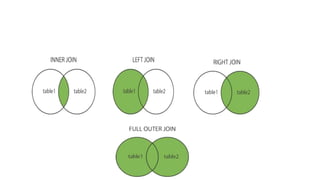
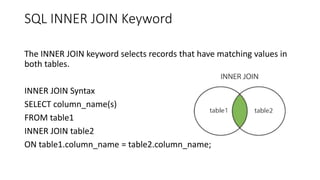
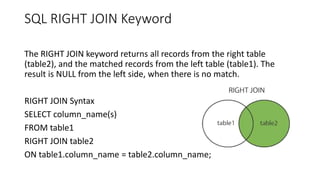
SQL JOIN allows combining rows from multiple tables based on related columns. There are different types of joins: inner joins return matching rows; left and right outer joins return all rows from the left/right table and matching rows from the right/left table; full outer joins return all rows when there are matches in either table. Joins are used with the SELECT statement to retrieve data from multiple tables based on column relationships.