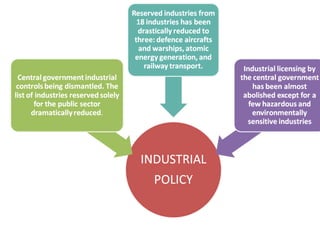
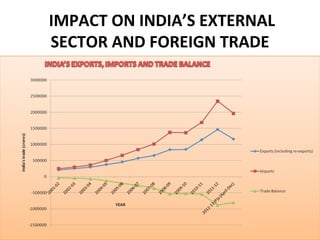
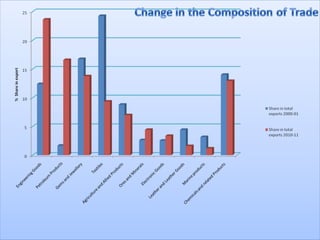
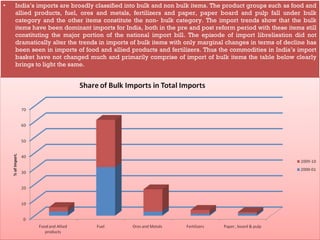
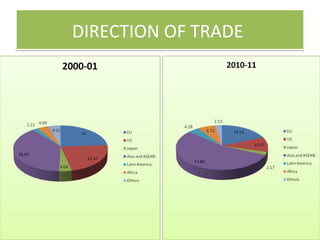
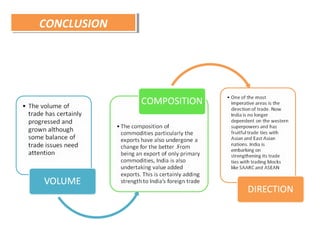
This document discusses trends in India's foreign trade sector following economic reforms introducing liberalization, privatization, and globalization policies from 1991 onward. It aims to analyze the impact of reforms on the volume, composition and direction of India's foreign trade. Key points discussed include trade and industry reforms promoting trade liberalization; India's continued dominant imports of bulk commodities like fuels, ores and metals; and shifts in the direction of India's trade toward East Asian countries under the "Look East" policy. The document examines these trends in India's external trade and concludes the analysis.