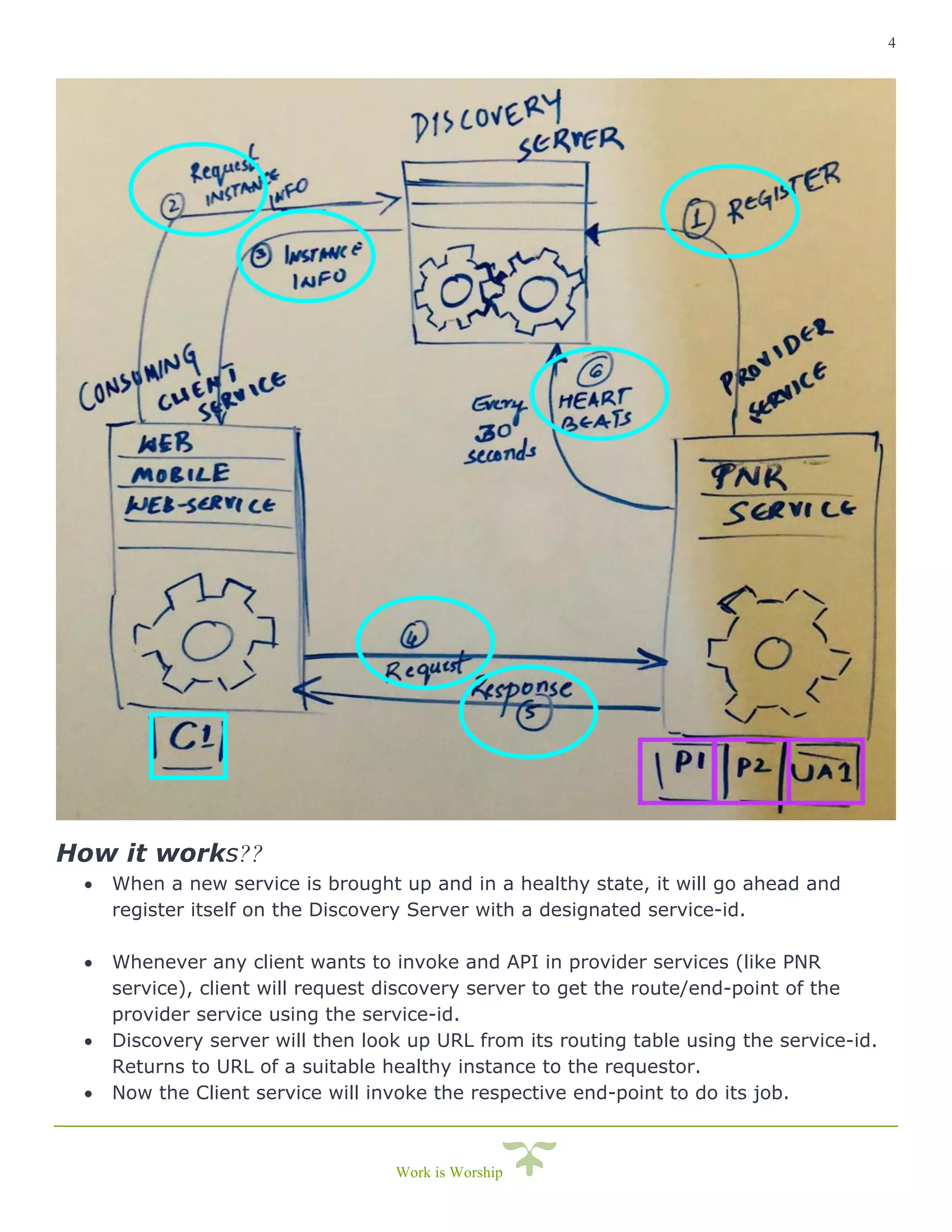
