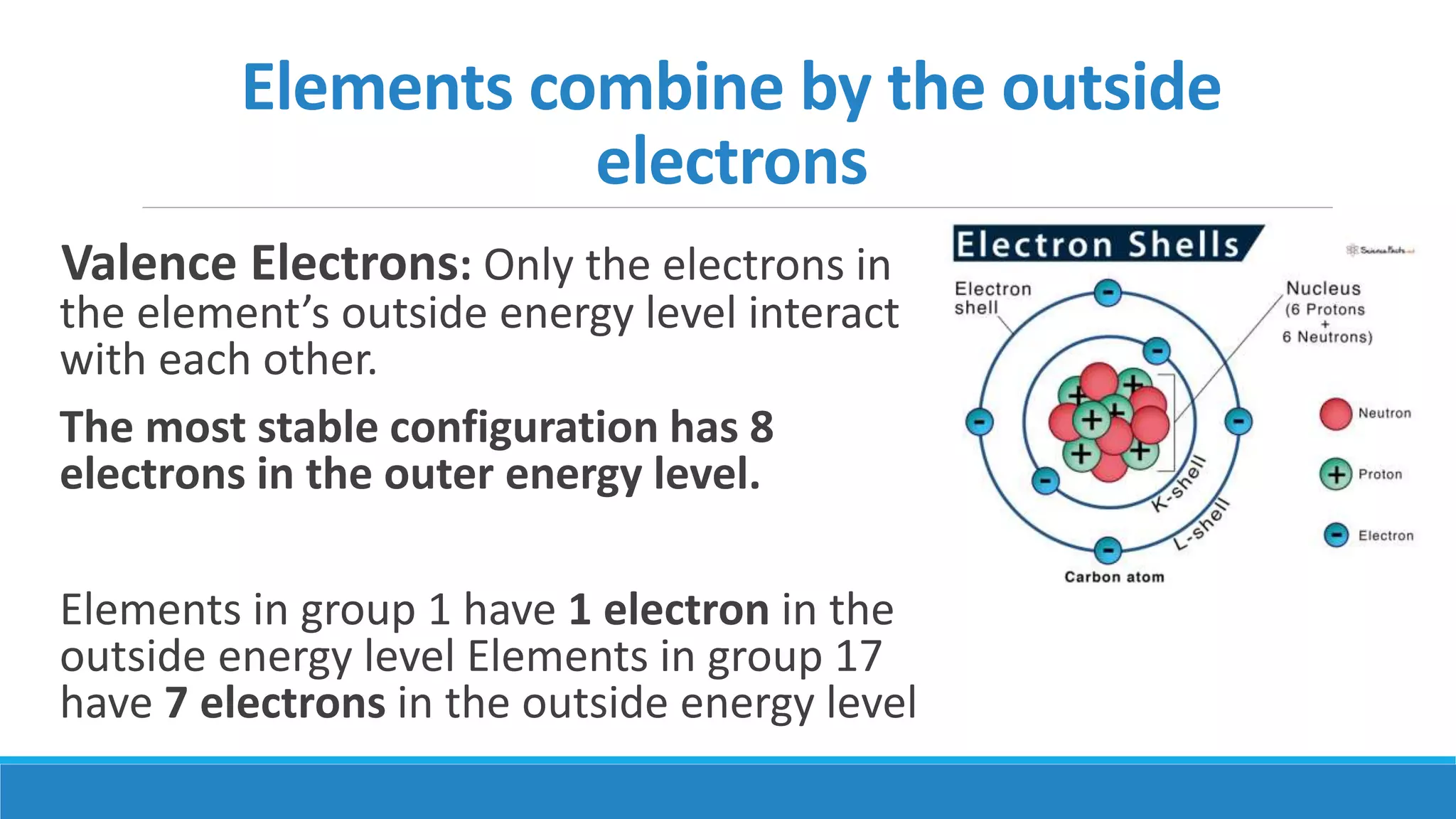
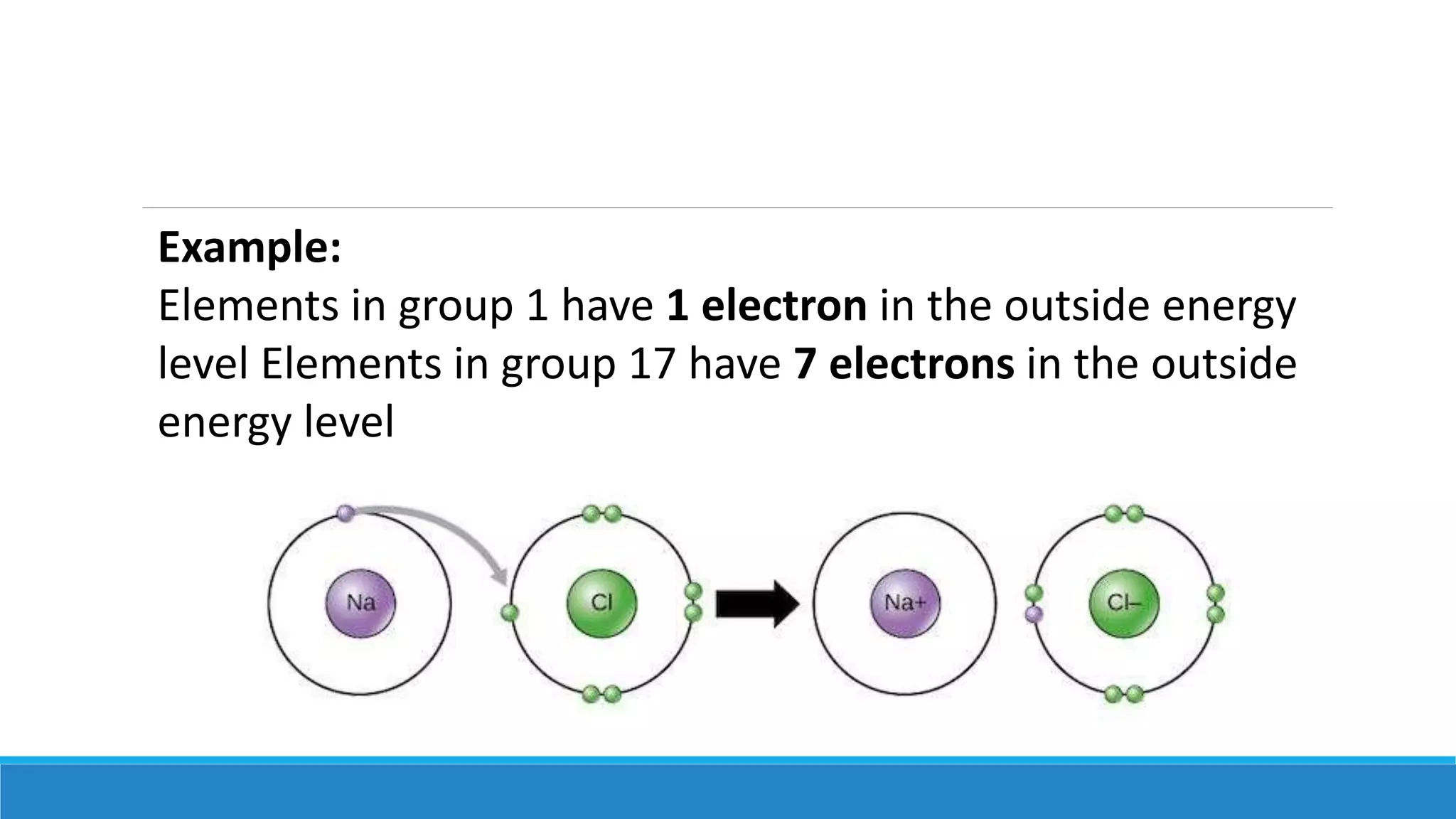
