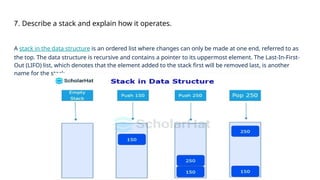
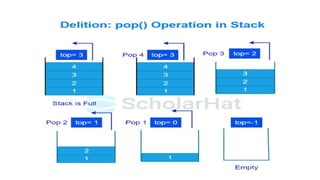
The document discusses stack data structures, highlighting their recursive nature and various operations such as push, pop, and peek. It explores the role of stacks in function call management, dynamic resizing, real-life applications, and algorithms for sorting and evaluating expressions. Additionally, it addresses stack overflow, balancing parentheses, and depth-first search implementation using stacks.







![5. implement a Queue Using Stacks
class Queue:
def __init__(self):
self.enqueue_stack = []
self.dequeue_stack = []
def enqueue(self, x):
# append the new element to the enqueue stack
self.enqueue_stack.append(x)
def dequeue(self):
# if dequeue stack is empty pop all the elements
# from enqueue stack and push them onto the dequeue stack
if not self.dequeue_stack:
while self.enqueue_stack:
self.dequeue_stack.append(self.enqueue_stack.pop())
# pop the element from the dequeue stack and return it
return self.dequeue_stack.pop()](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/stack20interviewquestions-241107044833-ab26e35a/85/STACK-20-INTERVIEW-QUESTIONS-and-answers-pptx-8-320.jpg)








![14. How can a stack be used to check for balanced parentheses in an expression?
A stack can be used to check for balanced parentheses by pushing opening
brackets (, {, [ onto the stack. For every closing bracket ), }, or ], check if the top of
the stack contains the corresponding opening bracket. If not, the parentheses are
unbalanced.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/stack20interviewquestions-241107044833-ab26e35a/85/STACK-20-INTERVIEW-QUESTIONS-and-answers-pptx-19-320.jpg)








![22. How does a stack help with balancing parentheses?
A stack can be used to check if parentheses in an expression are balanced. The idea is to push
every opening parenthesis onto the stack. For every closing parenthesis, you pop an opening
parenthesis from the stack. If at the end of the expression, the stack is empty, the parentheses are
balanced.
Algorithm:
1. Traverse the expression from left to right.
2. For every (, {, or [, push it onto the stack.
3. For every ), }, or ], check if the stack is empty. If it is not, pop the stack. If the top of the stack
does not match the corresponding opening bracket, the expression is unbalanced.
4. If the stack is empty after processing the entire expression, the parentheses are balanced.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/stack20interviewquestions-241107044833-ab26e35a/85/STACK-20-INTERVIEW-QUESTIONS-and-answers-pptx-28-320.jpg)
