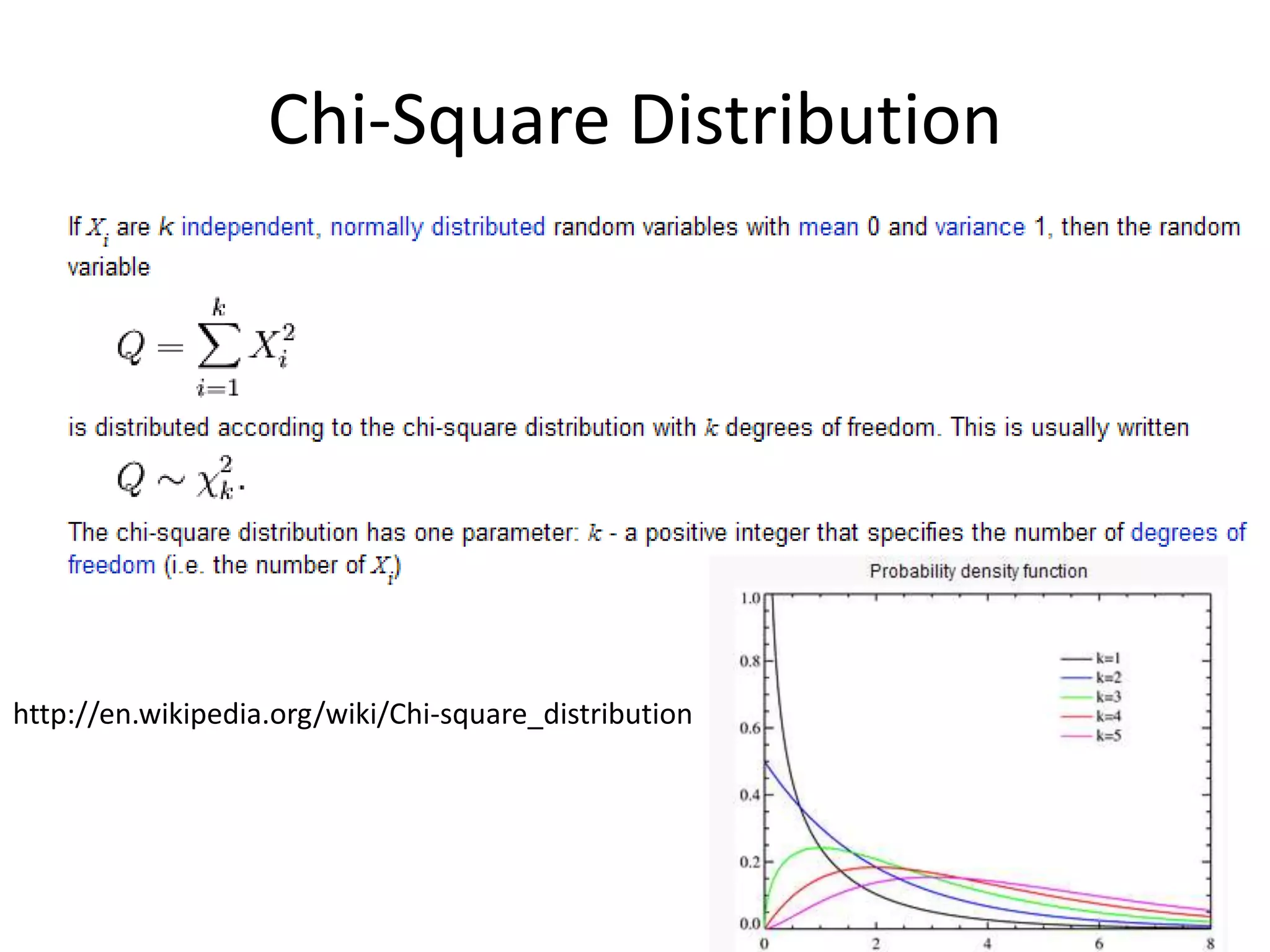
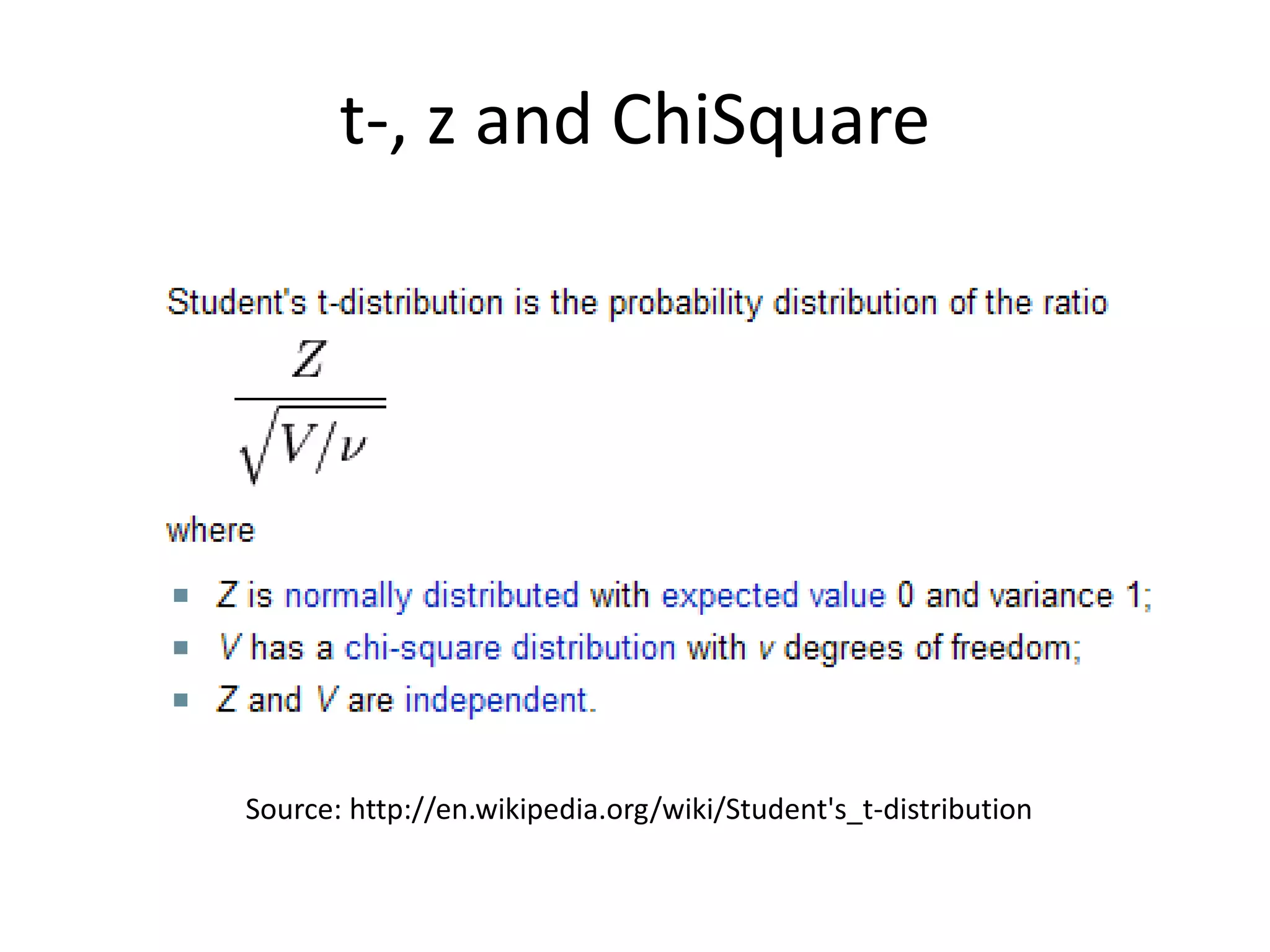
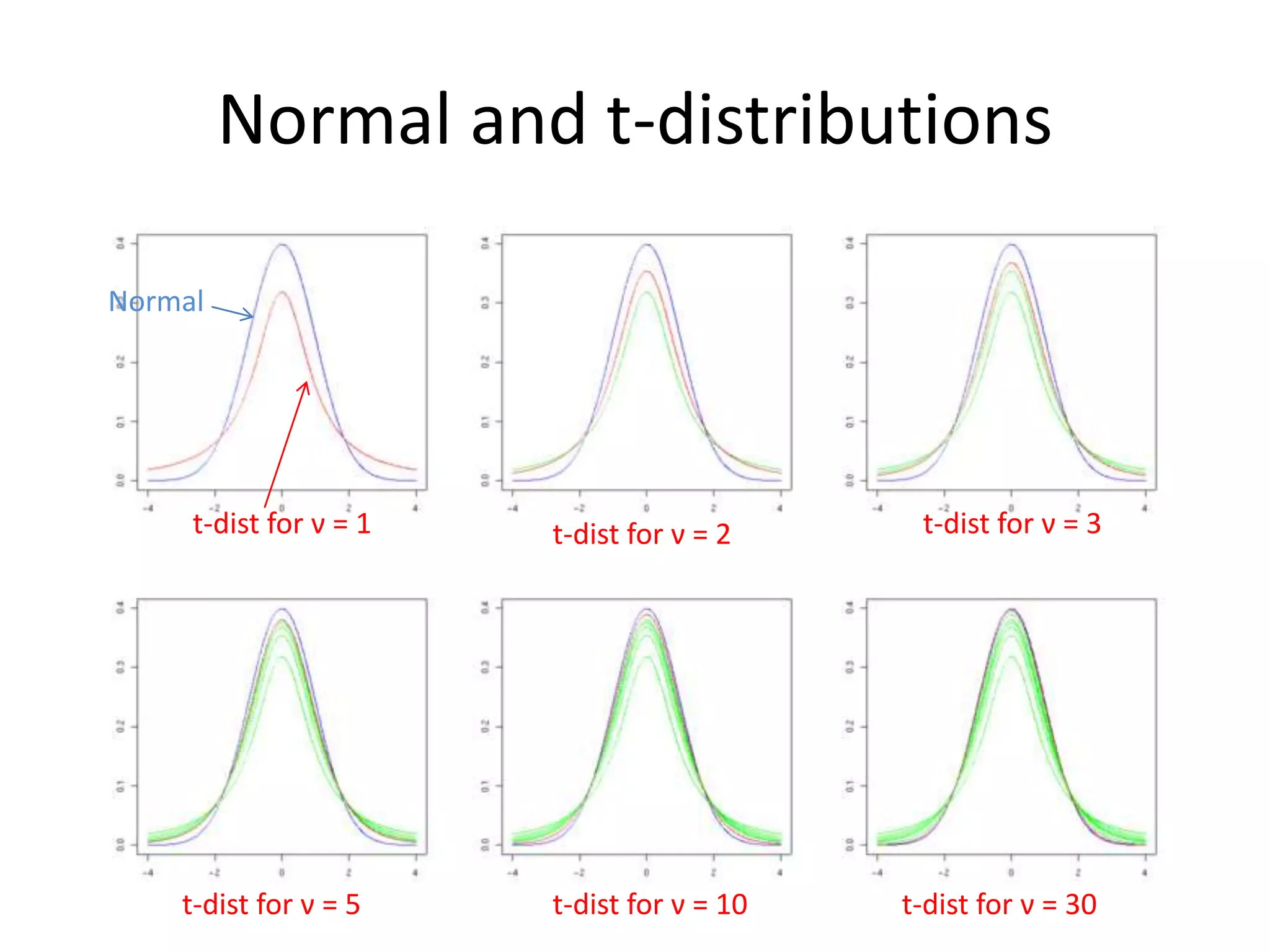
