There are three main ways to create and start a new thread in Java: 1) by extending the Thread class, 2) by implementing the Runnable interface, and 3) by using an anonymous class that implements Runnable. The Thread scheduler determines which thread will execute first based on priority and other factors. The main thread lifecycle states are new, runnable, running, and dead. Methods like yield(), join(), setPriority(), etc. allow controlling thread behavior.
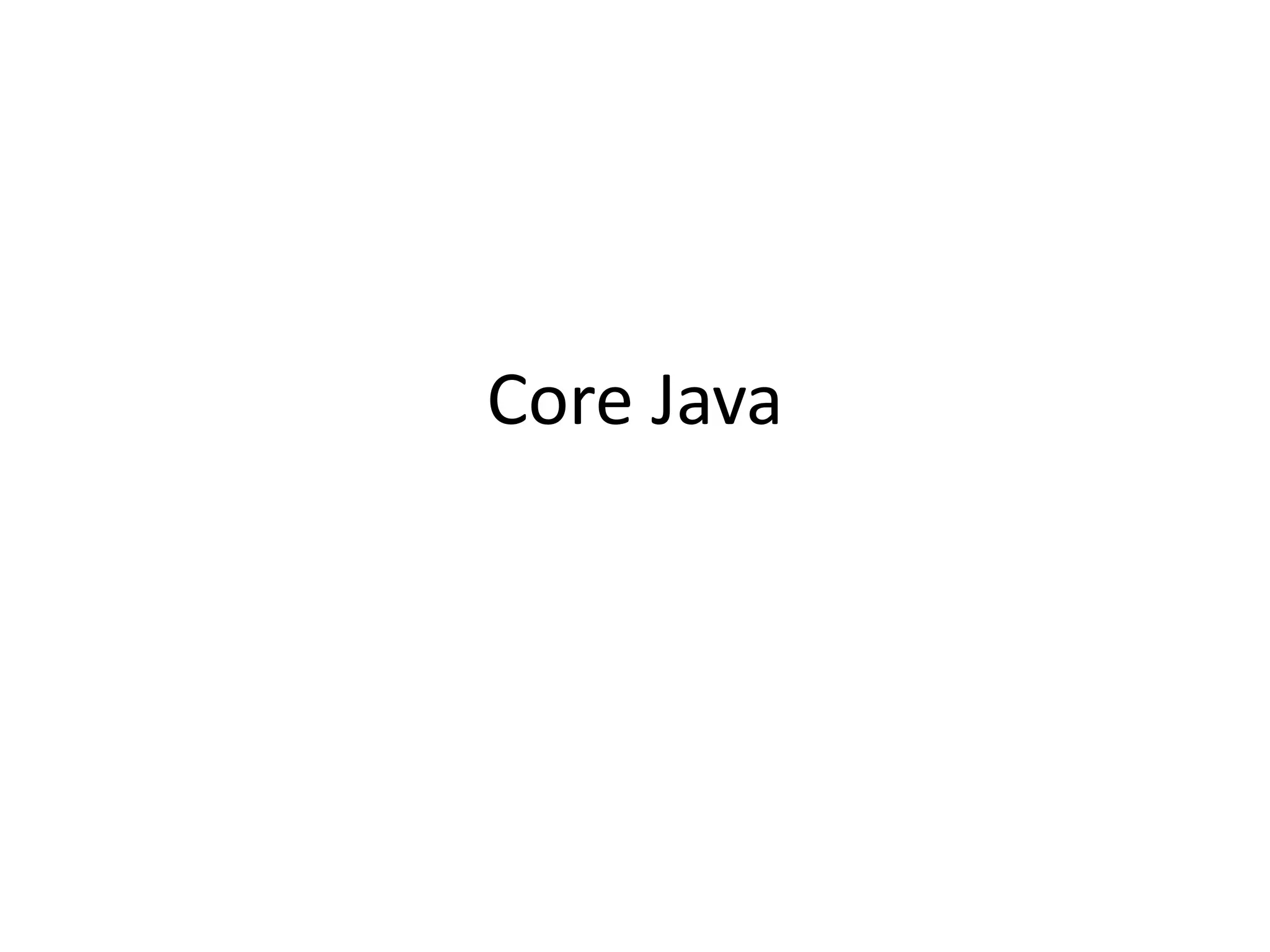