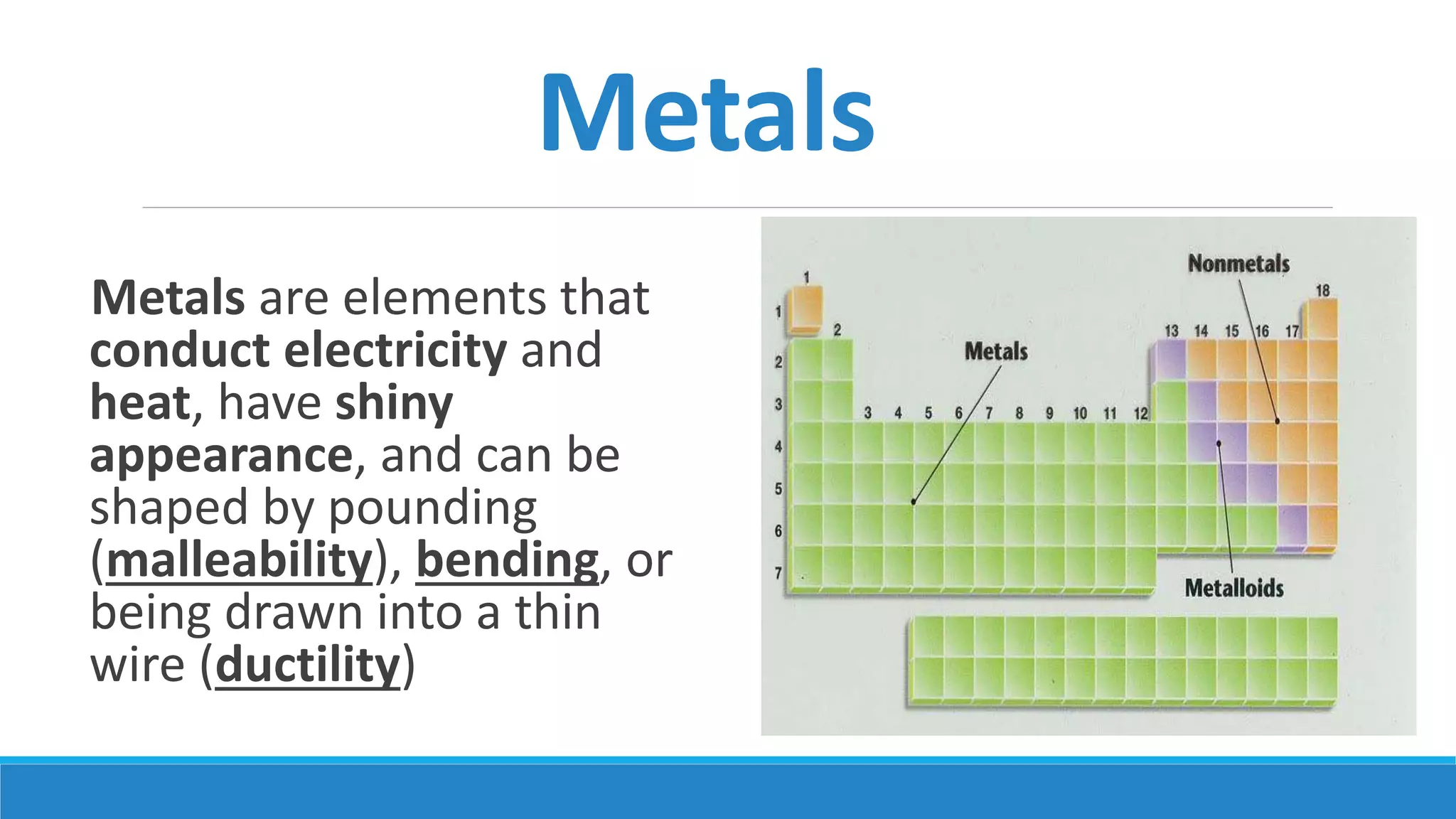
1) Matter is anything that occupies space and can be perceived by the senses. It exists in three physical states - solid, liquid, and gas - depending on its composition and structure.