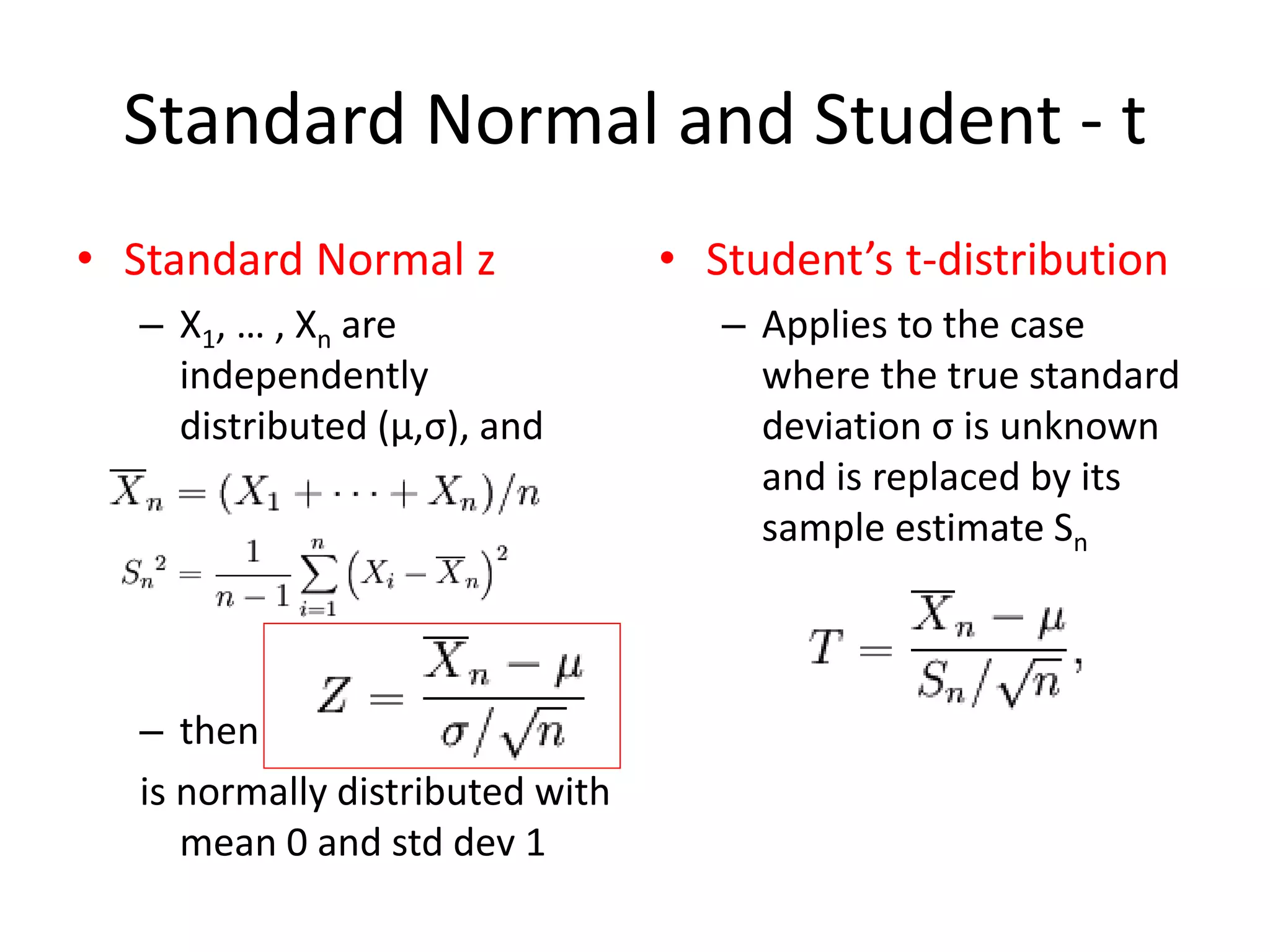
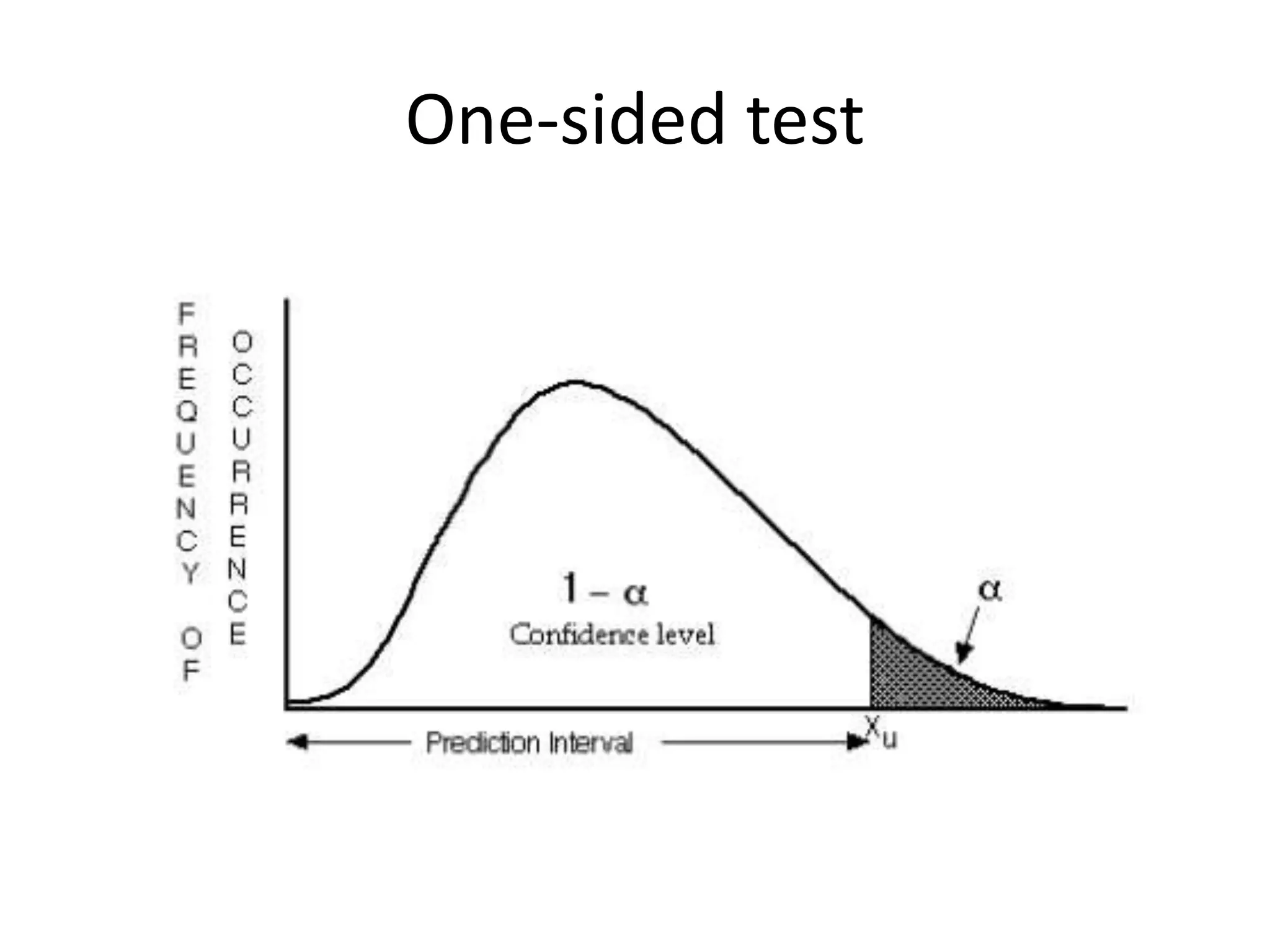
