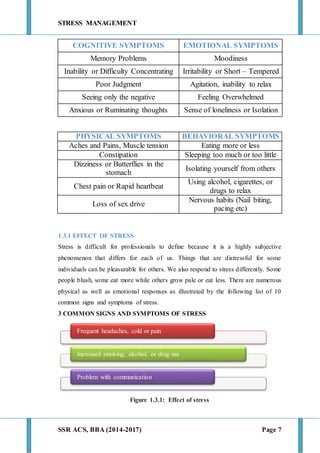
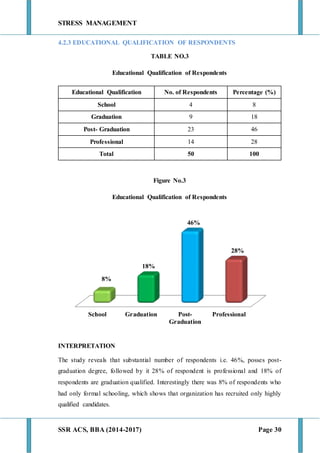
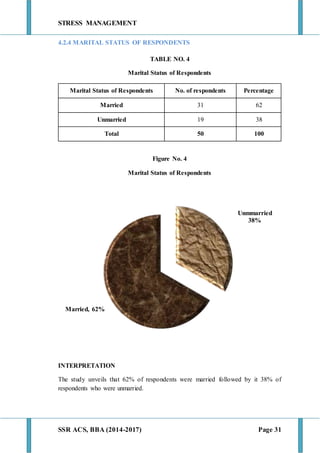
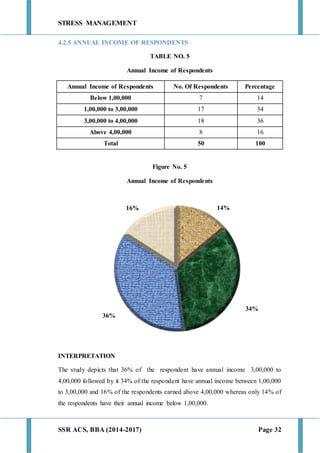
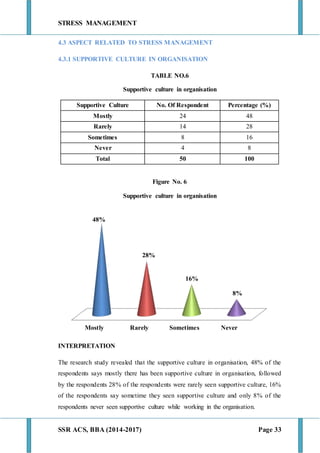
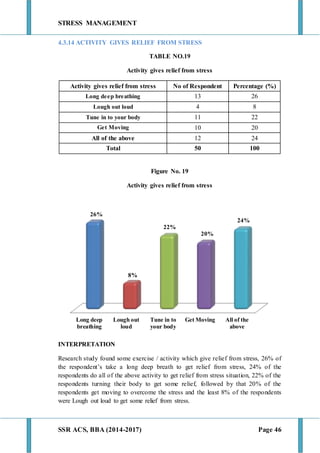
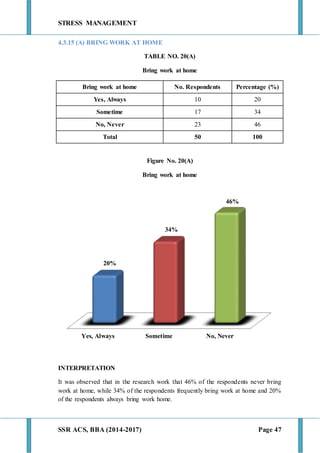
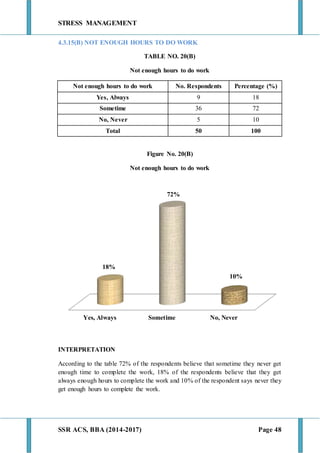
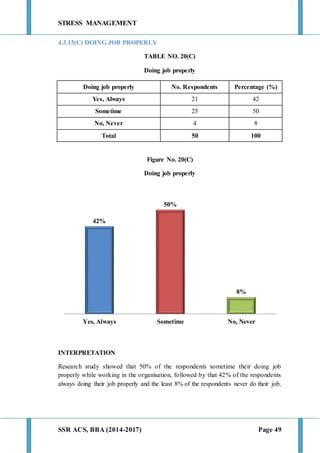
This document discusses stress management and defines stress. It explains that stress can come from various sources including the environment, social interactions, physiology, organizations, and one's thoughts. Both positive and negative stress are described. Signs and symptoms of stress are listed for cognitive, emotional, physical, and behavioral effects. Coping mechanisms are discussed at the individual level, including exercise, relaxation, cognitive therapy, and networking. Organizational coping strategies include supportive climates, job enrichment, role clarity, career planning, and stress workshops. The statement of problem indicates this research will study stress management practices at BIC Cello Exports Pvt. Ltd. given stress is inevitable and impacts productivity and health.