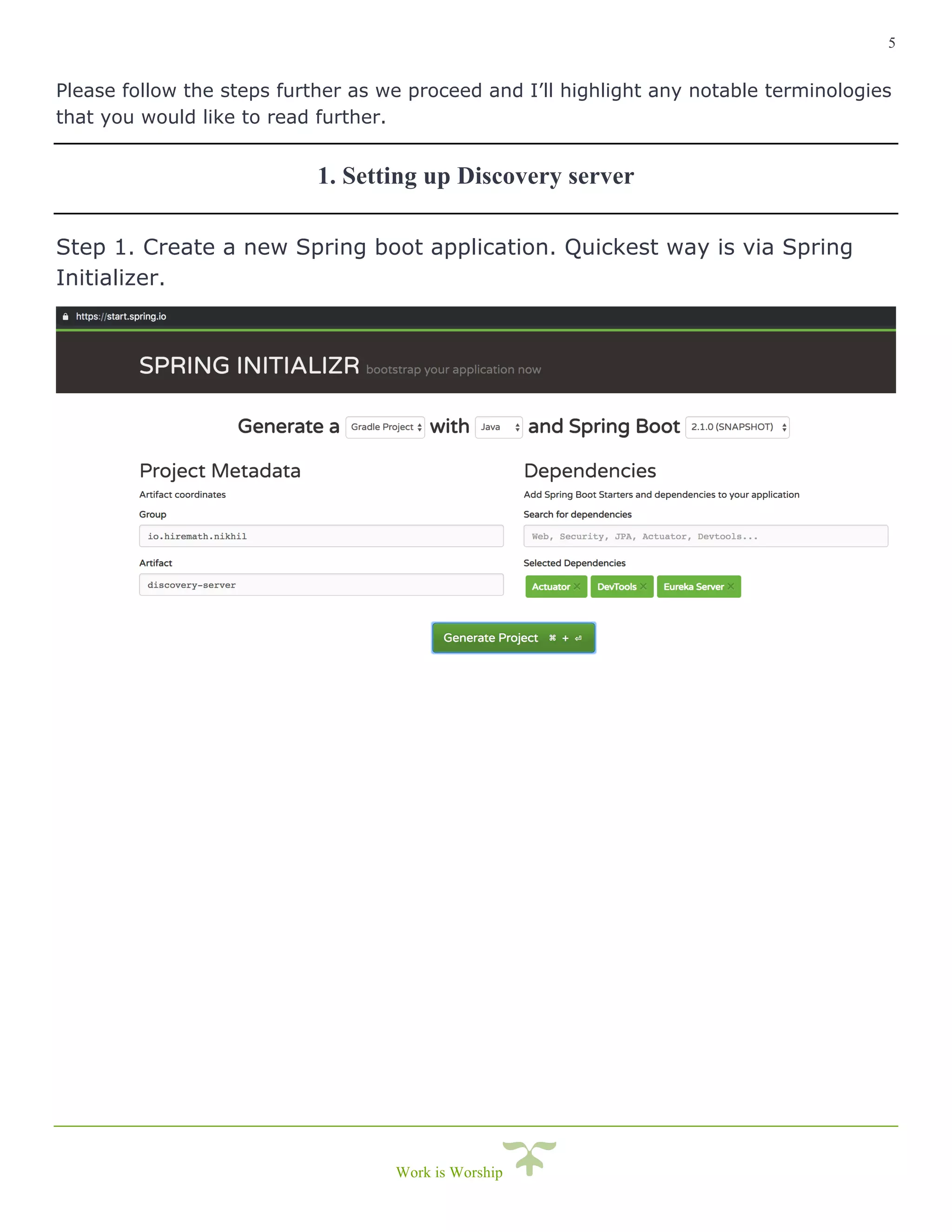