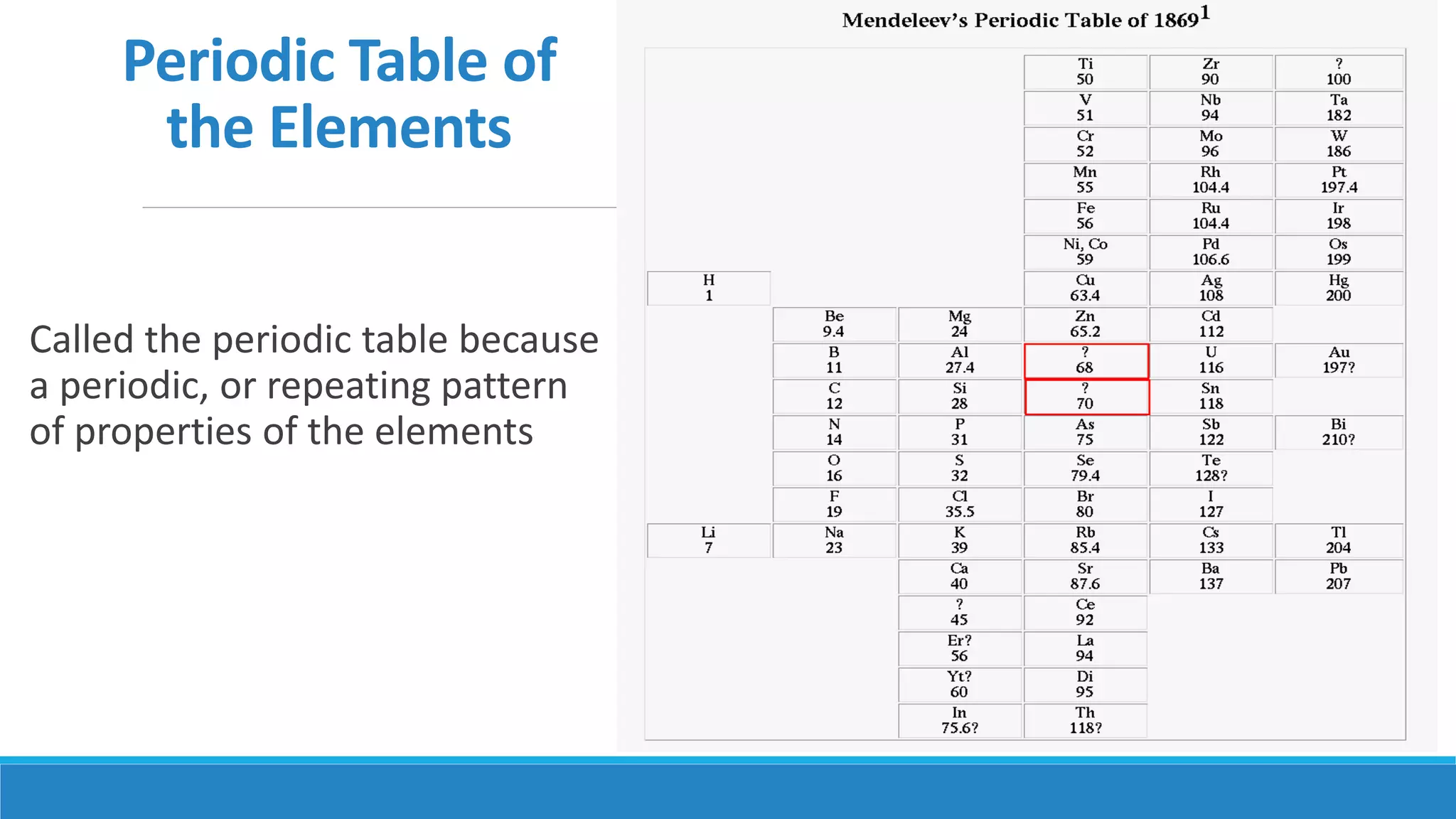
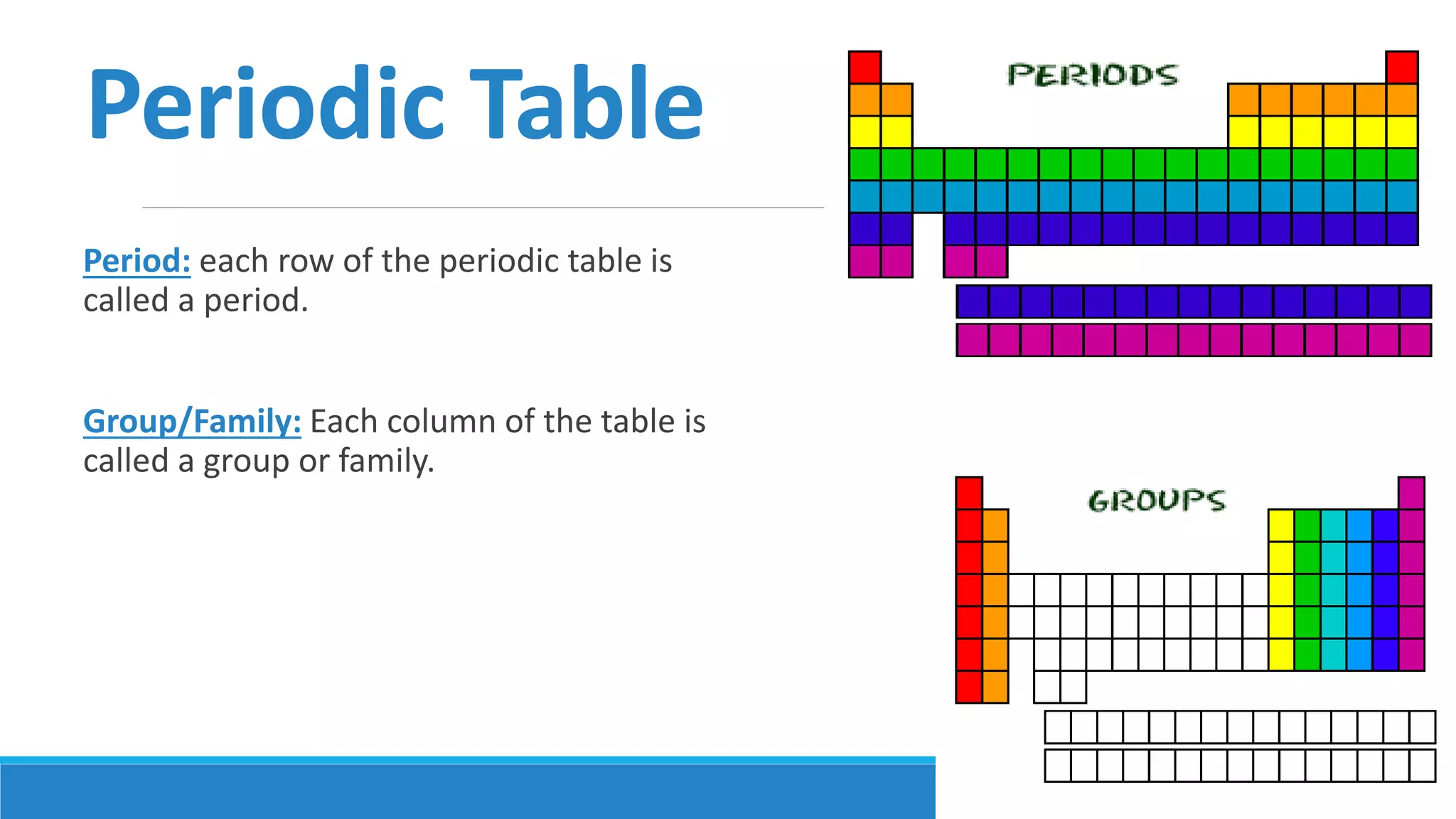
