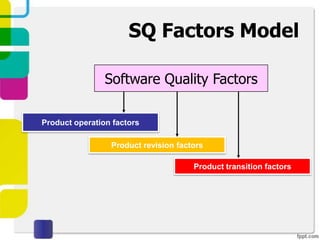
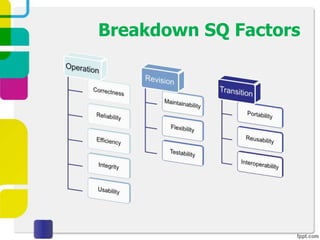
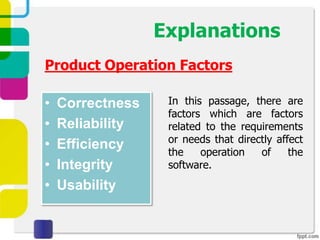
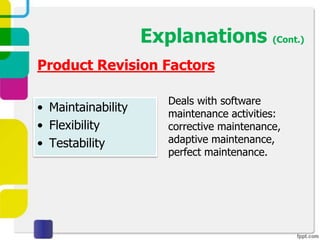
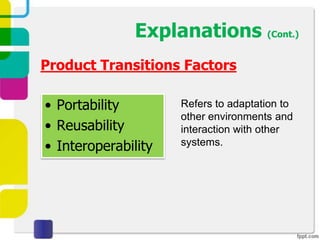
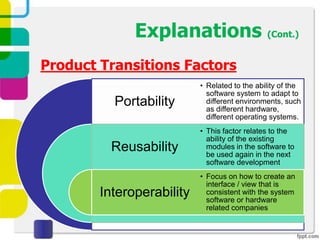
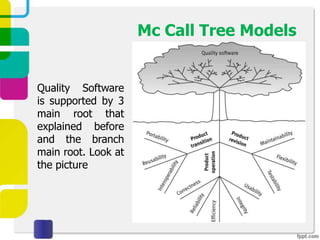
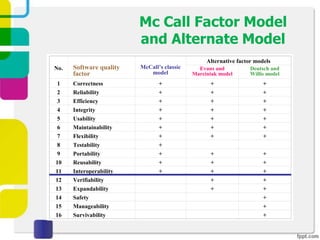
McCall proposed a model in 1977 to measure software quality based on quality factors related to software requirements. The model breaks quality factors into three main categories: product operation factors, product revision factors, and product transition factors. Alternative models by Evans/Marciniak and Deutsch/Willis also use these factors to evaluate software quality.