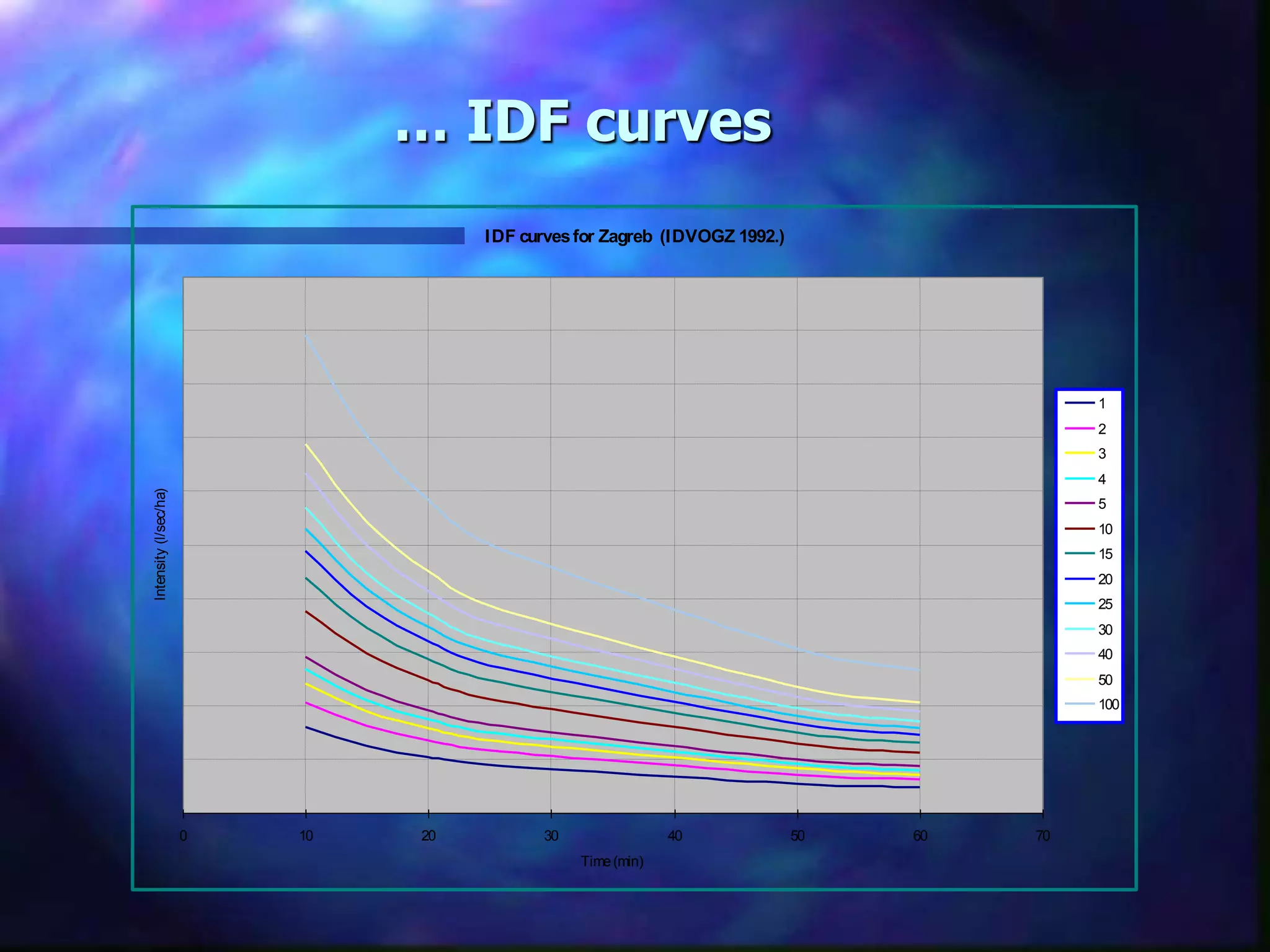
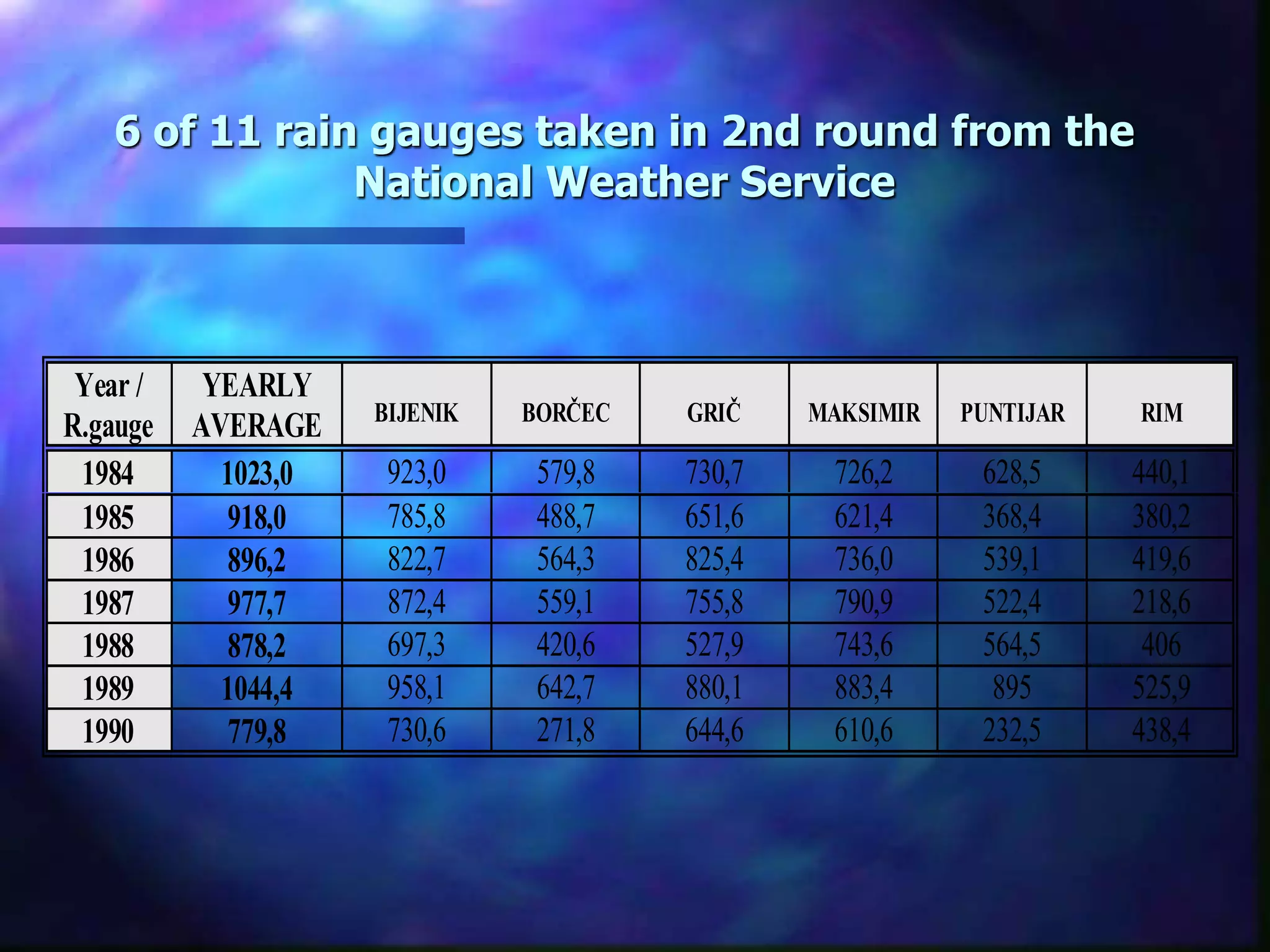
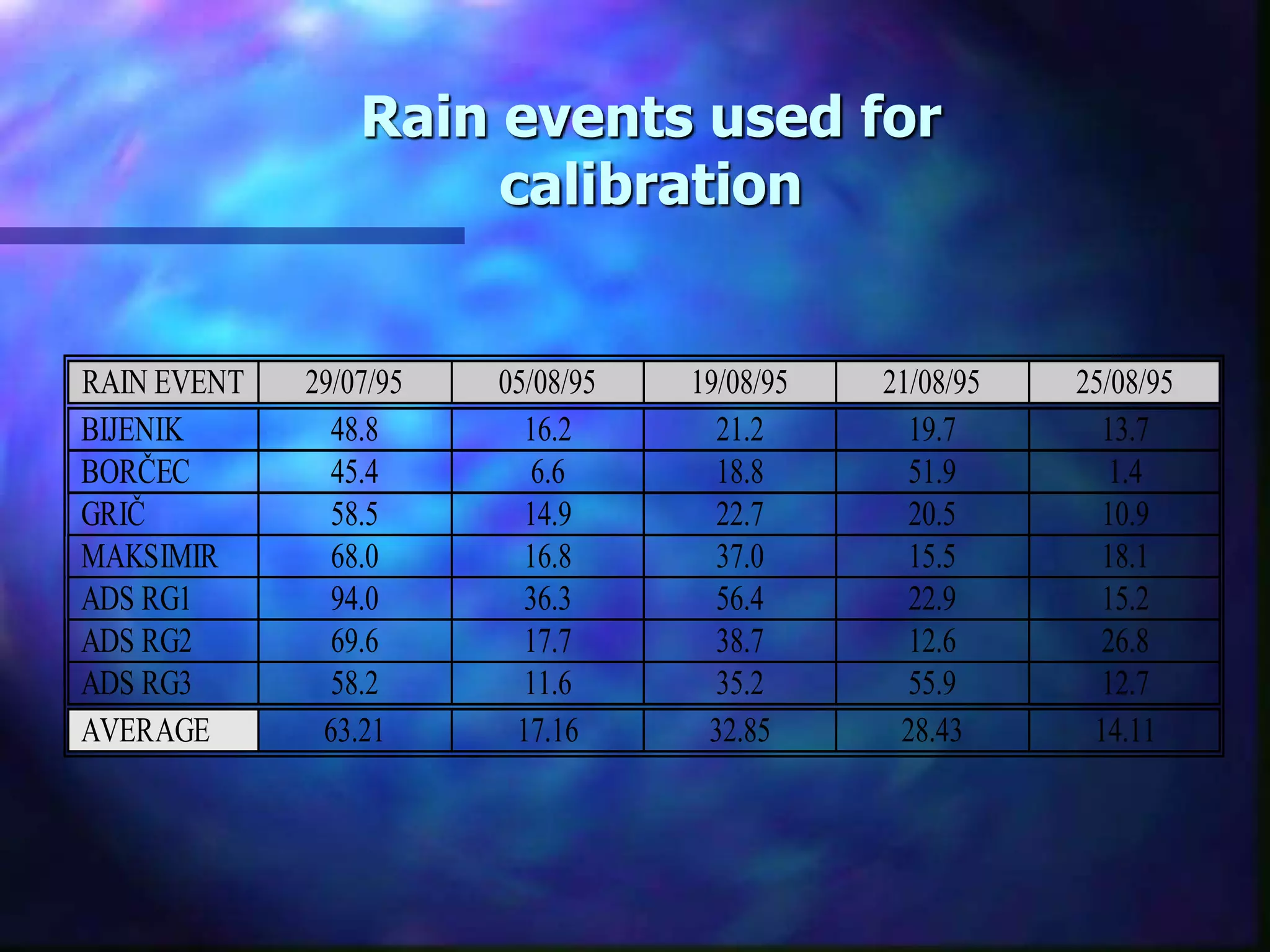
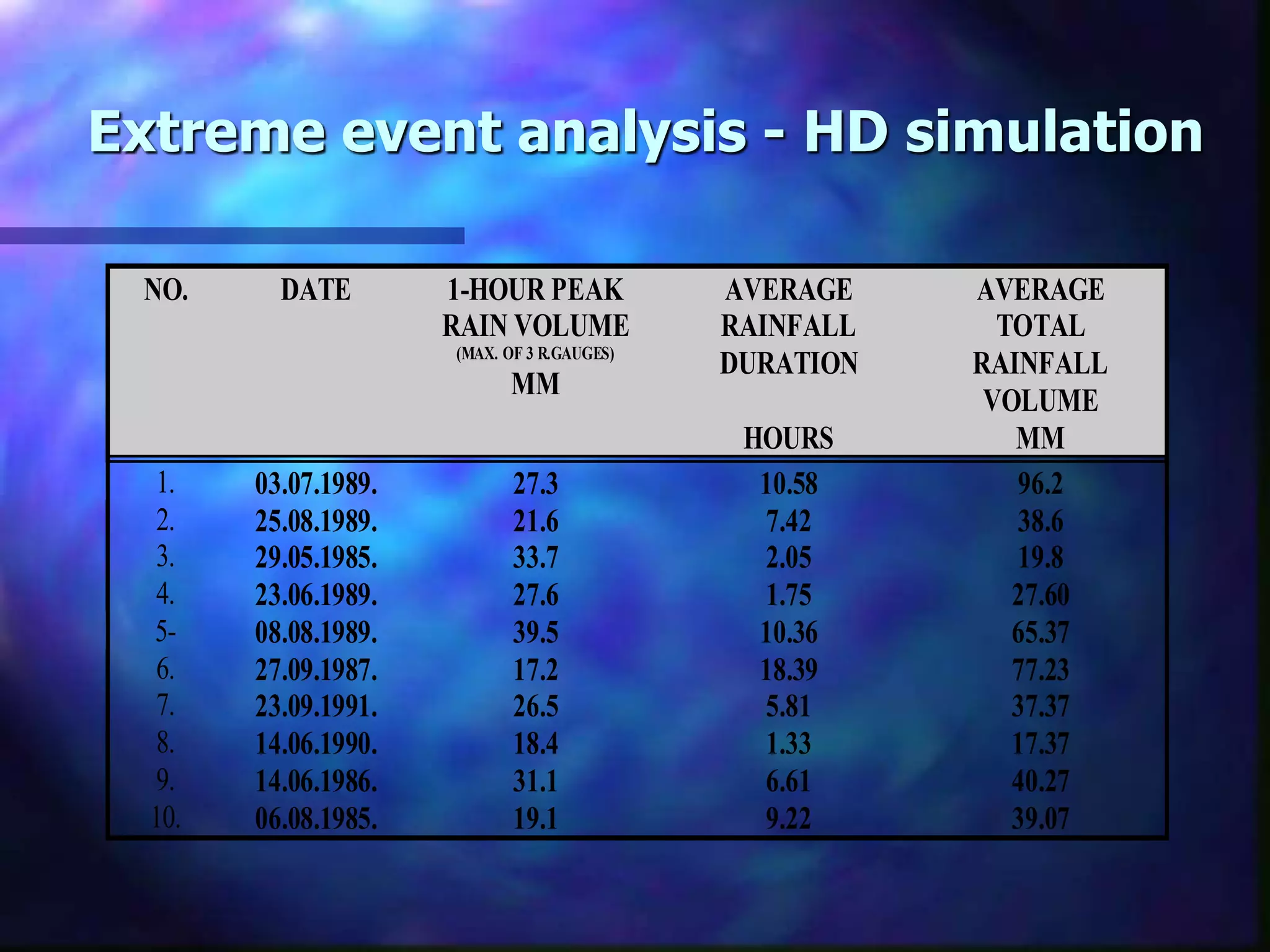
