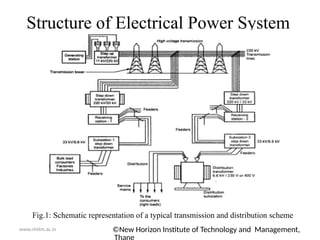
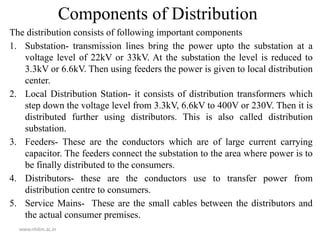
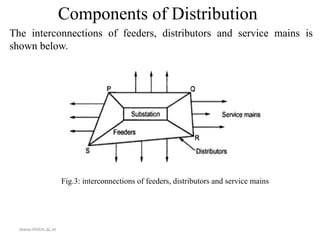
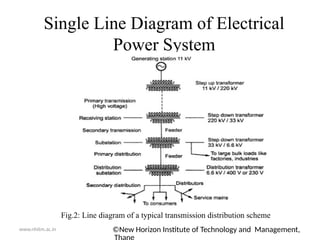
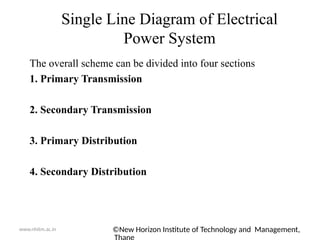
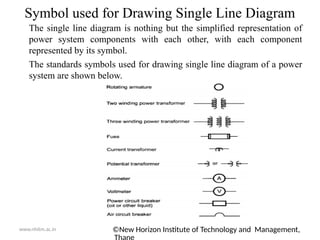
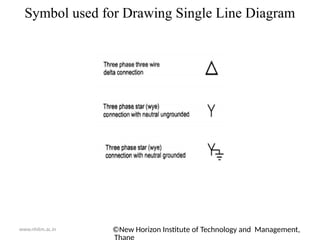
The document outlines the electrical power system for the academic year 2020-21, focusing on its components and structure, including generation, transmission, and distribution systems. Key elements such as generating stations, transformers, transmission lines, and distribution networks are detailed, emphasizing the conversion of various energy forms into electrical power. It also includes a diagrammatic representation of a typical transmission and distribution scheme, illustrating the flow of electrical power from generating stations to consumers.