![Exception
Exception Handling using try-catch:
Syntax: try{
risky code;
}
catch( xxx e){
handling code;
}
Ex.
Class Test{
public static void main(String[] args){
try{
System.out.println(10/0);
}
catch(ArithmeticException e){
System.out.println(10/2);
}
System.out.println(“Hello”);
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nalineejava-180327073237/85/Nalinee-java-6-320.jpg)



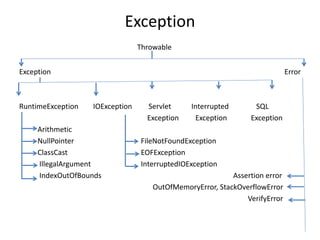
![Exception
finally Vs return :
Finally block dominates return statement. Hence, if there is any return statement present inside try or
catch block first finally will be executed & then return statement will be considered.
Ex.
class Test{
public static void main(String[] args){
try{
System.out.println(“try”);
return;
}
catch(AE e){
System.out.println(“catch”);
}
finally{
System.out.println(“finally”);
}
}
}
Only when we use System.exit(0), finally block will not be executed.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nalineejava-180327073237/85/Nalinee-java-11-320.jpg)



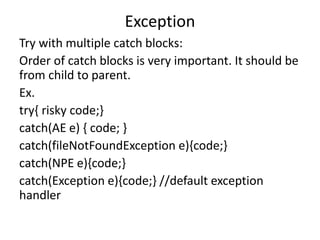
![Exception
Throws:
If our program has a chance of raising checked exception then we have to
handle it.
This can be handled in 2 ways
1. Using try-catch
2. Using throws
class Test
{
public static void main(String[] args) throws IE
{
thread.sleep(5000);
}
}
Exception Propagation: the process of delegating the responsibility of
exception handling from one method to another method by using throws
keyword.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nalineejava-180327073237/85/Nalinee-java-15-320.jpg)
![Exception
Customized Exceptions:
Ex.
class TooYoungException extends RuntimeException{
TooYoungException(String s){
super(s);
}
}
class TooOldException extends RuntimeException{
TooOldException(String s){
super(s);
}
}
class Test{
public static void main(String[] args){
int age=Integer.parseInt(args[0]);
if(age>65){
throw new TooOldException(“You have retired”);}
else if (age<18){
throw new TooYoungException(“You’re a child, go to school”)}
else{ System.out.println(“You’re eligible for a job”); }
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nalineejava-180327073237/85/Nalinee-java-16-320.jpg)

![Exception
Different Exceptions:
1. ArrayOutOfBounsException: child class of
RuntimeException; unchecked; raised
automatically by JVM when we try to access an
array element whose index is not present. Ex.
int[] a=new int[10]; System.out.println(a[100]);
2. NullPointerException: child class of
RuntimeException; unchecked; raised
automatically by JVM when we try to perform
any operation on null. Ex. String s=null;
System.out.println(s.length());](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nalineejava-180327073237/85/Nalinee-java-18-320.jpg)
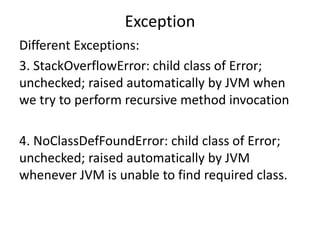



![Exception
Assertions:
There are 2 types of assert statement:
1. Simple version: assert(b); //b is boolean
Ex.
class Test{
public static void main(String[] args){
int x=10;
assert(x>10);
System.out.println(x);
}} AssertionError
If b is true, then program is executed successfully.
2. Augmented version: assert(b) : d
class Test{
public static void main(String[] args){
int x=10;
assert(x>10) : “Value is not greater than 10”;
System.out.println(x);
}} AssertionError: Value is not greater than 10
Hence, d will be executed if b is false.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nalineejava-180327073237/85/Nalinee-java-23-320.jpg)


