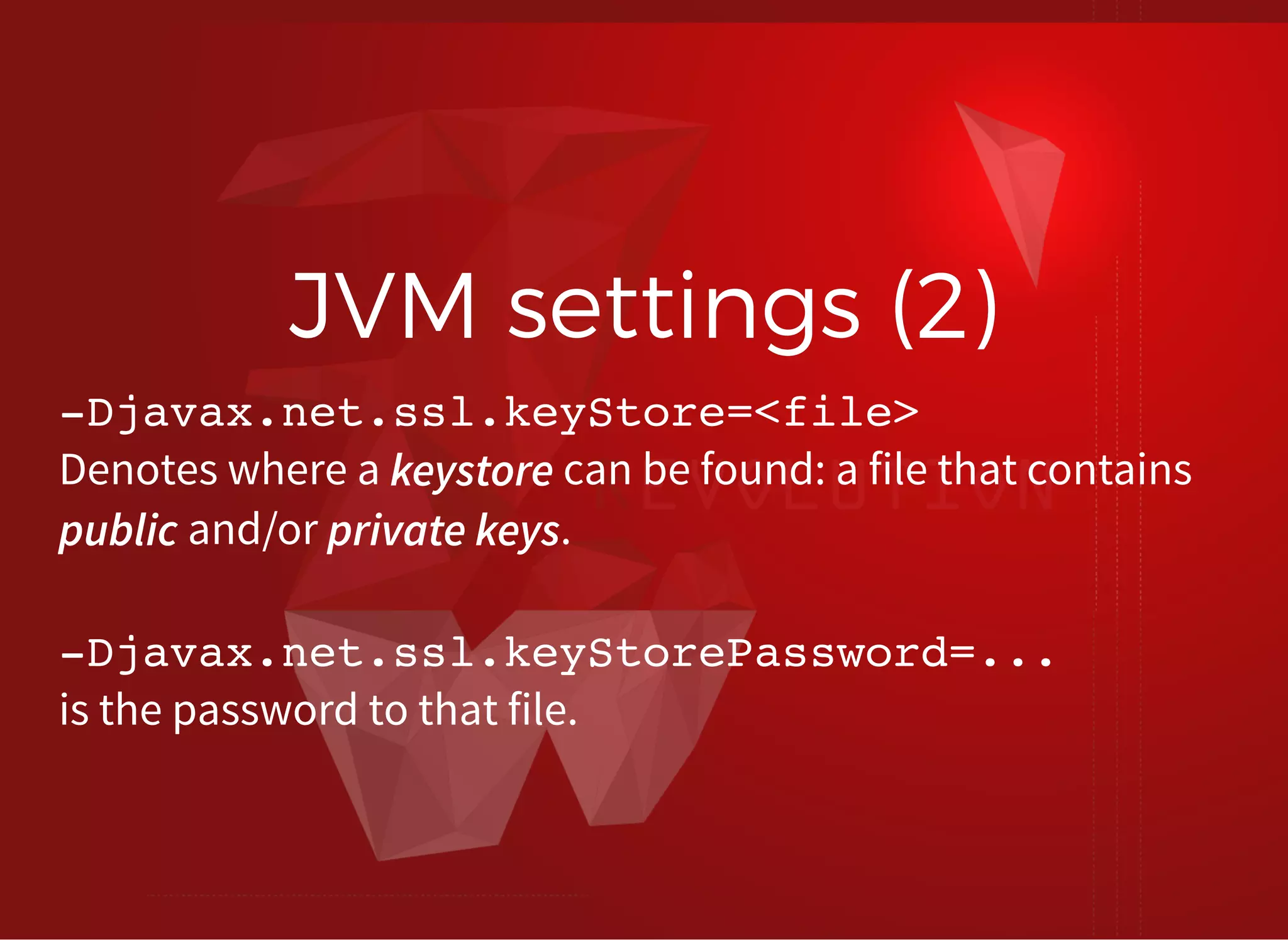
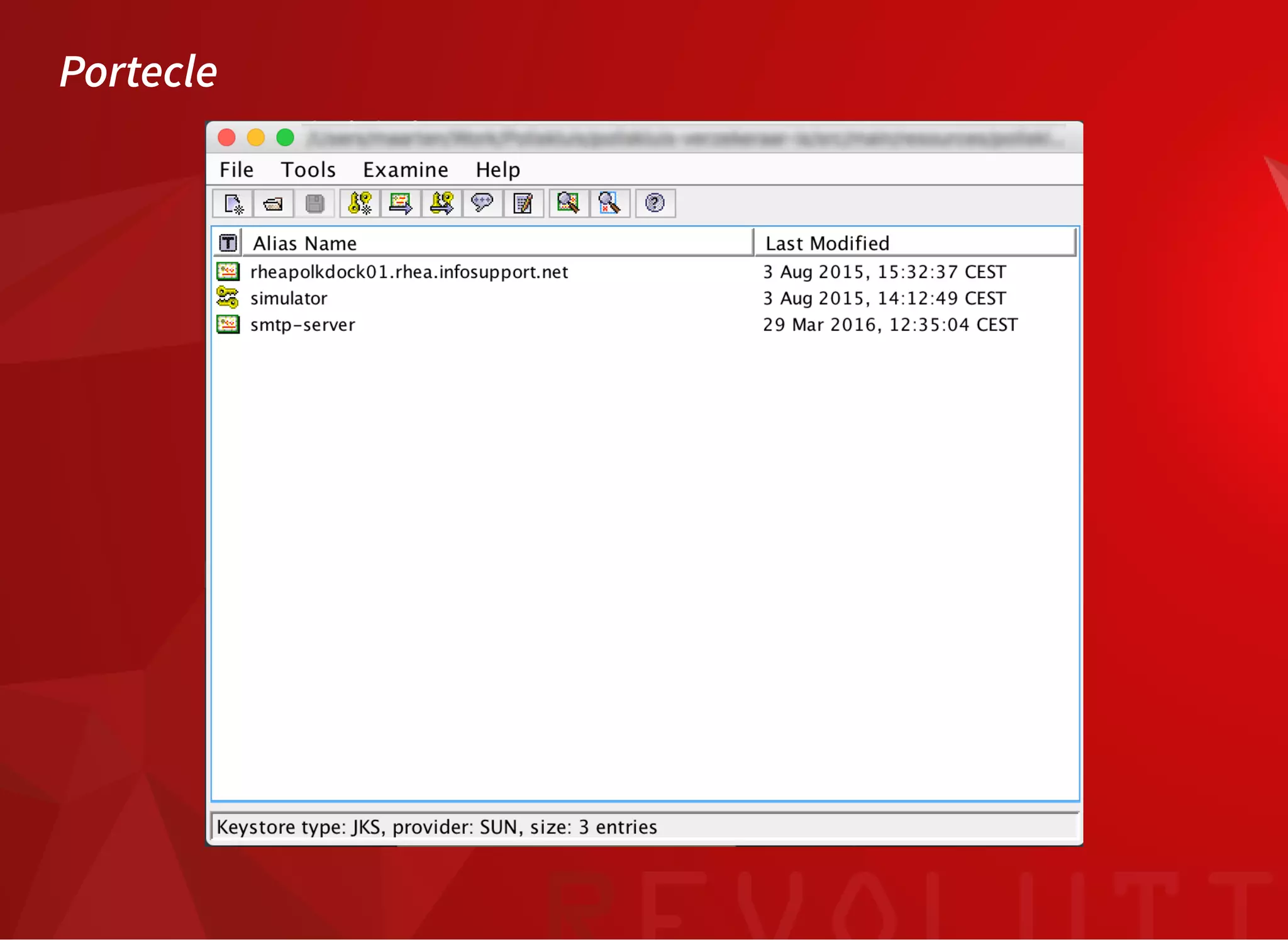
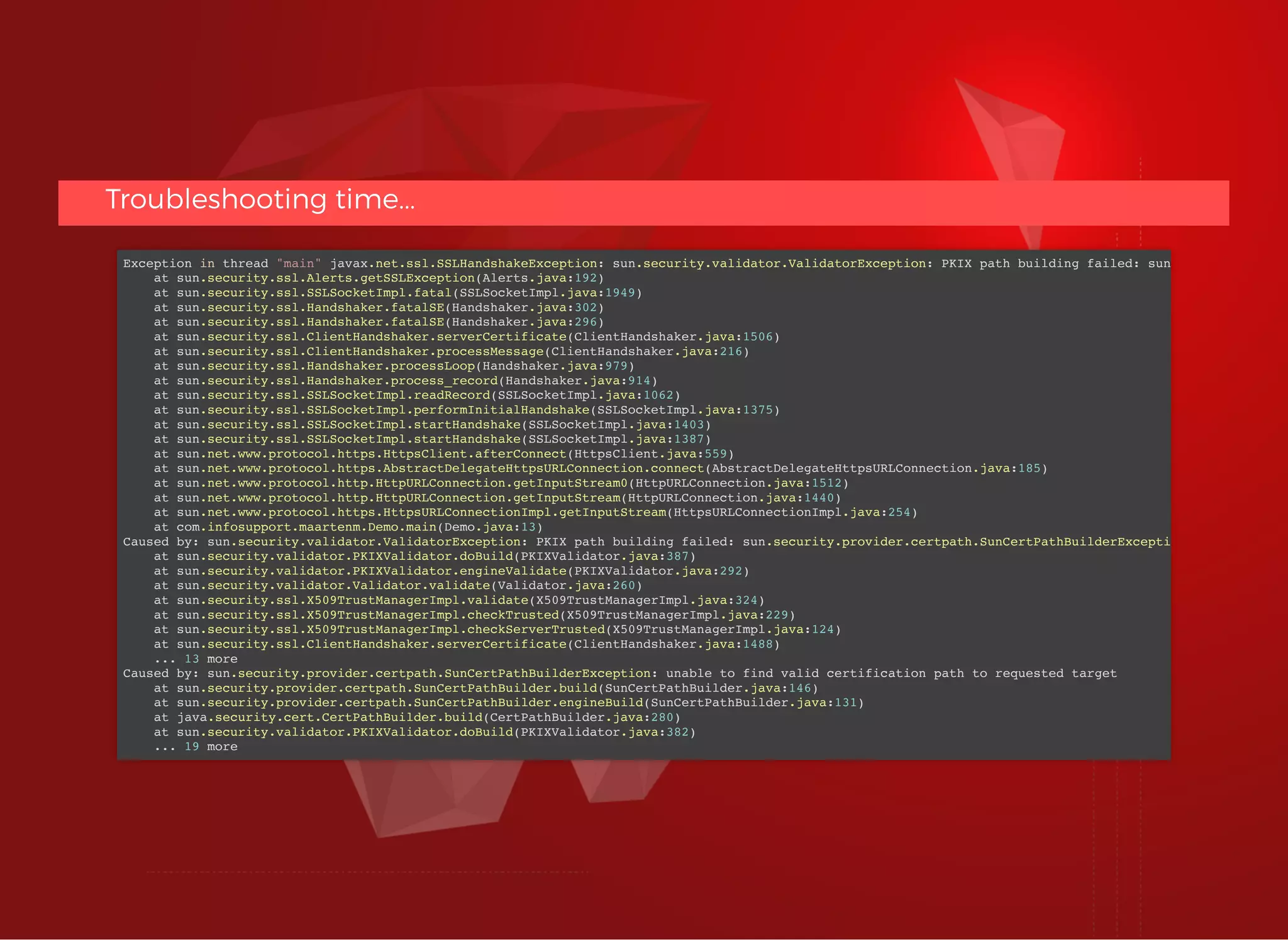
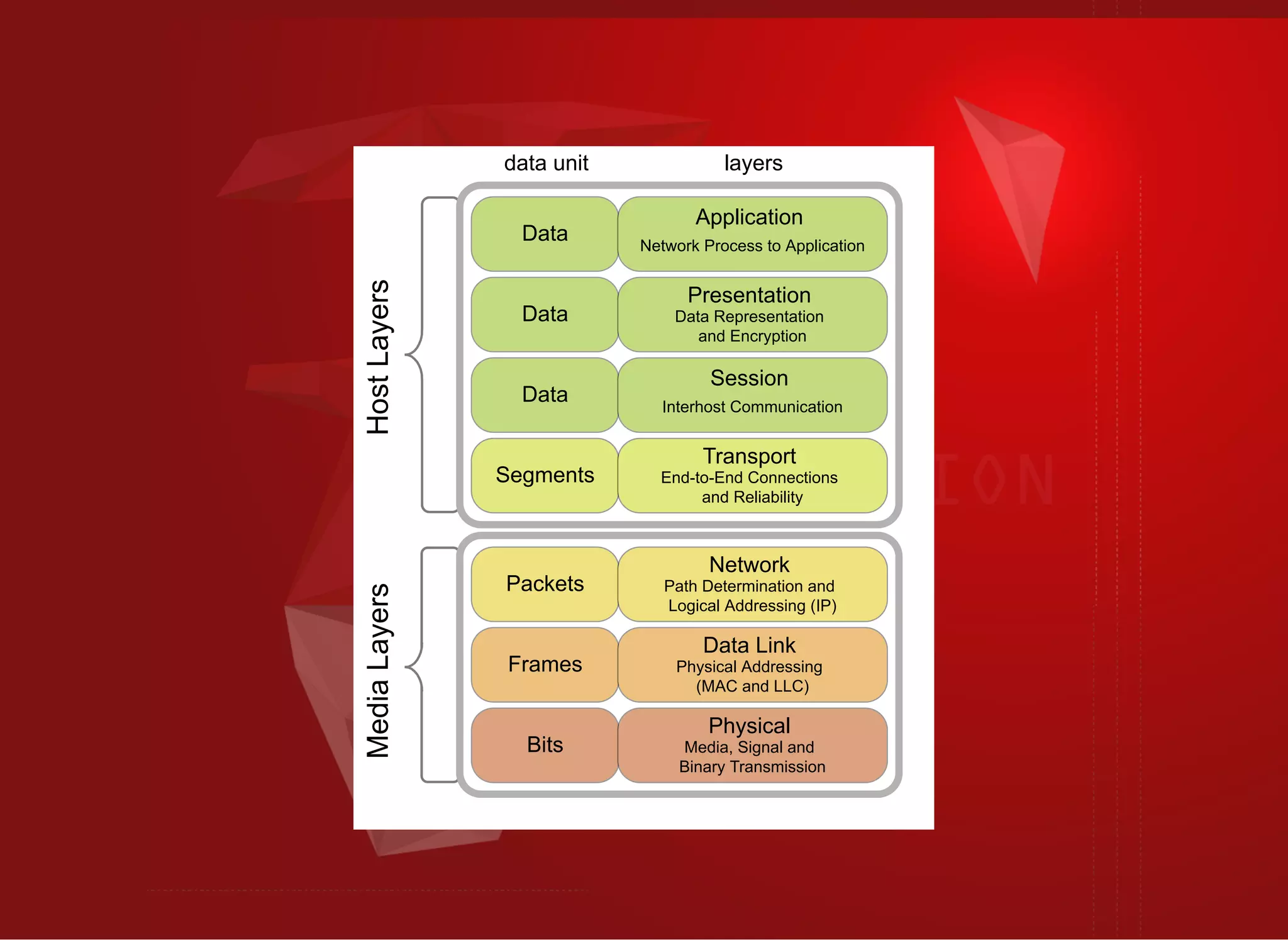
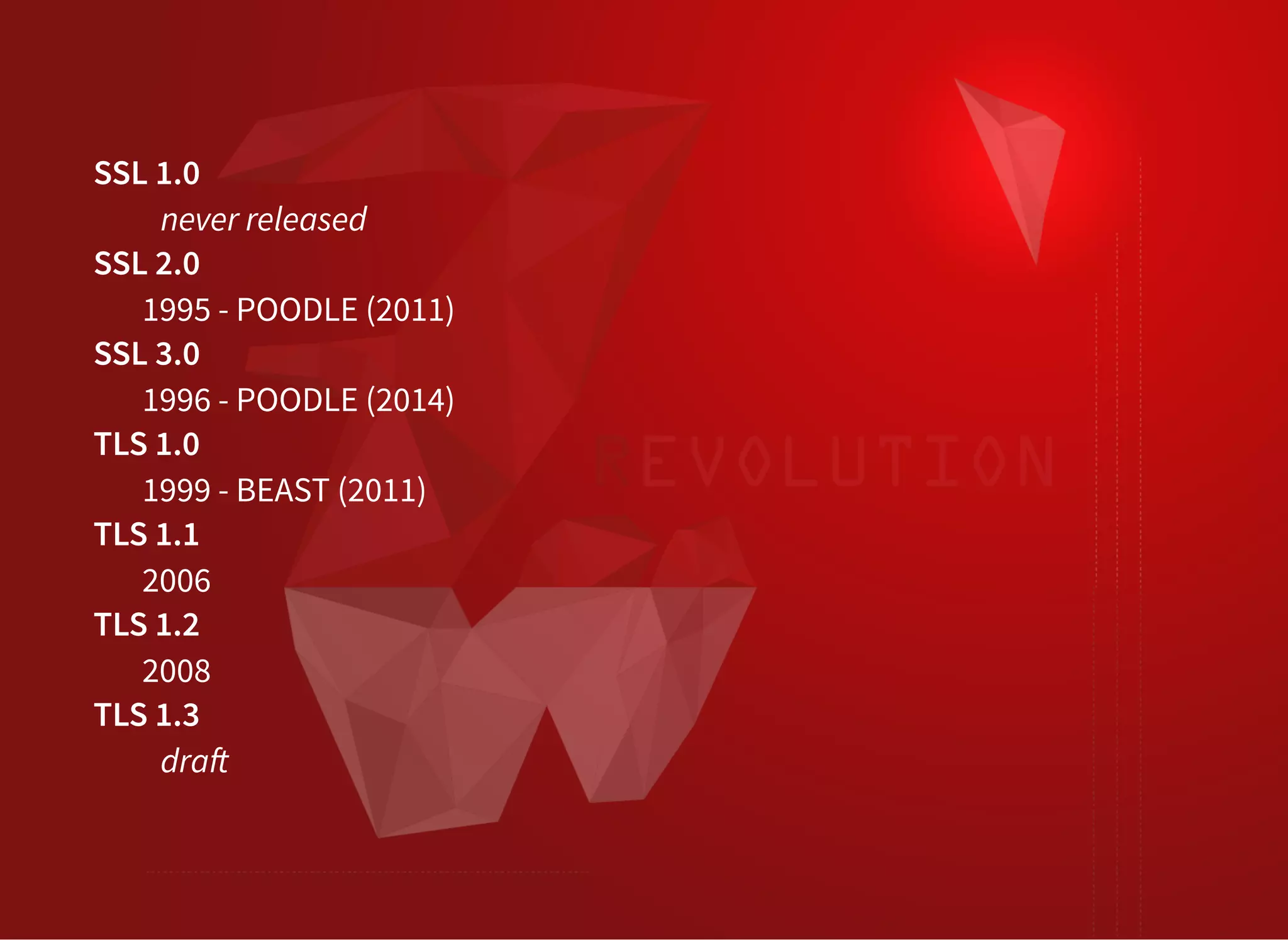
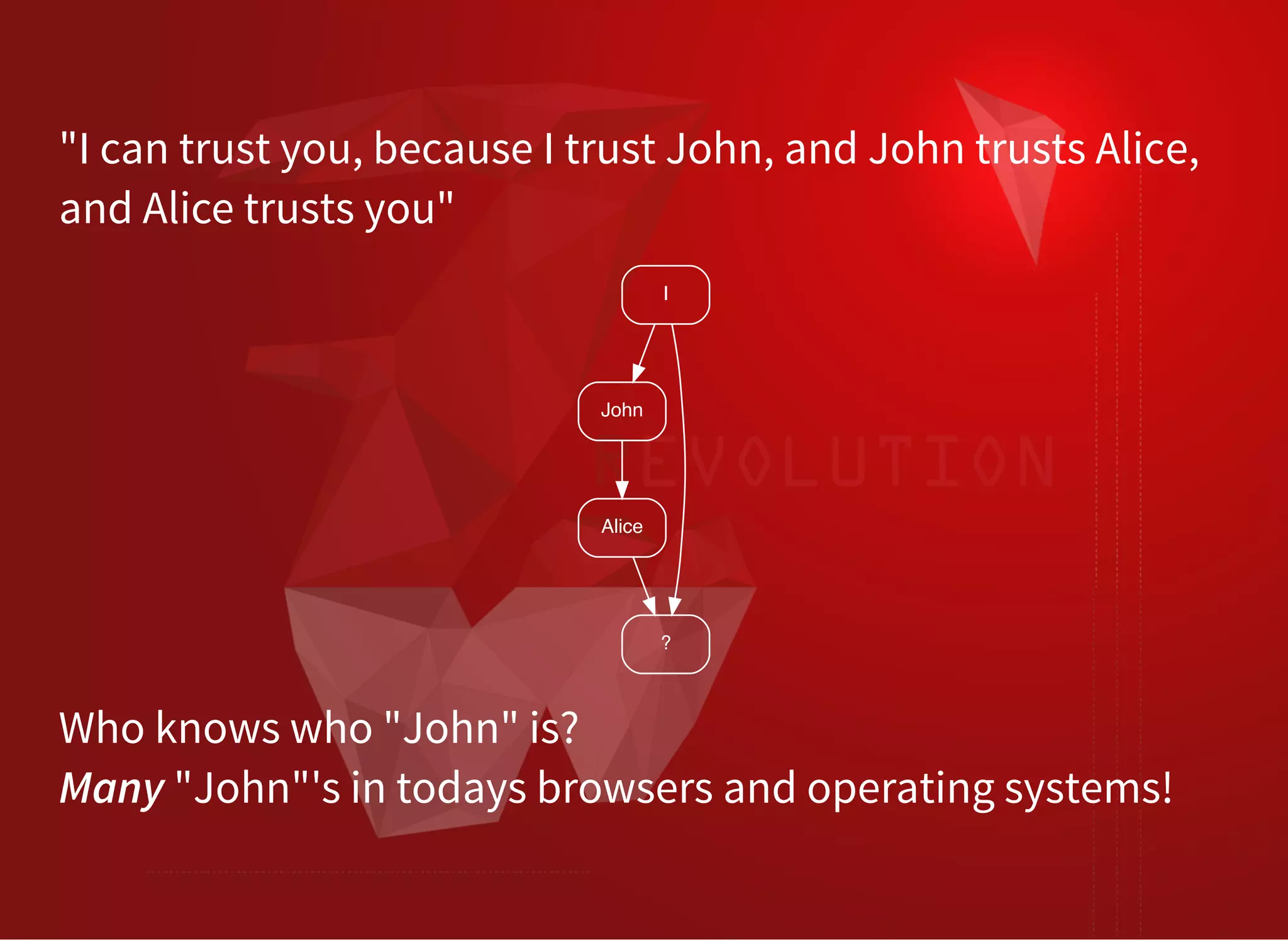
The document discusses SSL/TLS troubleshooting, specifically errors related to certificate validation failures and the need for secure connections between systems. It outlines key concepts such as public/private key encryption, signed certificates, and certificate authorities, along with a historical context of SSL/TLS protocols. A significant example highlighted is the compromise of the Dutch certificate authority DigiNotar, which led to widespread trust issues in digital certificates.
















![A is a mathematical relationship between a
message , a private key and a public key .
signature
x sk pk
It consists of two functions:
1. signing function
2. verifying function
t = f (sk, x)
[accept, reject] = g(pk, t, x)
So, given and and knowing ,
we can tell if is indeed signed by .
x t pk
x sk](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ssltlsformortalsdevoxxfr2018-180419171111/75/SSL-TLS-for-Mortals-Devoxx-FR-2018-23-2048.jpg)





![Due to the weak security of Windows
passwords it must be assumed that the
attacker was able to compromise the
passwords [...] of the accounts found on the
system. On the system, [...] the domain
administrator account [...] is present.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ssltlsformortalsdevoxxfr2018-180419171111/75/SSL-TLS-for-Mortals-Devoxx-FR-2018-30-2048.jpg)