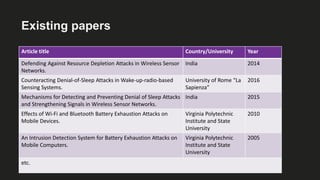
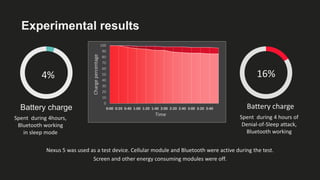
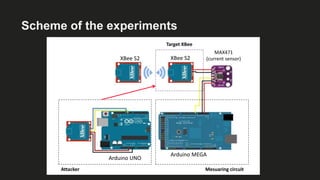
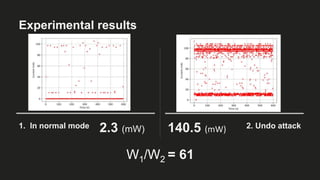
The document presents an analysis of energy depletion attacks on wireless devices, specifically focusing on smartphones and Zigbee-based networks. It discusses various attack types, including denial-of-sleep and electromagnetic interference, and provides experimental results demonstrating the effectiveness of these attacks. Conclusions emphasize the ease of implementing energy depletion attacks and suggest the need for protective measures against such vulnerabilities.