![Inner Classes
• Accessing inner class from static area of outer class:
class Outer{
class Inner{
public void m1(){
System.out.println(“Inner class method”);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args){
Outer o= new Outer();
Outer.Inner i = o.new Inner(); Outer.Inner i=new Outer().new Inner();
i.m1();
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nalineejava-180327073237/85/Nalinee-java-26-320.jpg)
![Inner Classes
• Accessing inner class from instance area of outer class:
class Outer{
class Inner{
public void m1(){
System.out.println(“Inner class method”);
}
}
public void m2(){
Inner i=new Inner();
i.m1();
}
public static void main(String[] args){
Outer o=new Outer();
o.m2();
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nalineejava-180327073237/85/Nalinee-java-27-320.jpg)

![Inner Classes
2. Method Local Inner class: A class declared inside a method.
The scope of these inner classes lies within the method. It cannot be static.
Ex.
class Test{
public void m1(){
class Inner{
public void sum(int x, int y){
System.out.println(x+y);
}
}
Inner i=new Inner();
i.sum(10,20);
}
public static void main(String[] a){
new Test().m1();
}
}
We cannot access local variable of m1() inside Inner class unless the variable if final.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nalineejava-180327073237/85/Nalinee-java-29-320.jpg)
![Inner Classes
3. Anonymous inner class: nameless inner class.
a) Anonymous inner class that extends a class:
Ex.
class Popcorn{
public void taste(){
System.out.println(“Salty”);
}
}
class Test{
public static void main(String[] args){
Popcorn p = new Popcorn{
public void taste(){
System.out.println(“Sweet”);
}
};
p.taste(); Sweet
Popcorn p1=new Popcorn();
p1.taste(); Salty
}
}
We are creating child class for the Popcorn class & for that child class we are creating an object with
parent reference.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nalineejava-180327073237/85/Nalinee-java-30-320.jpg)
![Inner Classes
3. Anonymous inner class: nameless inner class.
b) Anonymous inner class that implements an Interface:
Ex.
class Test{
public static void main(String[] args){
Runnable r = new Runnable()
{
public void run(){
for(int i=0;i<10;i++){
System.out.println(“child thread”);
}
}
};
Thread t=new Thread( r ) ; //r is the object of Runnable
t.start();
for (int i=0; i<10; i++){
System.out.println(“main thread”);
}
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nalineejava-180327073237/85/Nalinee-java-31-320.jpg)
![Inner Classes
3. Anonymous inner class: nameless inner class.
c) Anonymous inner class that defines inside method arguments:
Ex.
class Test{
public static void main(String[] args){
new Thread( new Runnable()
{
public void run(){
for(int i=0;i<10;i++){
System.out.println(“child thread”);
}
}
}).start();
for (int i=0; i<10; i++){
System.out.println(“main thread”);
}
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nalineejava-180327073237/85/Nalinee-java-32-320.jpg)

![Inner Classes
4. Static Nested Classes:
Inner class declared with static modifier.
These class objects can exist without the existence of outer class object.
Ex.
class Outer{
static class Nested{ //can access only static members of Outer
public void m1(){
System.out.println(“Static nested class”);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args){
Outer.Nested n=new Outer.Nested();
n.m1();
}
}
We can declare static methods, hence main() can be declared. So it is possible to
invoke nested class directly from command prompt.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nalineejava-180327073237/85/Nalinee-java-34-320.jpg)



![Threads
The ways to define & start a new thread:
1. By extending Thread class.
class MyThread extends Thread{
public void run(){
for (int i=0;i<=10;i++){
System.out.println(“child thread”);
}
}
}
class ThreadDemo {
public static void main(String[] args){
MyThread t= new MyThread();
t.start();
for (int i=0; i<=10;i++ ){
System.out.println(“main thread”);
}
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nalineejava-180327073237/85/Nalinee-java-38-320.jpg)