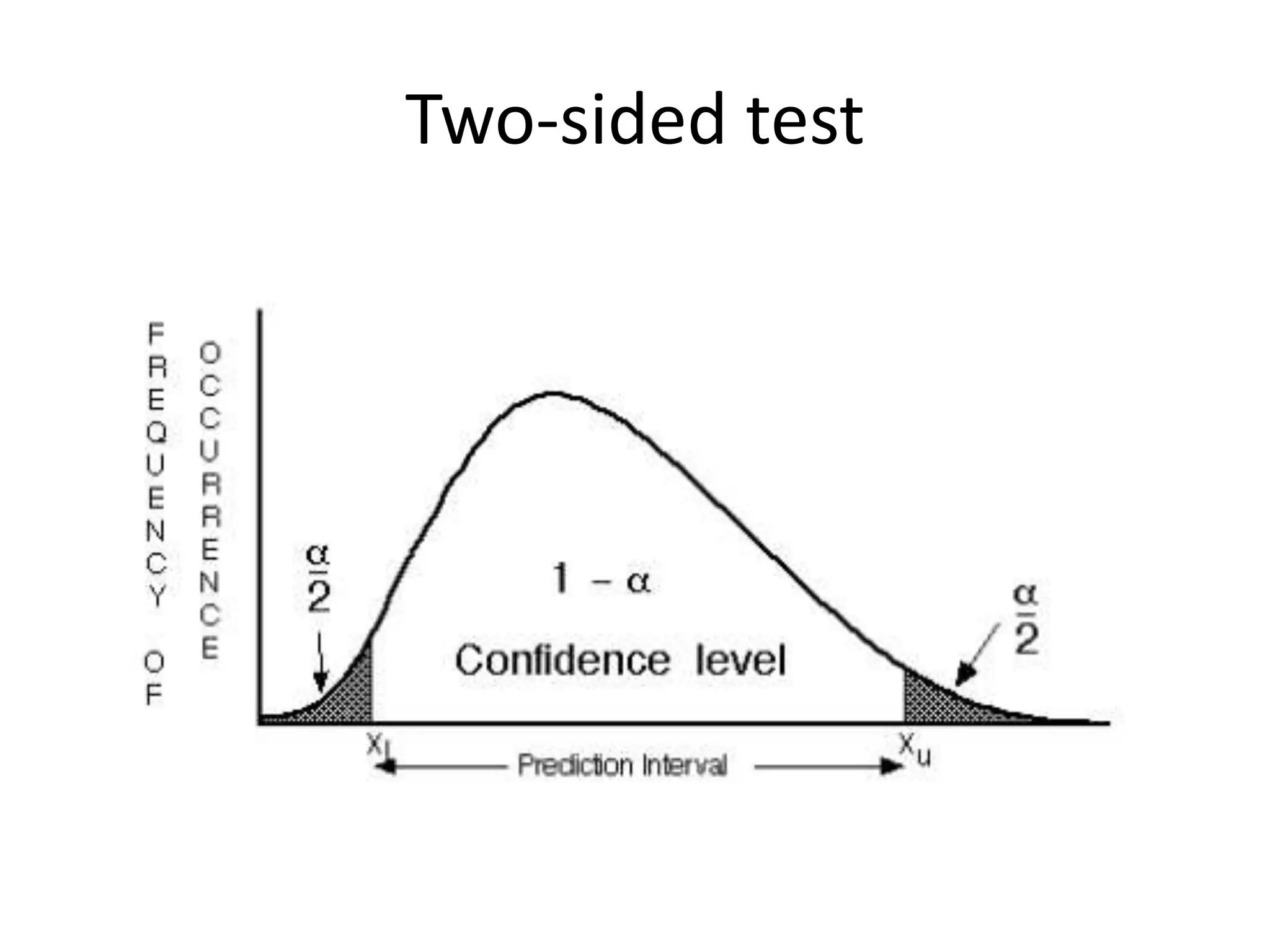
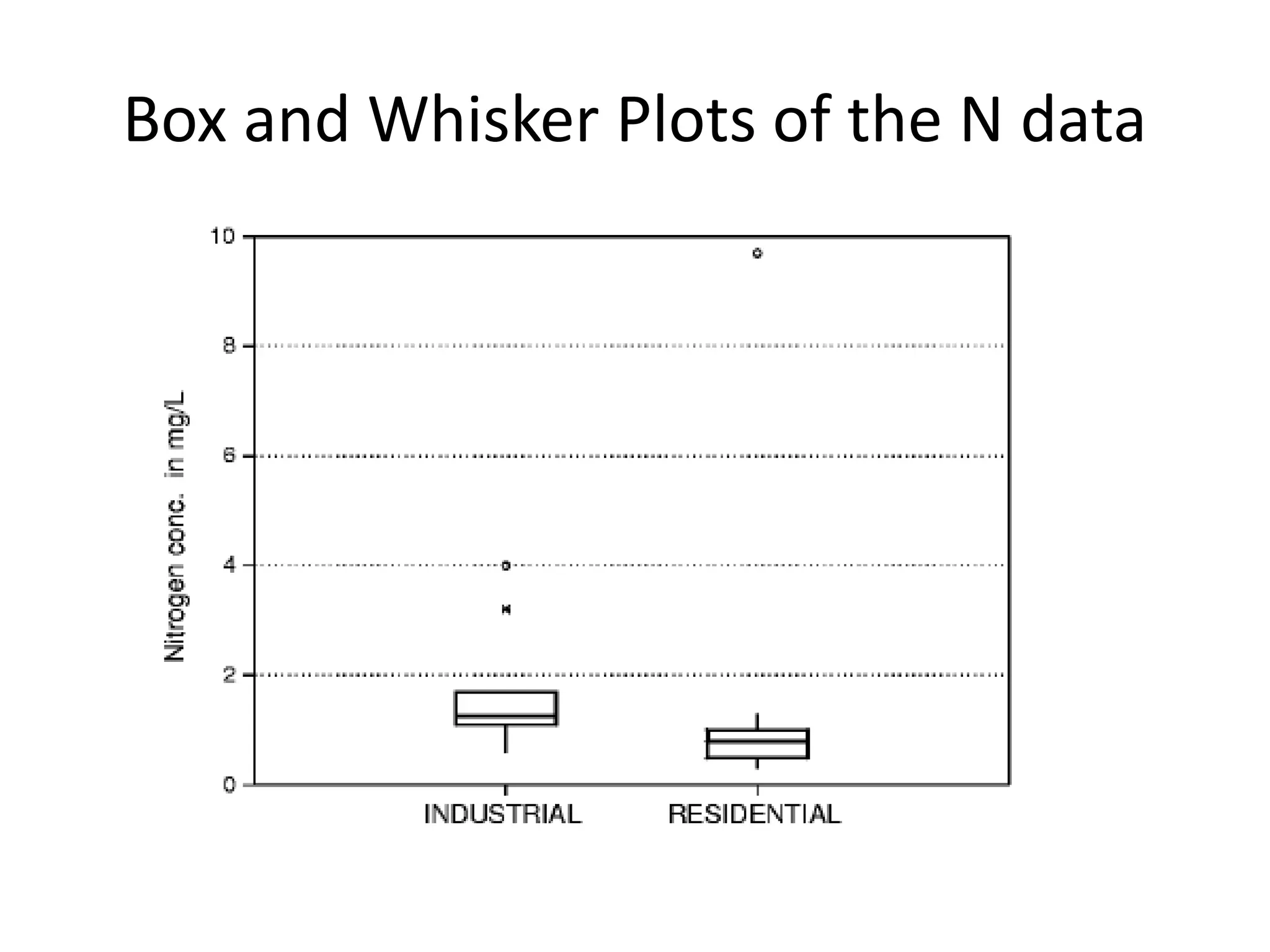
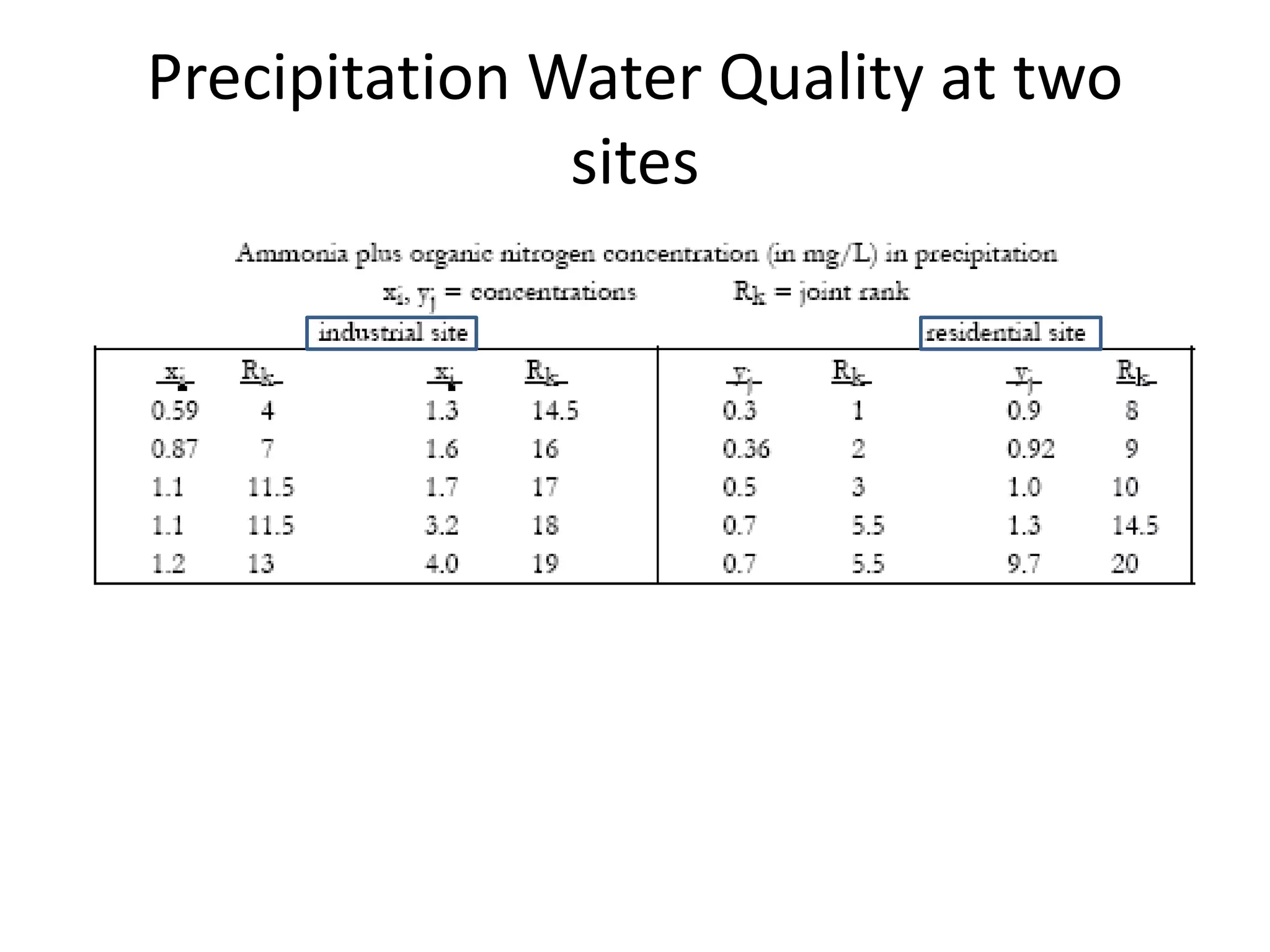