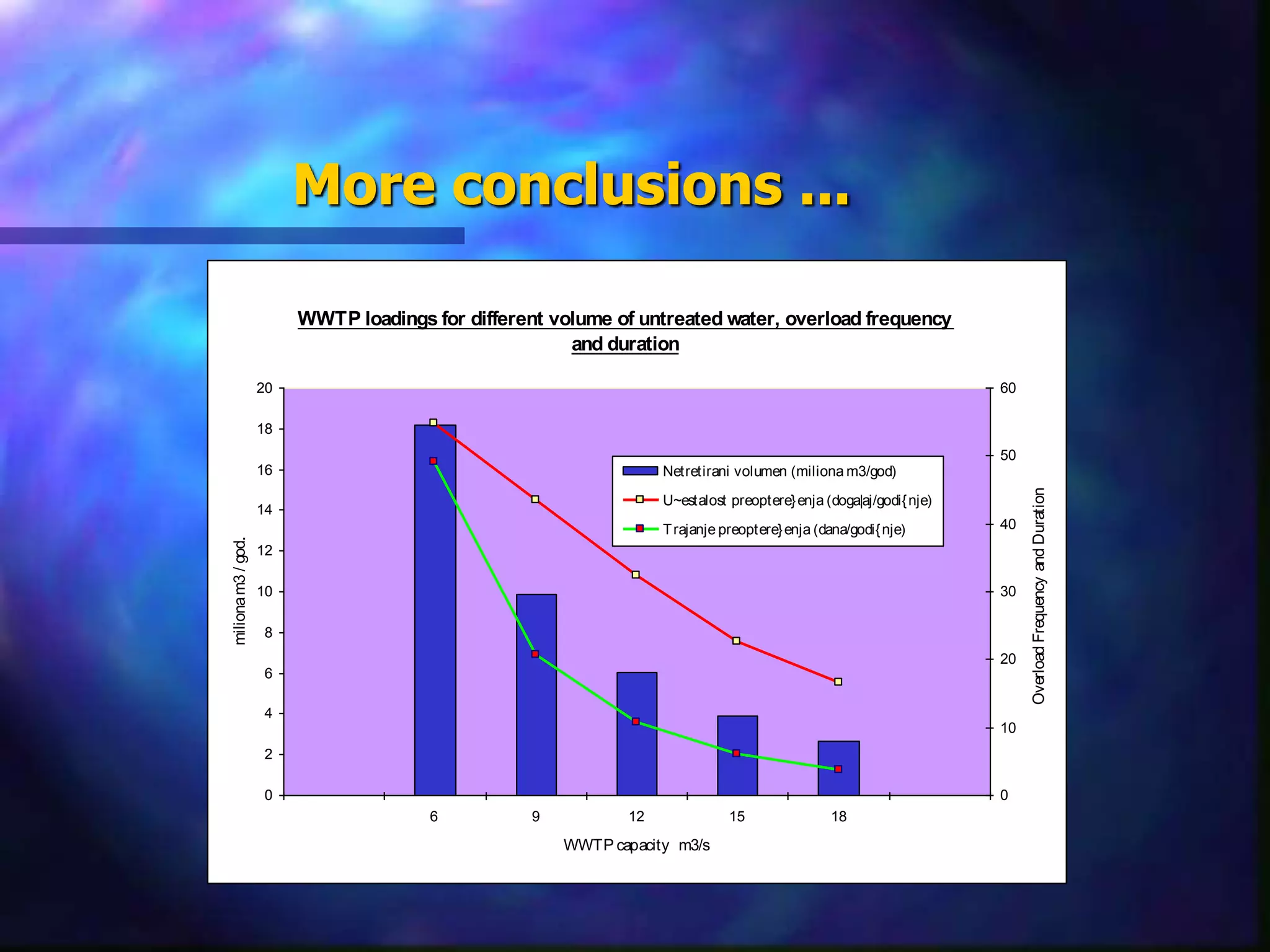
The document outlines the objectives and phases of the Zagreb Sewerage Optimization Project including the creation and verification of models to analyze rainfall-runoff patterns and their impact on sewer performance. It highlights the historical rain data collection efforts, the development of IDF curves specific to Zagreb, and advises on the applicability of various modeling approaches for flood risk assessment. Conclusions emphasize the importance of considering hydrological history, spatial differences in rainfall, and the need for guidelines in designing the sewer system.