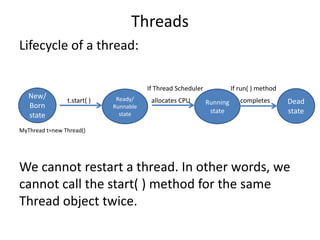
![Threads
The ways to define & start a new thread:
2. By implementing Runnable Interface:
class MyRunnable implements Runnable{
public void run(){
for (int i=0;i<=10;i++){
System.out.println(“child thread”);
}
}
}
class ThreadDemo {
public static void main(String[] args){
MyRunnable r = new MyRunnable();
Thread t=new Thread( r );
t.start();
for (int i=0; i<=10;i++ ){
System.out.println(“main thread”);
}
}
}
t1.start(); t1.run(); t2.start() ; t2.run(); r.start() ; r.run();](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nalineejava-180327073237/85/Nalinee-java-41-320.jpg)
![Threads
Getting & Setting name of a thread:
class Test{
public static void main(String[] args){
System.out.println(thread.currentThread().getName());
Thread.currentThread().setName(“thread-1”);
System.out.println(thread.currentThread().getName());
}
}
So the methods public final String getName() and public final
void setName(String name) are used to get and set the thread
names.
public static thread CurrentThread() gives current
executing thread reference.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nalineejava-180327073237/85/Nalinee-java-43-320.jpg)

![Threads
To set & get the priority:
public final int getPriority();
public final void setPriority();
class MyThread extends Thread{
public void run(){
for(int i=0; i<10; i++){
System.out.println(“child thread”);
}
}
}
class threadPriorityDemo{
public static void main(String[] args){
MyThread t=new MyThread();
t.setPriority(10);
t.start()
for(int i=0;i<10;i++){
System.out.println(“main thread”);
}
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nalineejava-180327073237/85/Nalinee-java-45-320.jpg)
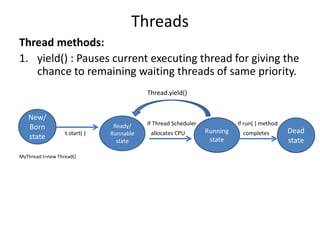
![class MyThread extends Thread{
public void run(){
for(int i=0; i<10;i++){
Thread.yield();
System.out.println(“child thread”);
}
}
}
class ThreadYieldDemo{
public static void main(String[] args){
MyThread t=new MyThread();
t.start();
for(int i=0; i<10;i++){
System.out.println(“main thread”);
}
}
}
Main thread will complete first in this case.
Threads](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nalineejava-180327073237/85/Nalinee-java-47-320.jpg)
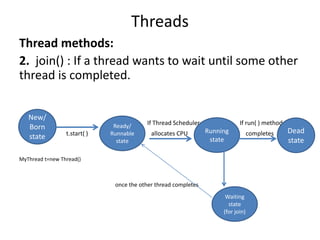
![class MyThread extends Thread{
public void run(){
for(int i=0; i<10;i++){
System.out.println(“child thread”);
try{ Thread.sleep(2000);}
catch(IE e){ }
}
}
}
class ThreadJoinDemo{
public static void main(String[] args){
MyThread t=new MyThread();
t.start();
t.join();
for(int i=0; i<10;i++){
System.out.println(“main thread”);
}
}
}
Main thread will wait until the completion of child thread.
Threads](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nalineejava-180327073237/85/Nalinee-java-49-320.jpg)
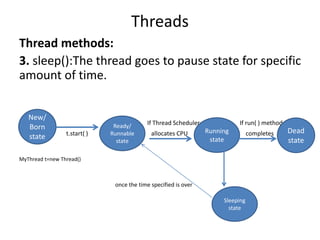
![Interruption of a thread:
interrupt(): a thread can interrupt another sleeping or waiting thread.
class MyThread extends Thread{
public void run(){
for(int i=0; i<100;i++){
System.out.println(“Lazy thread”);
try{ Thread.sleep(5000);}
catch(IE e){
System.out.println(“I got Interrupted”);}
}
}
}
class InterruptDemo{
public static void main(String[] args){
MyThread t=new MyThread();
t.start();
t.interrupt();
}
}
}
Threads](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nalineejava-180327073237/85/Nalinee-java-51-320.jpg)
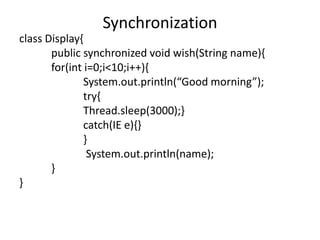
![class SynchronizedDemo{
public static void main(String[] args){
Display d1=new Display();
MyThread t1=new MyThread(d1, “Dhoni”);
MyThread t2=new MyThread(d1, “Kohli”);
t1.start();
t2.start();
}
}
Synchronization](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nalineejava-180327073237/85/Nalinee-java-55-320.jpg)

