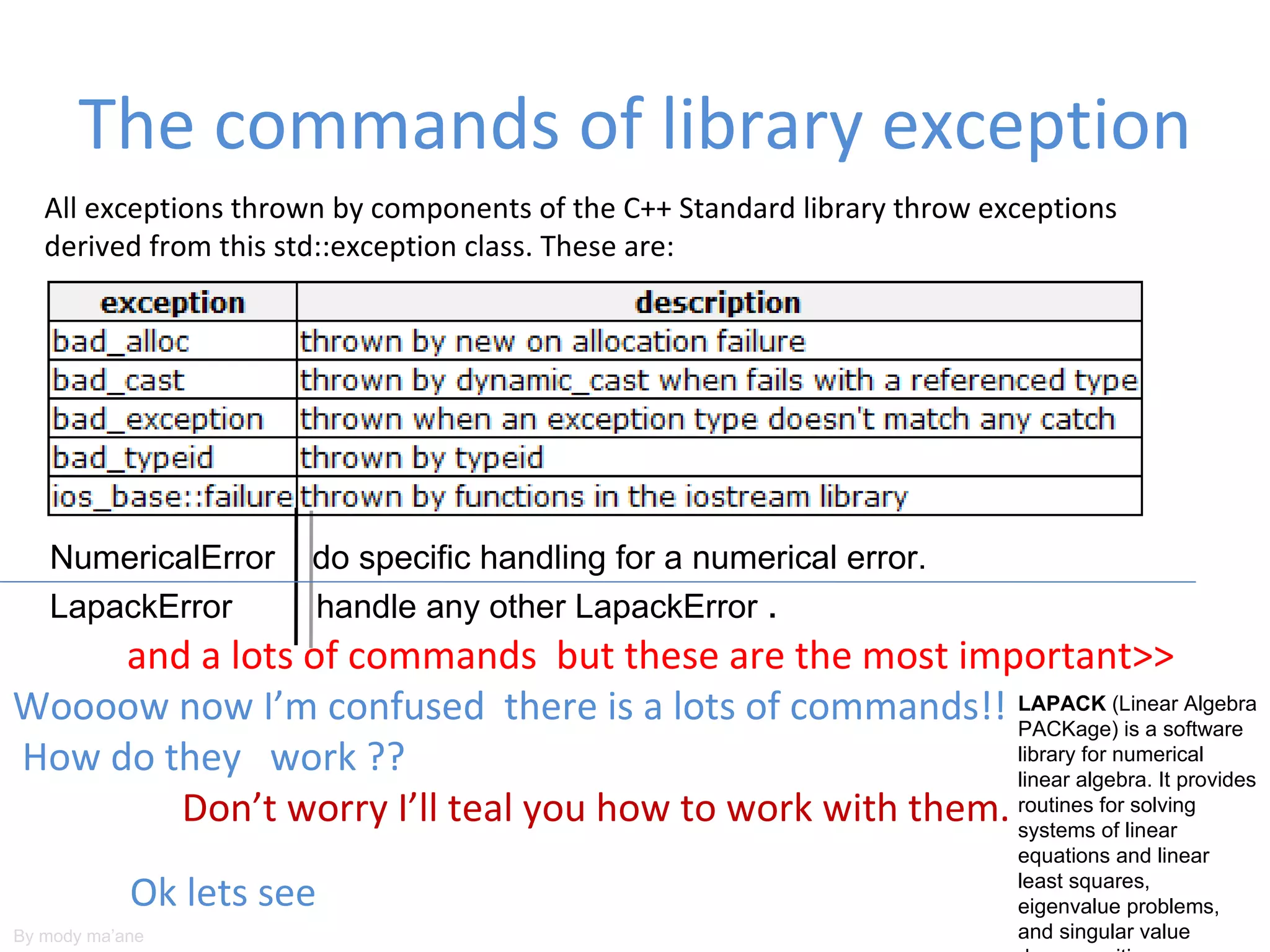
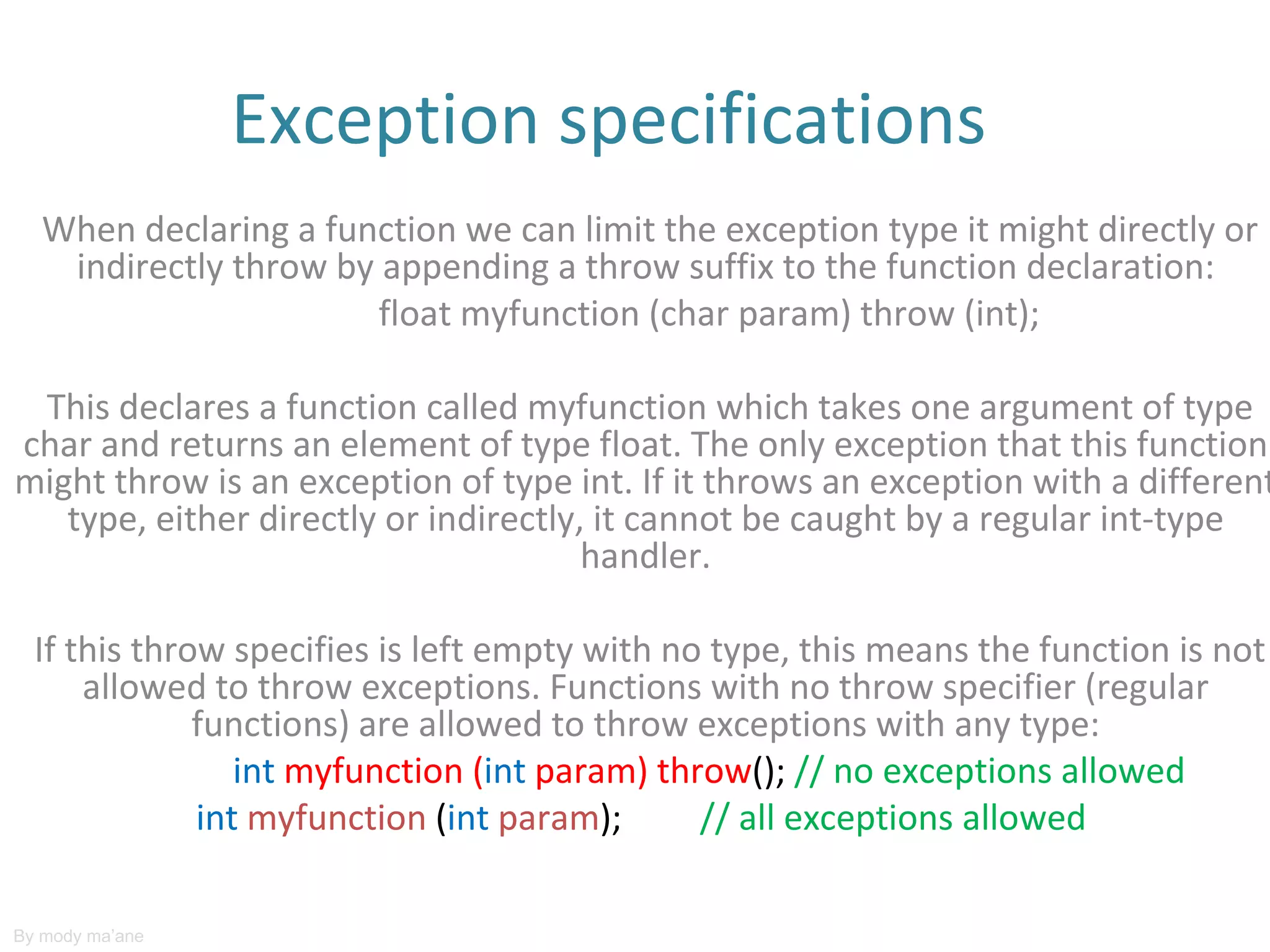
Standard exceptions provide a way to handle errors and unexpected situations in code. They allow code to be enclosed in a try block and any exceptions thrown will be passed to catch blocks to handle the error. Common exception types include bad_alloc for memory errors and exceptions from the standard library like out_of_range. Function declarations can specify which exceptions they can throw using a throw specifier to limit the exception types handled.