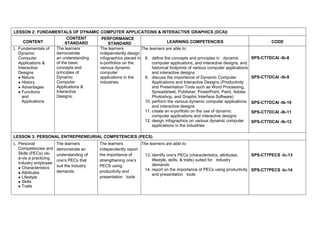
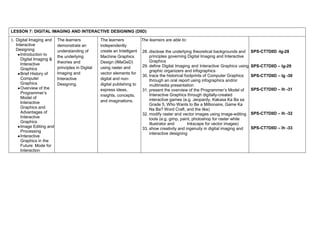
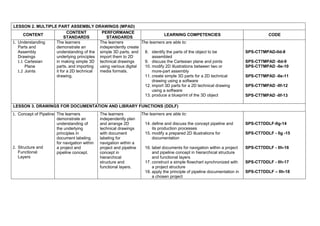
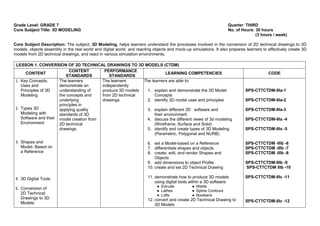
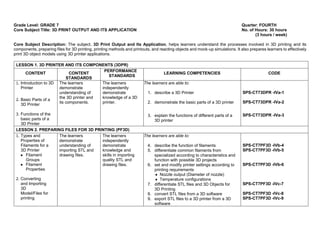
The document provides the curriculum guide for the subject Creative Technologies for Grade 7 learners under the Special Program in Science (Secondary) in the Department of Education Region VII – Central Visayas, Philippines. Creative Technologies is a contextualized Technology and Livelihood Education subject that aims to support the research interests of scientifically inclined learners. The curriculum is project-based, with half of learner time spent on laboratory work developing various projects applying ideas in different fields. By the end of Grade 7, learners will understand product design and development processes and apply engineering design methodologies to solve real-world problems using computer design tools and 3D printing.