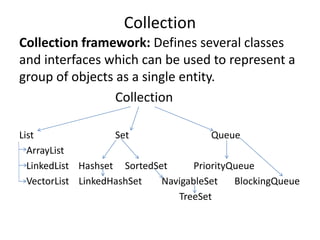



![import java.util.*;
class ArrayListDemo{
public static void main(String[] args){
ArrayList a = new ArrayList();
a.add(‘A’);
a.add(10);
a.add(null);
System.out.println(a);
a.remove(2);
System.out.println(a);
a.add(2, ‘M’);
System.out.println(a);
a.add(‘N’);
System.out.println(a);
}}
Collection](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nalineejava-180327073237/85/Nalinee-java-62-320.jpg)



![import java.util.*;
class LinkedListDemo{
public static void main(String[] args){
LinkedList l= new LinkedList();
l.add(“Nalinee”);
l.set(1);
l.add(null);
l.add(“Nalinee”);
l.set(0,”Software”);
l.add(0,”zekeLabs”);
l.removeLast();
l.addFirst(“edYoda”);
System.out.println(l);
}
}
Collection](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nalineejava-180327073237/85/Nalinee-java-66-320.jpg)

![import java.util.*;
class ListIteratorDemo{
public static void main(String[] args){
LinkedList l = new LinkedList();
l.add(“Nalinee”);
l.add(“Choudhary”);
l.add(“zekeLabs”);
l.add(“Training”);
System.out.println(l);
ListIterator lr = new ListIterator();
while(lr.hasNext()){
String s = (String) lr.next();
if(s.equals(“zekeLabs”)){
lr.remove();
}
if(s.equals(“Nalinee”)){
lr.set(“Miss Nalinee”);
}
if(s.equals(“Training”)){
lr.add(“Software”);
}
}
System.out.println(l);
}
}
Collection](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nalineejava-180327073237/85/Nalinee-java-68-320.jpg)
![import java.util.*;
class IteratorDemo{
public static void main(String[] args){
ArrayList l = new ArrayList();
for(int i=0; i<=10; i++){
l.add(i);
}
System.out.println(l);
Iterator itr=new Iterator();
while(itr.hasNext()){
Integer i = (Integer) itr.next();
if(i%2==0){
System.out.println(i);
}
else{
itr.remove();
}
} System.out.println(l);
Collection](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nalineejava-180327073237/85/Nalinee-java-69-320.jpg)


![import java.util.*;
class HashDemo{
public static void main(String[] args){
Hashset h=new HashSet();
h.add(“B”);
h.add(“C”);
h.add(“D”);
h.add(“null”);
h.add(10);
System.out.println(h);
}
}
Collection](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nalineejava-180327073237/85/Nalinee-java-72-320.jpg)


![import java.util.*;
class TreeSetDemo{
public static void main(String[] args){
TreeSet h=new TreeSet();
t.add(“A”);
t.add(“a”);
t.add(“Z”);
t.add(“L”);
t.add(“null”); // NPE
t.add(10); // CCE
System.out.println(t);
}
}
Collection](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nalineejava-180327073237/85/Nalinee-java-75-320.jpg)

![import java.util.*;
class Test{
public static void main(String[] args){
System.out.println(“A”.compareTo(“Z”);
System.out.println(“Z”.compareTo(“A”);
System.out.println(“A”.compareTo(“A”);
}
}
Collection](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nalineejava-180327073237/85/Nalinee-java-77-320.jpg)