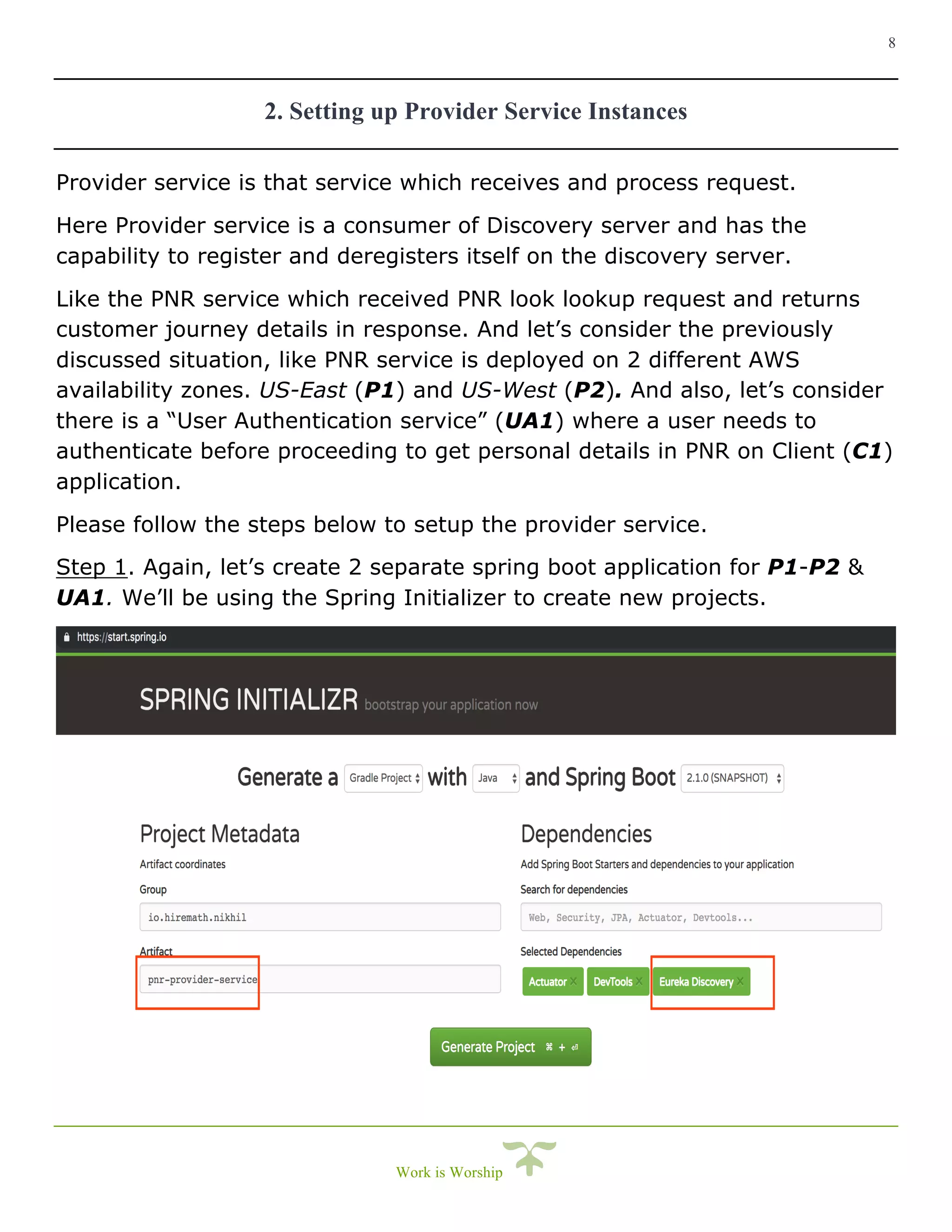
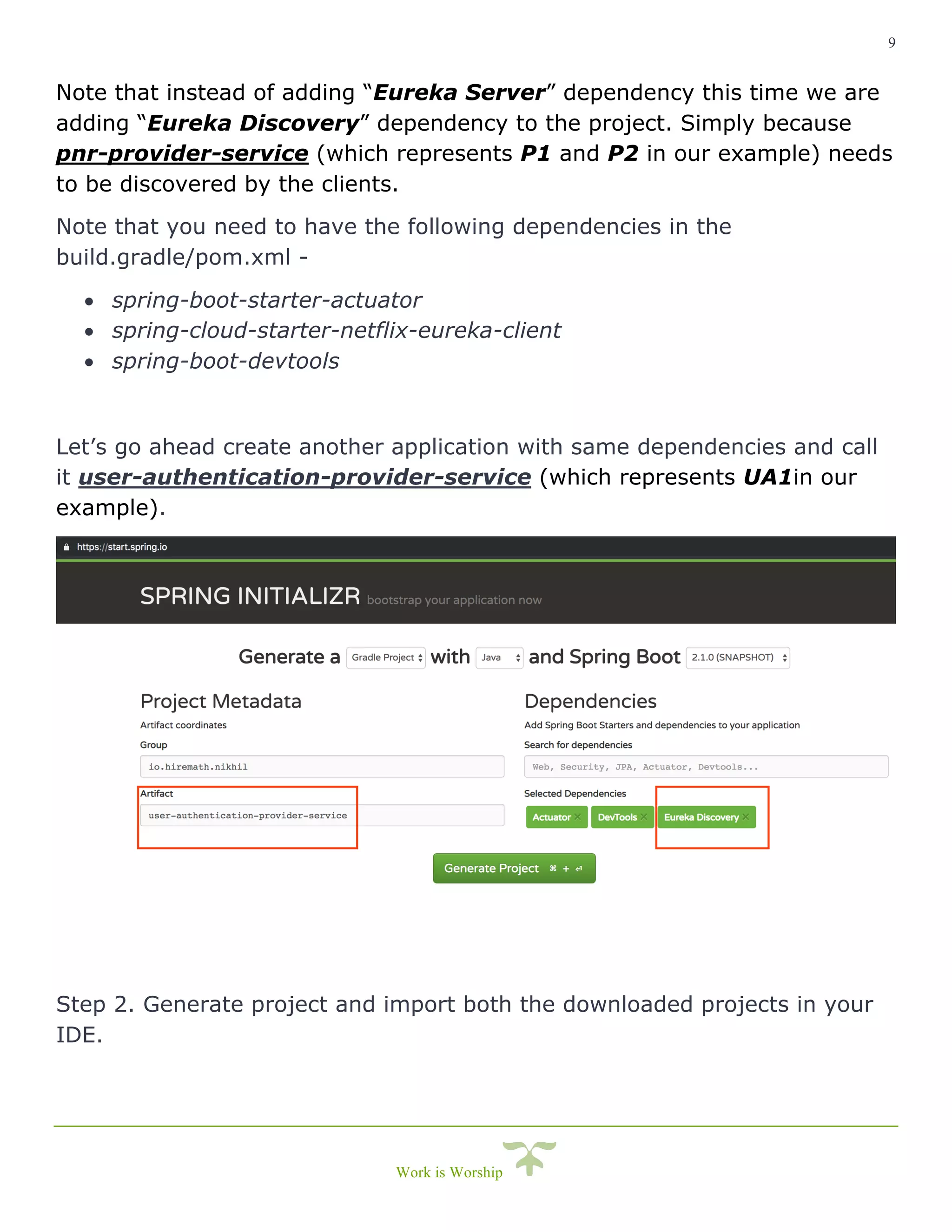