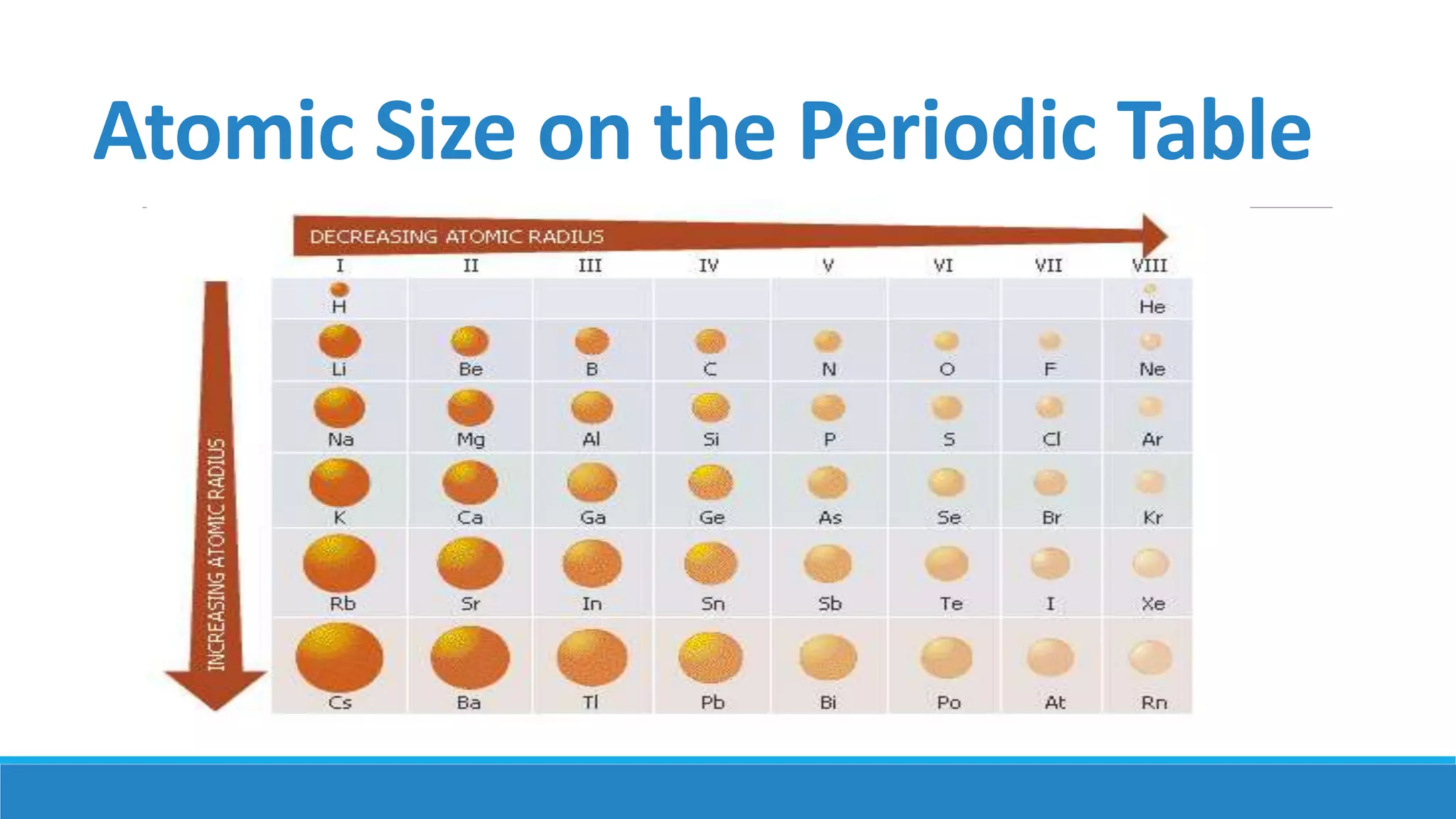
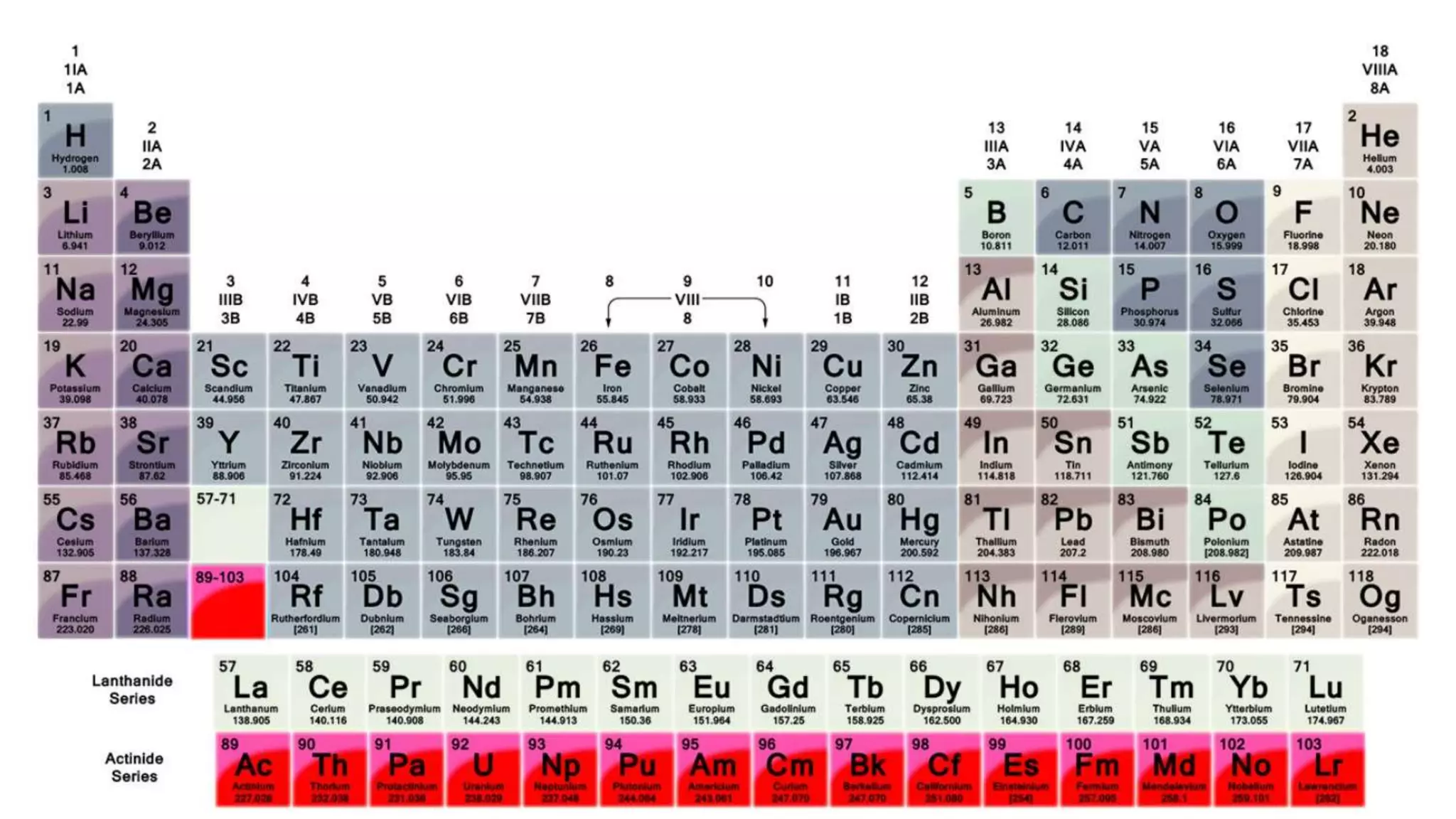
2) Atoms are the fundamental units that make up elements, which in turn make up all matter. John Dalton established the atomic theory, proposing that atoms are extremely small particles that retain their identity in chemical reactions.