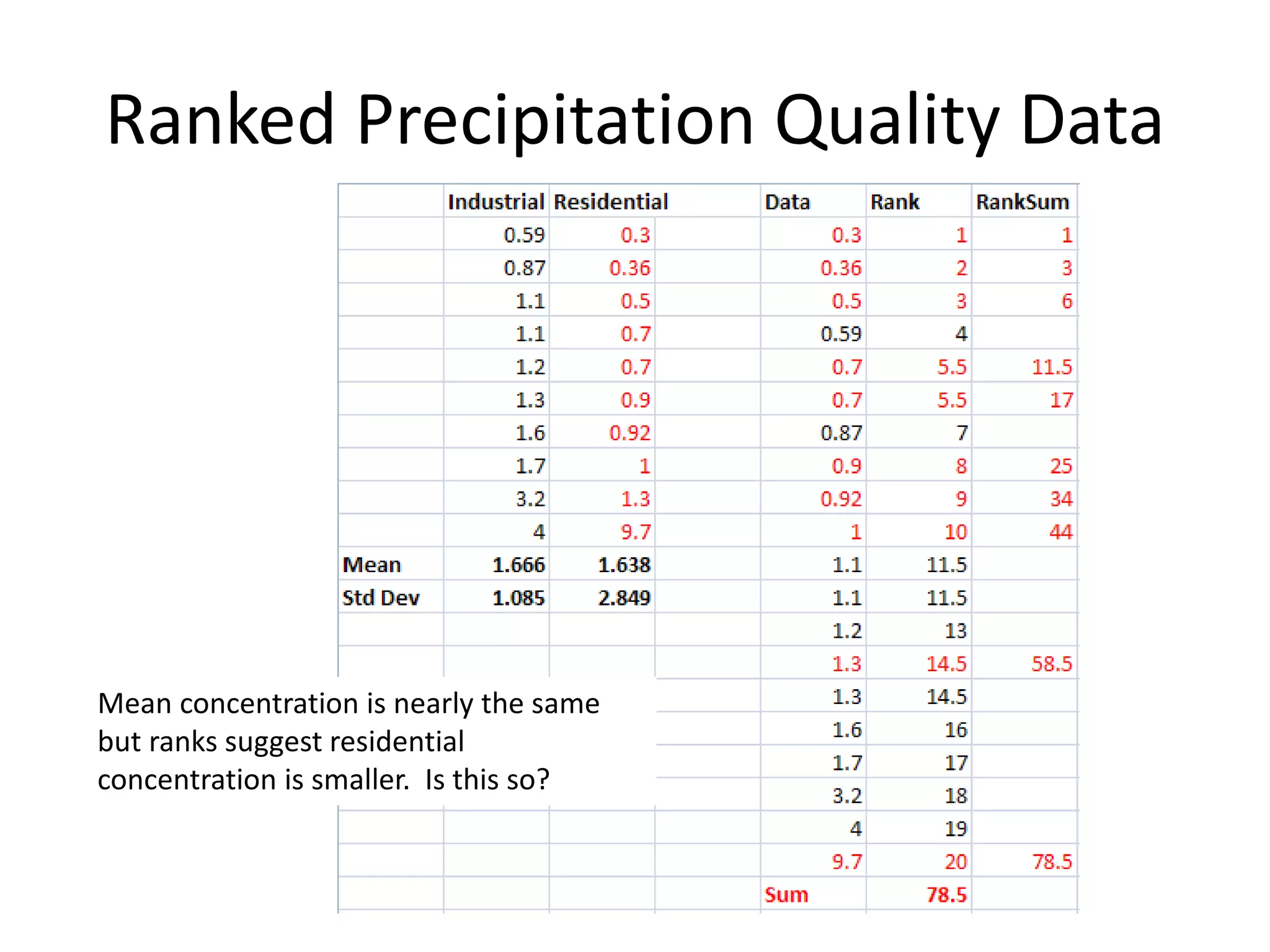
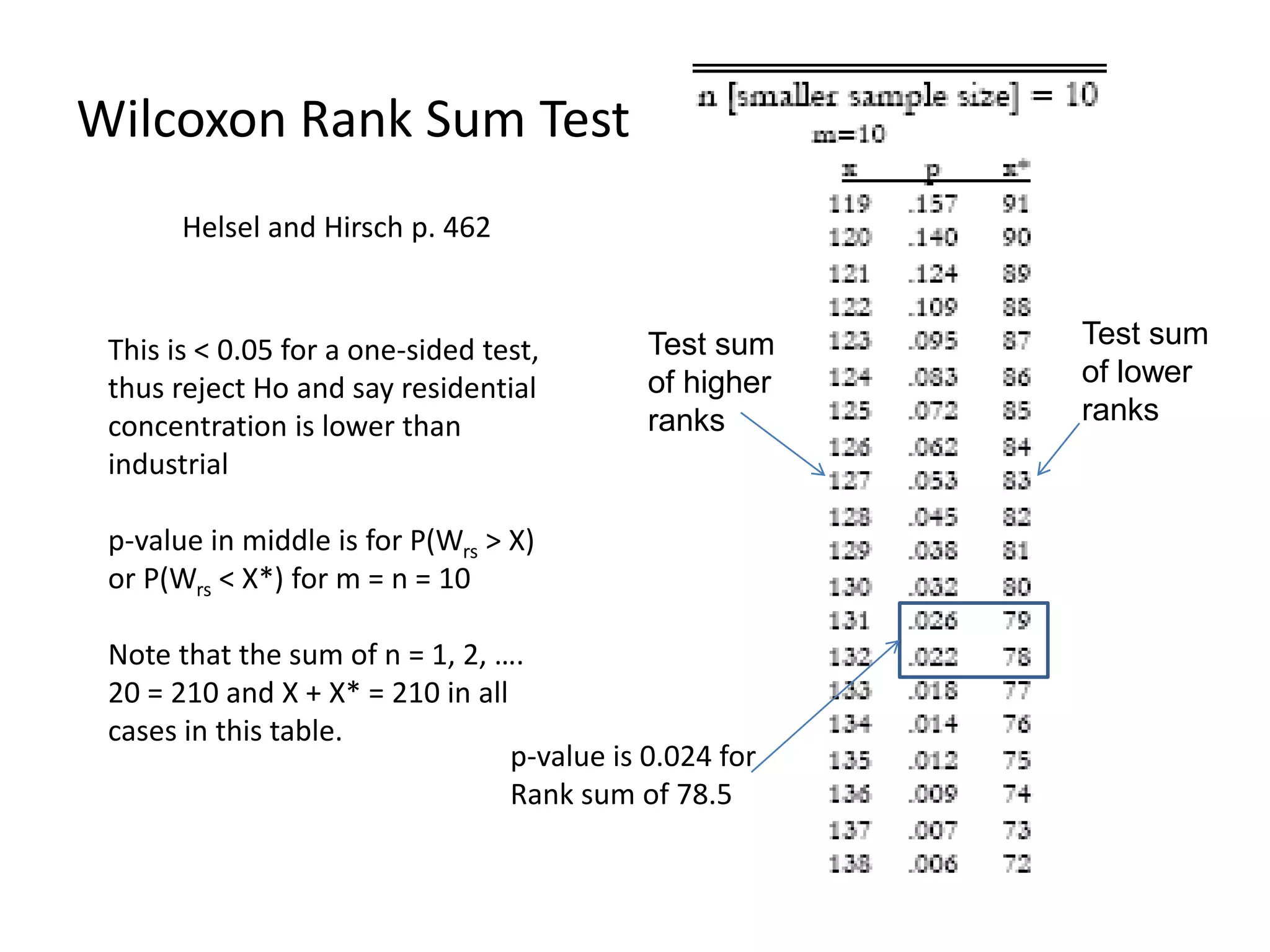
This document discusses statistical techniques for comparing two sets of data, including the t-distribution for unknown standard deviations, hypothesis testing, and the Wilcoxon rank-sum test. It provides examples of using the Wilcoxon rank-sum test to compare precipitation water quality data from two sites and determine that the residential concentration is lower than the industrial concentration with a p-value of 0.024.