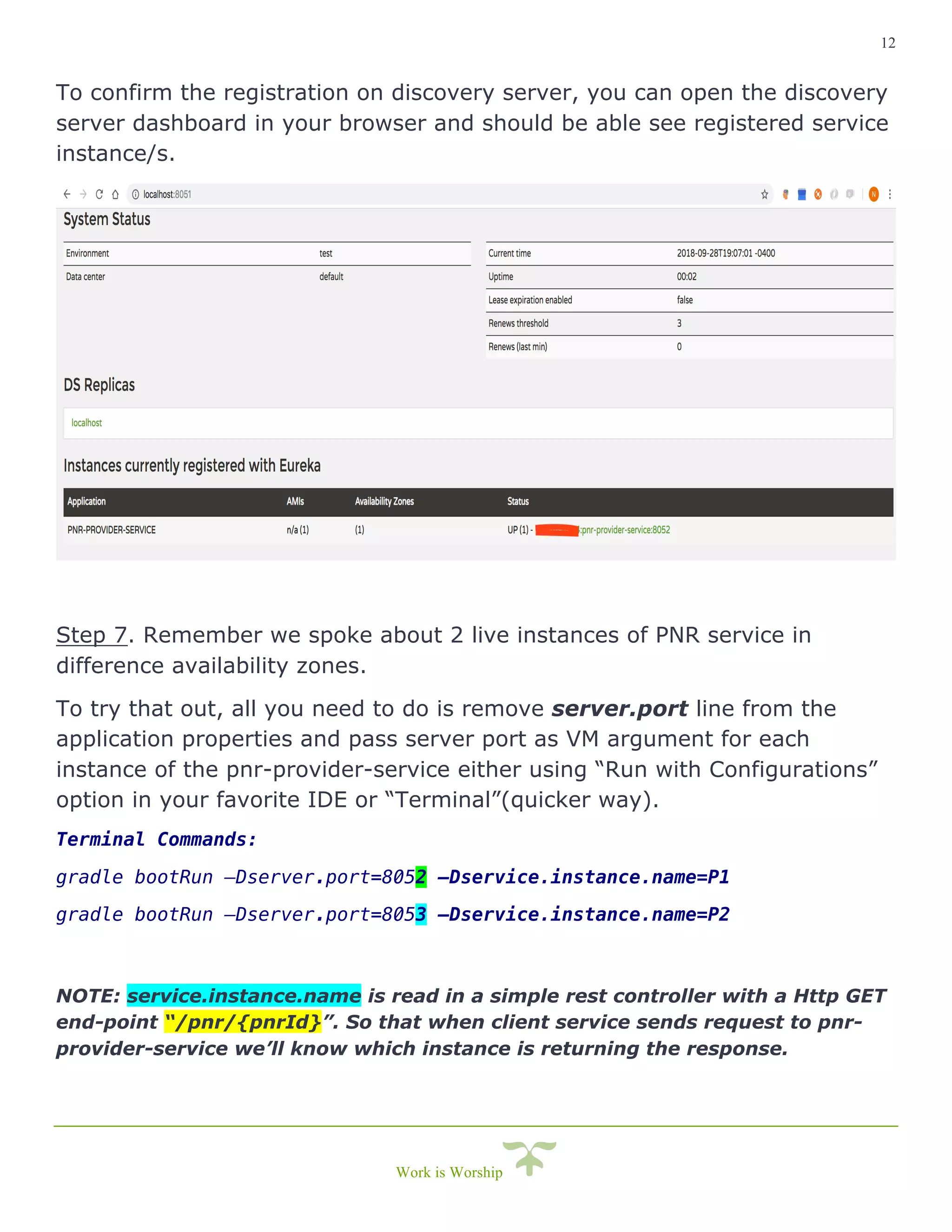
