1) Surgical site infections are caused by contamination of the incision site during surgery by microorganisms from the patient or environment. Staphylococcus aureus is the most common cause.
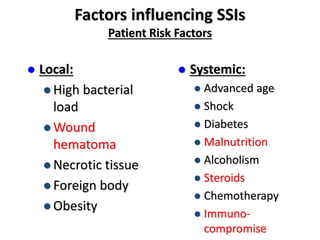
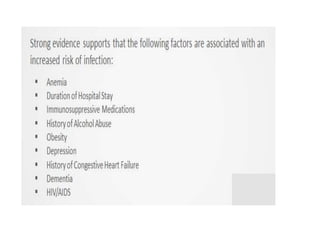
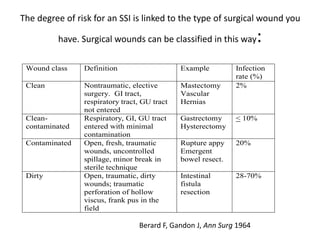
2) Risk factors for SSIs include longer surgeries, contaminated/dirty wounds, diabetes, obesity, and poor wound care after surgery. Proper antibiotic use, sterile technique, and monitoring wounds post-operatively can help prevent infections.
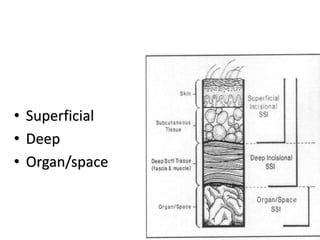
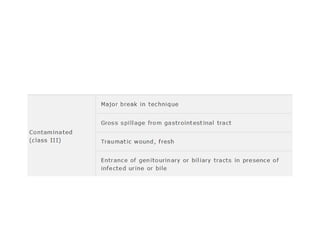
3) SSIs are classified as superficial, deep, or organ/space based on the involved tissue layers. Treatment involves removing sutures and draining pus from infected sites.