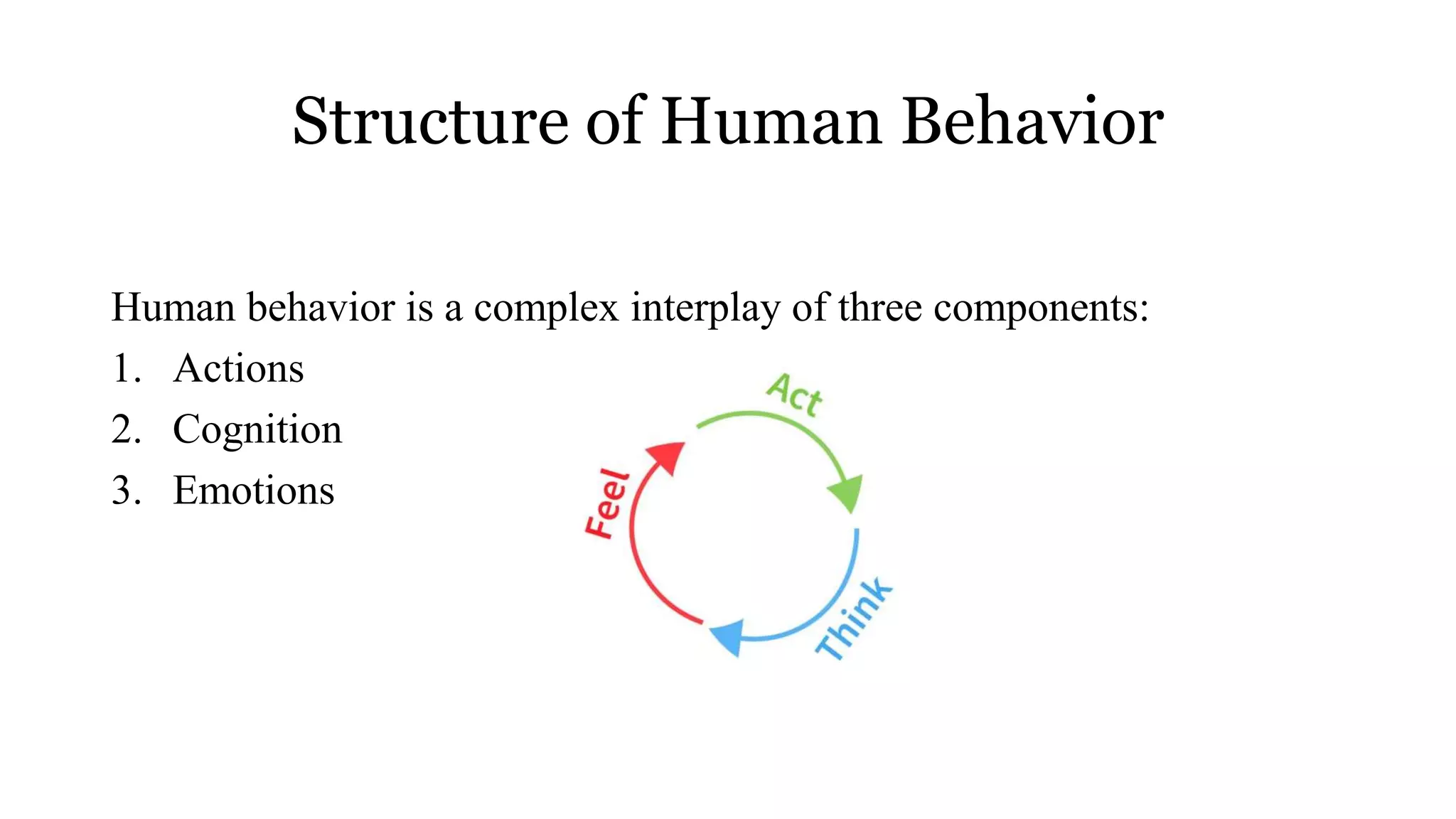
Human behavior is influenced by genetic, cultural, and individual factors and is composed of actions, cognitions, and emotions. Organizational behavior studies how individuals and groups act within organizations and considers factors like individual differences, perception, motivation, and values. It is important because it can contribute to personal and organizational growth, reduce conflicts, improve employee satisfaction, and facilitate management. The scope of organizational behavior includes studying individual, inter-individual, and group behaviors within organizations.