![import java.util.*;
class TreeSetDemo{
public static void main(String[] args){
TreeSet h=new TreeSet(new MyComparator());
t.add(20);
t.add(0);
t.add(15);
t.add(5);
t.add(10);
System.out.println(t);
}
}
Collection](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nalineejava-180327073237/85/Nalinee-java-80-320.jpg)


![import java.util.*;
class TreeSetDemo2{
public static void main(String[] args){
TreeSet h=new TreeSet(new MyComparator());
t.add(“A”);
t.add(“Z”);
t.add(“K”);
t.add(“B”);
t.add(“a”);
System.out.println(t);
}
}
Collection](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nalineejava-180327073237/85/Nalinee-java-83-320.jpg)




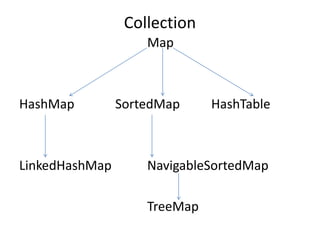


![import java.util.HashMap;
class HashMapDemo{
public static void main(String[] args){
HashMap m= new HashMap();
m.put(“Nalinee”,500);
m.put(“zekeLabs”,1000);
m.put(“Tom”, 200);
m.put(“Jerry”, 800);
System.out.println(m);
System.out.println(m.put(“John”,1200));
Set s=m.keySet();
System.out.println(s);
Collection c= m.values();
System.out.println(c);
Collection](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nalineejava-180327073237/85/Nalinee-java-91-320.jpg)



![import java.util.TreeMap;
class TreeMapDemo3{
public static void main(String[] args){
TreeMap m=new TreeMap();
m.put(100,”zzz”);
m.put(103, “yyy”);
m.put(101,”xxx”);
m.put(104,106);
m.put(107, null);
m.put(“FFFF”, “xxx”);//CCE
m.put(null,”xxx”); //NPE
System.out.println(m);
}
}
Collection](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nalineejava-180327073237/85/Nalinee-java-95-320.jpg)
![import java.util.TreeMap;
class TreeMapDemo3{
public static void main(String[] args){
TreeMap t=new TreeMap(new MyComparator());
t.put(”zzz”,10);
m.put(“AAA”,20);
m.put(”xxx”,30);
m.put(“LLL”,40);
System.out.println(m);
}
}
class MyComparator implements Comparator(){
public int compare(Object obj1, Object obj2){
String s1=obj1.toString();
String s2=obj2.toString();
return s2.compareTo(s1);
}
}
Collection](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nalineejava-180327073237/85/Nalinee-java-96-320.jpg)


![import java.util.HashTable;
class HashTableDemo{
public static void main(String[] args){
HashTable h=new HashTable();
h.put( new Temp(5), “A”);
h.put(new Temp(2), “B”);
h.put(new Temp(6), “C”);
h.put(new Temp(15), “D”);
h.put(new Temp(23), “E”);
System.out.println(m);
}
}
class Temp{
int I;
Temp(int i){
this.i=i;
}
public int hashCode(){
return i;
}
public String toString(){
return i+ “ “;
}
}
Collection](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nalineejava-180327073237/85/Nalinee-java-99-320.jpg)




![Important methods of File class:
boolean exists();
boolean createNewFile();
boolean mkdir();
boolean isFile();
boolean isDirectory();
String[] list();
boolean delete();
long length();
IO Package](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nalineejava-180327073237/85/Nalinee-java-104-320.jpg)