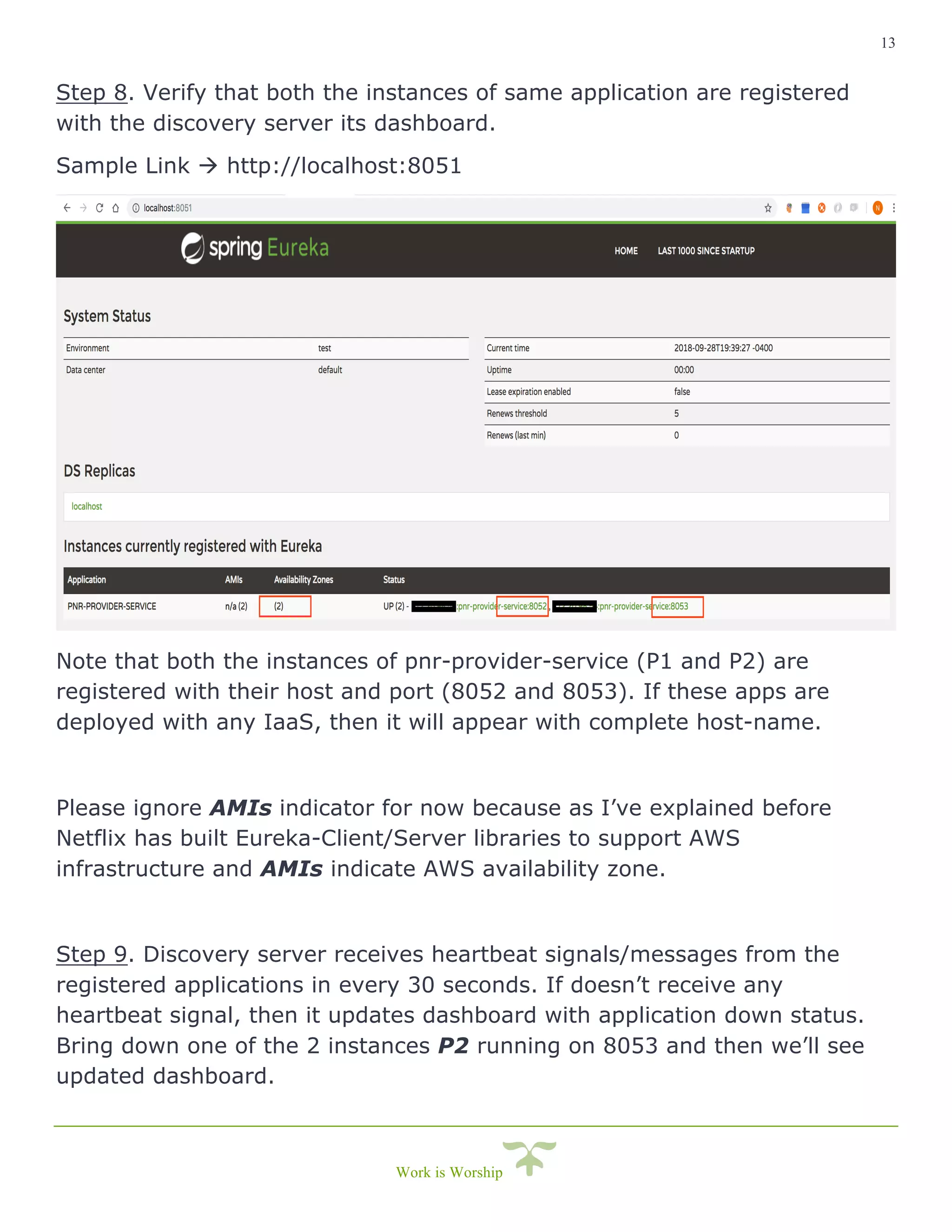
