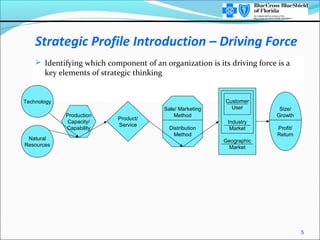
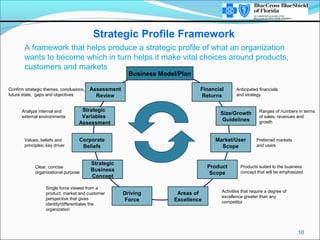
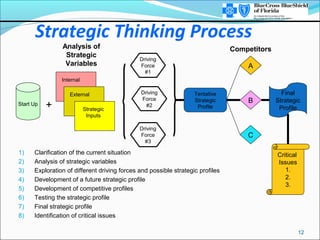
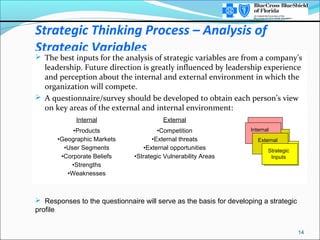
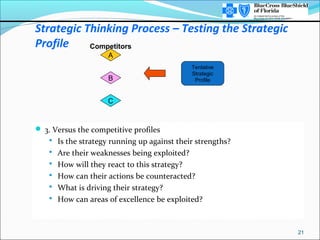
This document provides an overview of strategic thinking and the strategic profile framework. It outlines a process for developing a future strategic profile that includes clarifying the current situation, analyzing strategic variables, exploring potential driving forces, developing a tentative strategic profile, testing the profile against competitors and inputs, and finalizing the strategic profile and identifying critical issues. The strategic profile encompasses elements like the business concept, driving force, required areas of excellence, product/market scope, size/growth guidelines, and corporate beliefs. It is a framework to help organizations determine their future strategic direction and make choices around products, customers and markets.