![Methods of FileWriter:
write(int ch); to write a single character
write(char[] ch); to write an array of characters
write(String s); to write a string
flush(); to return the last character of the data to
the file.
close();
IO Package](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nalineejava-180327073237/85/Nalinee-java-106-320.jpg)
![import java.io.FileWriter;
class FileWriterDemo{
public static void main(String[] args){
FileWriter fw=new FileWriter(“wc.txt”,true);
fw.write(100); //will add ‘d’
fw.write(“HinHow are you?”);
char[] ch1={‘a’,’b’,’c’};
fw.write(‘n’);
fw.write(ch1);
fw.write(‘n’);
fw.flush();
fw.close();
}
}
IO Package](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nalineejava-180327073237/85/Nalinee-java-107-320.jpg)
![FileReader:
To read character data from the file
FileReader fr= new FileReader(String name);
FileReader fr= new FileReader(File f);
Methods :
int read()
int read(char[] ch)
close()
IO Package](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nalineejava-180327073237/85/Nalinee-java-108-320.jpg)
![import java.io.FileReader;
class FileReaderDemo throws IOExceptions{
public static void main(String[] args){
File f=new File(“wc.text”);
FileReader fr=new FileReader(f);
System.out.println(fr.read()); //unicode of the first character
char[] ch1=new char[(int)(f.length())];
fr.read(ch2);
for (char c1 : ch2){
System.out.println(c1);
}
FileReader fr1= new FileReader(f);
int i=fr1.read();
while(i!= -1){
System.out.println((char) i);
i=fr1.read();
}
}
}
IO Package](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nalineejava-180327073237/85/Nalinee-java-109-320.jpg)

![Methods:
write(int ch)
write(char[] ch)
write(String s)
flush()
close()
newLine()
IO Package](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nalineejava-180327073237/85/Nalinee-java-111-320.jpg)
![import java.io.BufferedWriter;
class BufferedWriterDemo{
public static void main(String[] args){
File f=new File(“wc.txt”);
FileWriter fw=new FileWriter(f);
BufferedWriter bw=new BufferedWriter(fw);
bw.write(100);
bw.newLine();
char[] ch1={‘a’,’b’,’c’,’d’};
bw.write(ch1);
bw.newLine();
bw.write(“zekeLabs”);
bw.flush();
bw.close();
}
}
IO Package](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nalineejava-180327073237/85/Nalinee-java-112-320.jpg)

![Methods:
int read();
int read(char[] ch);
close();
String readLine();
IO Package](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nalineejava-180327073237/85/Nalinee-java-114-320.jpg)
![import java.io.BufferedReader;
class BufferedReaderDemo{
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
FileReader fr= new FileReader(“wc.txt”);
BufferedReader br=new BufferedReader(fr);
String line=br.readLine();
while(line != null){
System.out.println(line);
line=br.readLine();
}
br.close();
}
}
IO Package](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nalineejava-180327073237/85/Nalinee-java-115-320.jpg)

![Methods:
write(int ch);
write(char[] ch);
write(String s);
flush()
close()
print(char ch)
print(int/long/double/String/char[] i)
println(char/int/long/double/String/char[] ch)
IO Package](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nalineejava-180327073237/85/Nalinee-java-117-320.jpg)
![import java.io.PrintWriter;
class PrintWriterDemo{
public static void main(string[] args) throws
IOException{
FileWriter fw=new FileWriter(“wc.txt”);
PrintWriter pw=new PrintWriter(fw);
pw.write(100); //d
pw.println(100); //100
pw.println(true);
pw.flush();
pw.close();
}
}
IO Package](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nalineejava-180327073237/85/Nalinee-java-118-320.jpg)
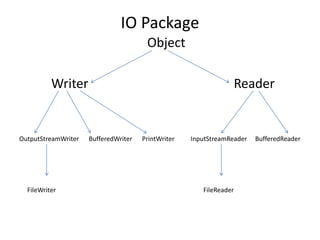


![import java.io.*;
class Dog implements Serializable{
int i=10, j=20;
}
class SerializableDemo{
public static void main(String[] args){
Dog d1=new Dog();
FileOutputStream fos=new FileOutputStream(“abc.txt”);
ObjectOutputStream oos=new ObjectOutputStream(fos);
oos.writeObject(d1);
FileInputStream fis=new FileInputStream(“abc.txt”);
ObjectInputStream ois=new ObjectInputStream(fis);
Dog d2=(Dog) ois.readObject();
System.out.println(d2.i + d2.j);
}
}
IO Package](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nalineejava-180327073237/85/Nalinee-java-122-320.jpg)
