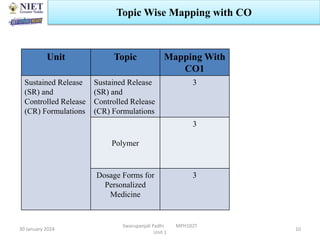
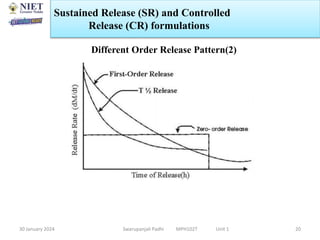
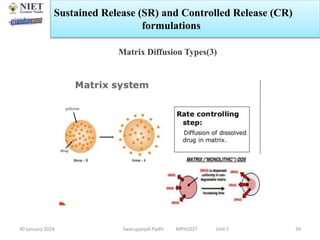
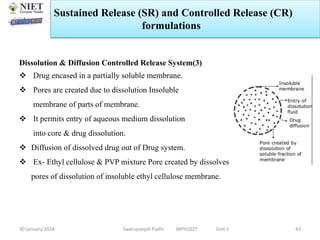
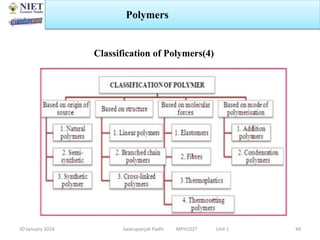
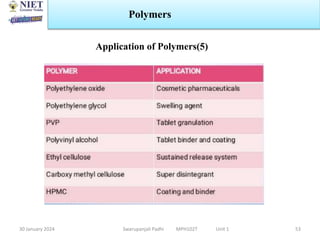
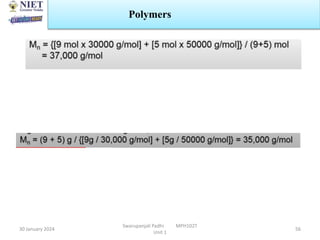
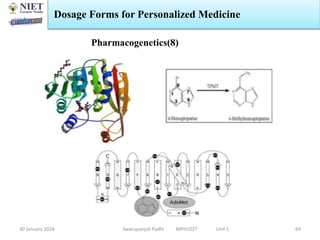
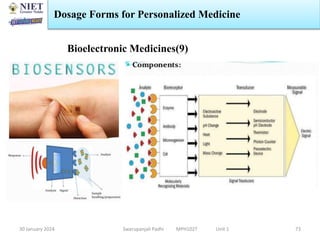
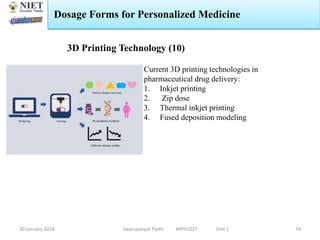
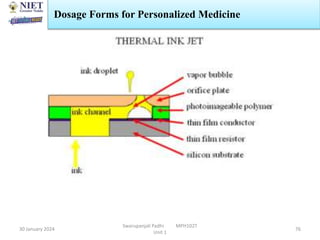
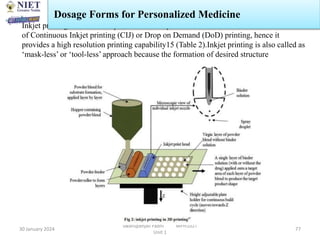
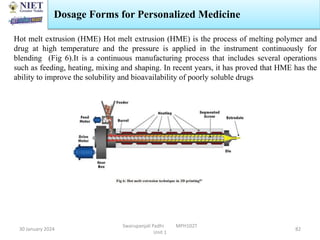
The document provides an overview of a course on sustained release and controlled release formulations being taught by Swarupanjali Padhi at Noida Institute of Engineering and Technology. The course covers topics such as basic concepts of sustained and controlled release, factors influencing drug delivery from sustained release formulations, approaches for developing sustained and controlled release formulations including chemical, biological and pharmaceutical approaches, and mechanisms of drug delivery from sustained and controlled release systems such as dissolution, diffusion and combinations. The syllabus, objectives, outcomes and mapping are also outlined.