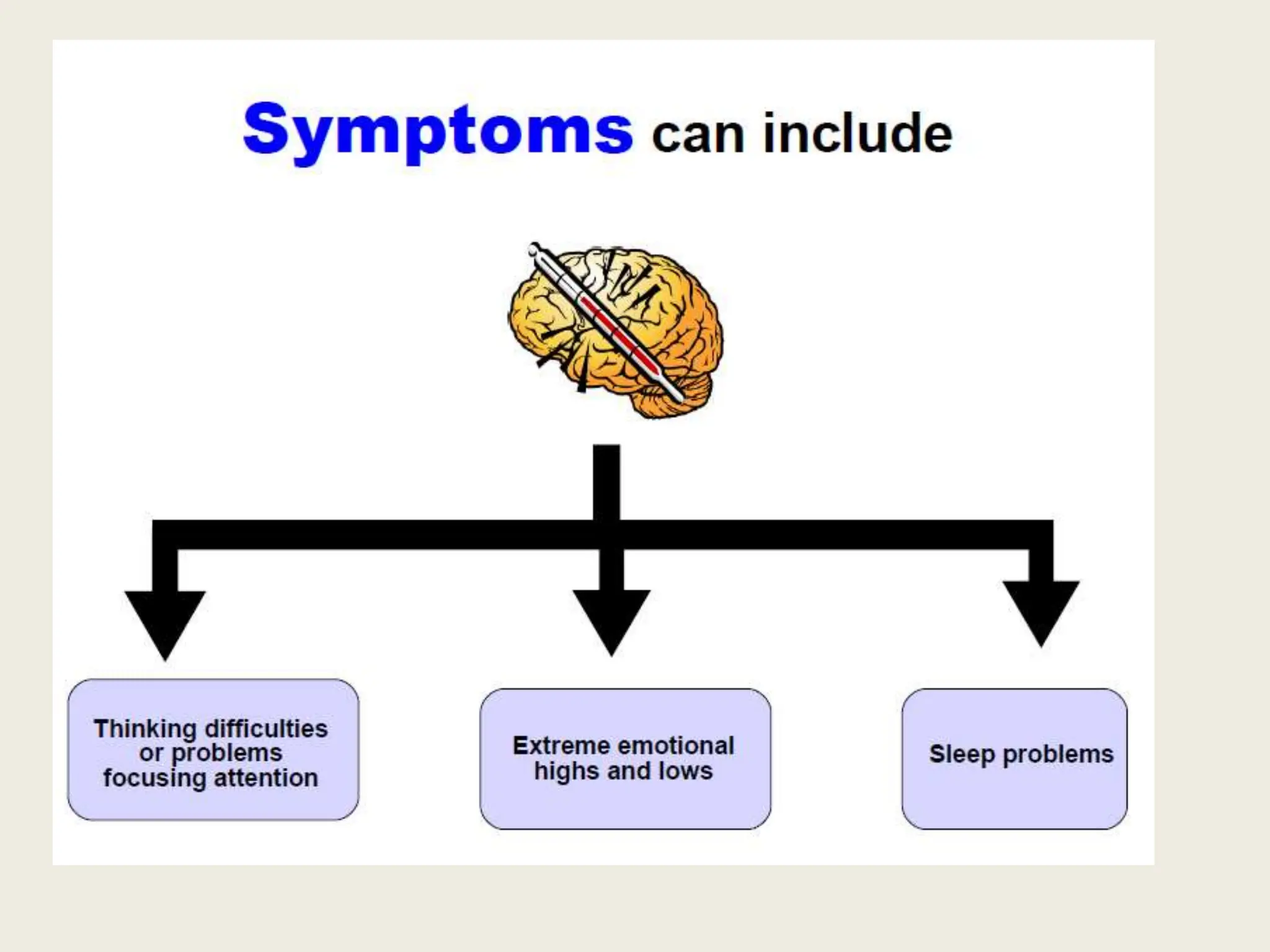
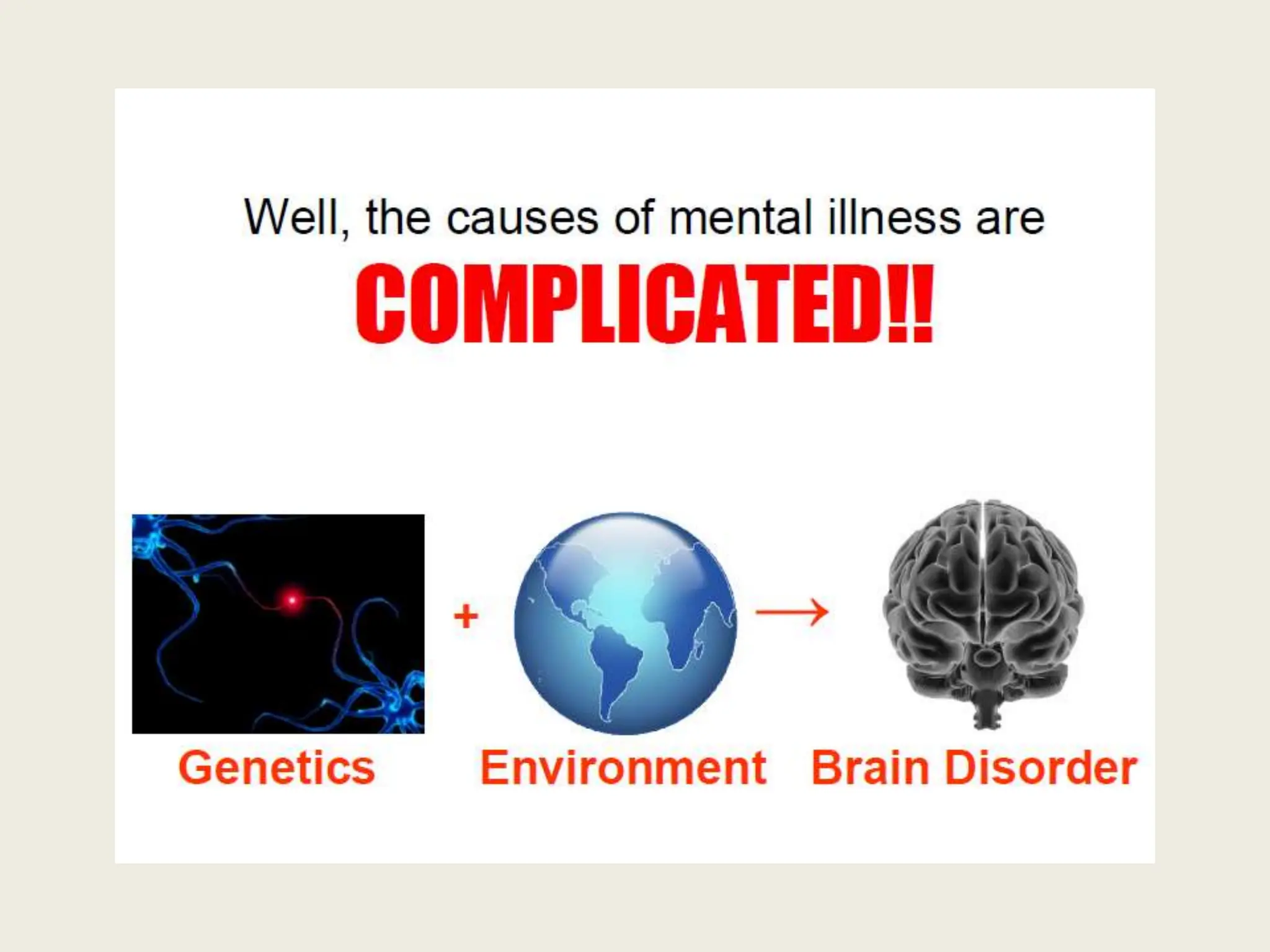
This document discusses the history of understandings and treatments of mental health and illness from ancient times through modernity across various cultures and religions. It covers early Greek, Roman, Hindu, Mesopotamian, Biblical, and early Christian views that attributed mental disorders to supernatural causes like gods, demons, spirits, and witchcraft. It then discusses the early medicalization of mental illness beginning with Hippocrates' natural explanations. The document also outlines signs and symptoms of mental disorders as well as traditional and modern treatments used in non-Western and Indian contexts.