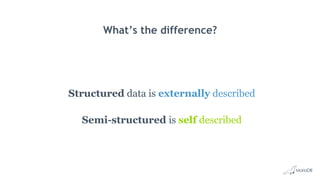
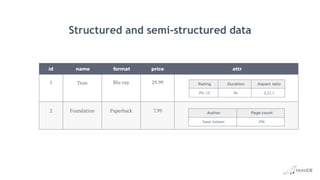
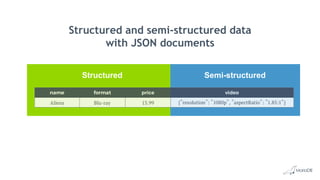
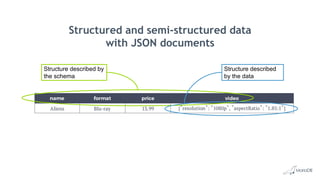
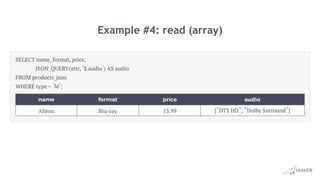
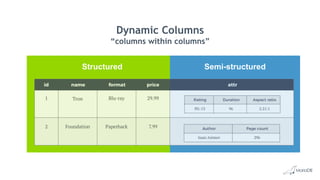
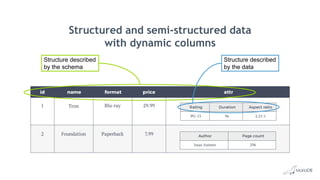
The document discusses using structured and semi-structured data together in modern applications. It describes how MariaDB Server handles both types of data through features like dynamic columns and JSON functions that allow storing and querying JSON documents. The presentation provides examples of defining, creating, reading, updating, and constraining both JSON documents and dynamic columns to bring the flexibility of semi-structured data to the reliability of relational databases.