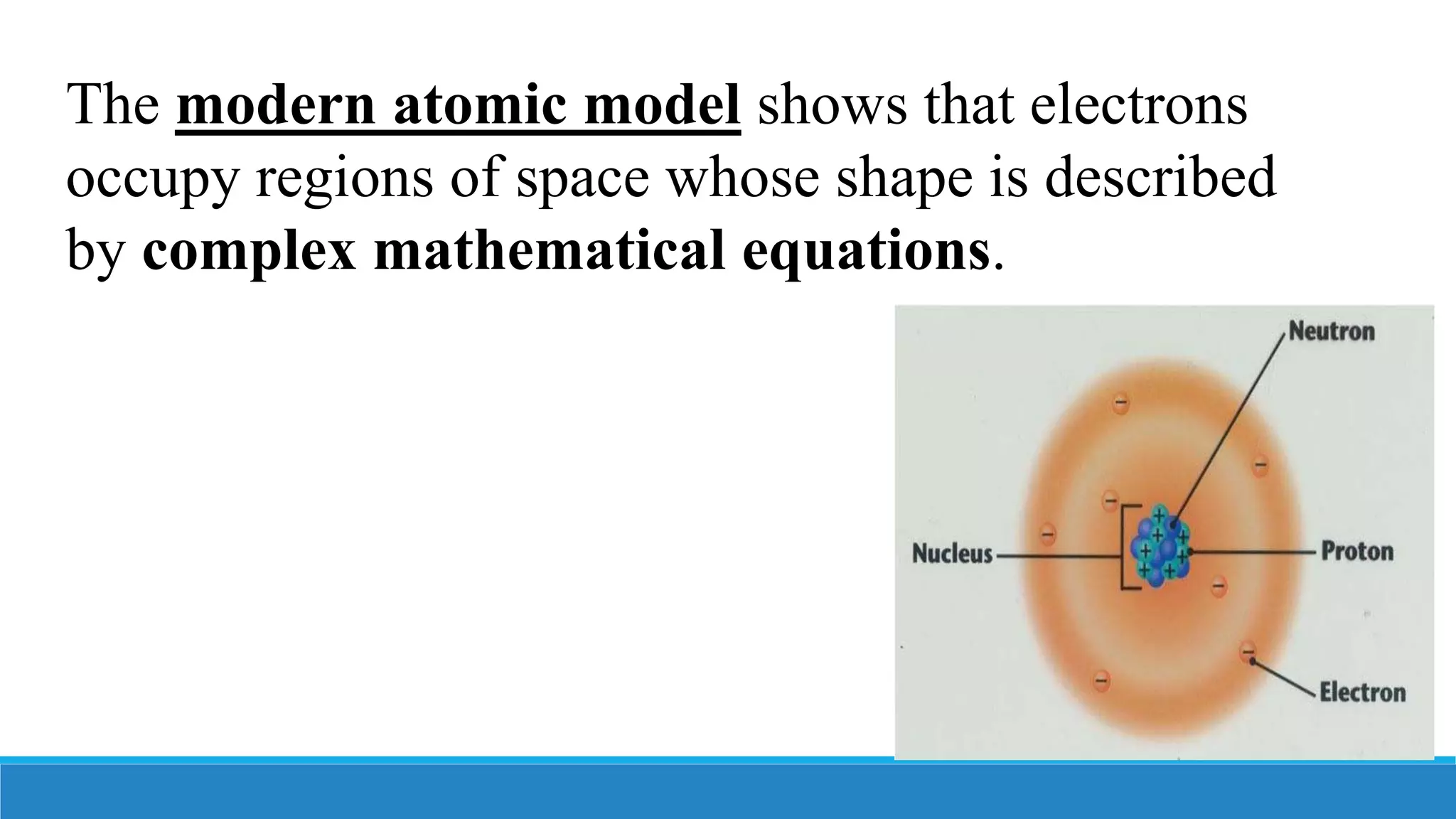
3) The modern atomic model shows that atoms consist of a dense nucleus containing protons and neutrons, surrounded by electrons in regions described by mathematical equations. The discovery and refinement of this structure advanced through the work of scientists like Thomson, Rutherford, and Bohr.