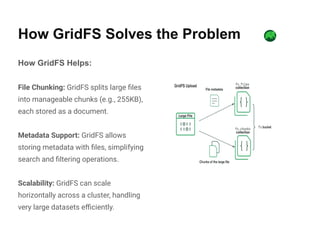
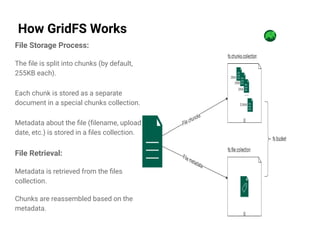
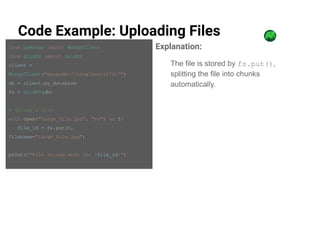
GridFS is a MongoDB specification for storing and retrieving large files by breaking them into manageable chunks, overcoming the 16MB limit per document. It facilitates efficient media management systems by allowing scalability, easy metadata retrieval, and partial file retrieval, making it suitable for applications dealing with large unstructured data. The document outlines how GridFS works, its advantages, and best practices for implementation.