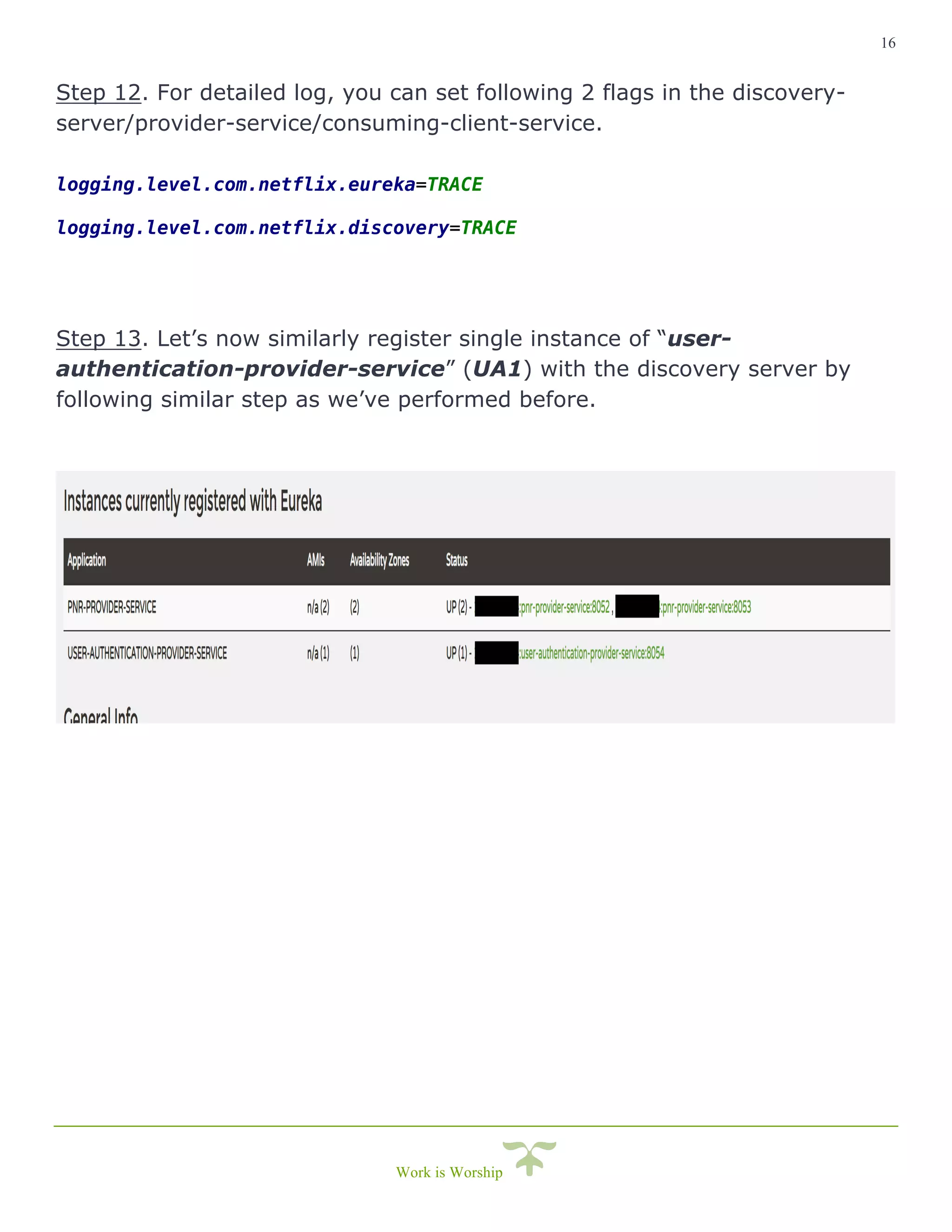
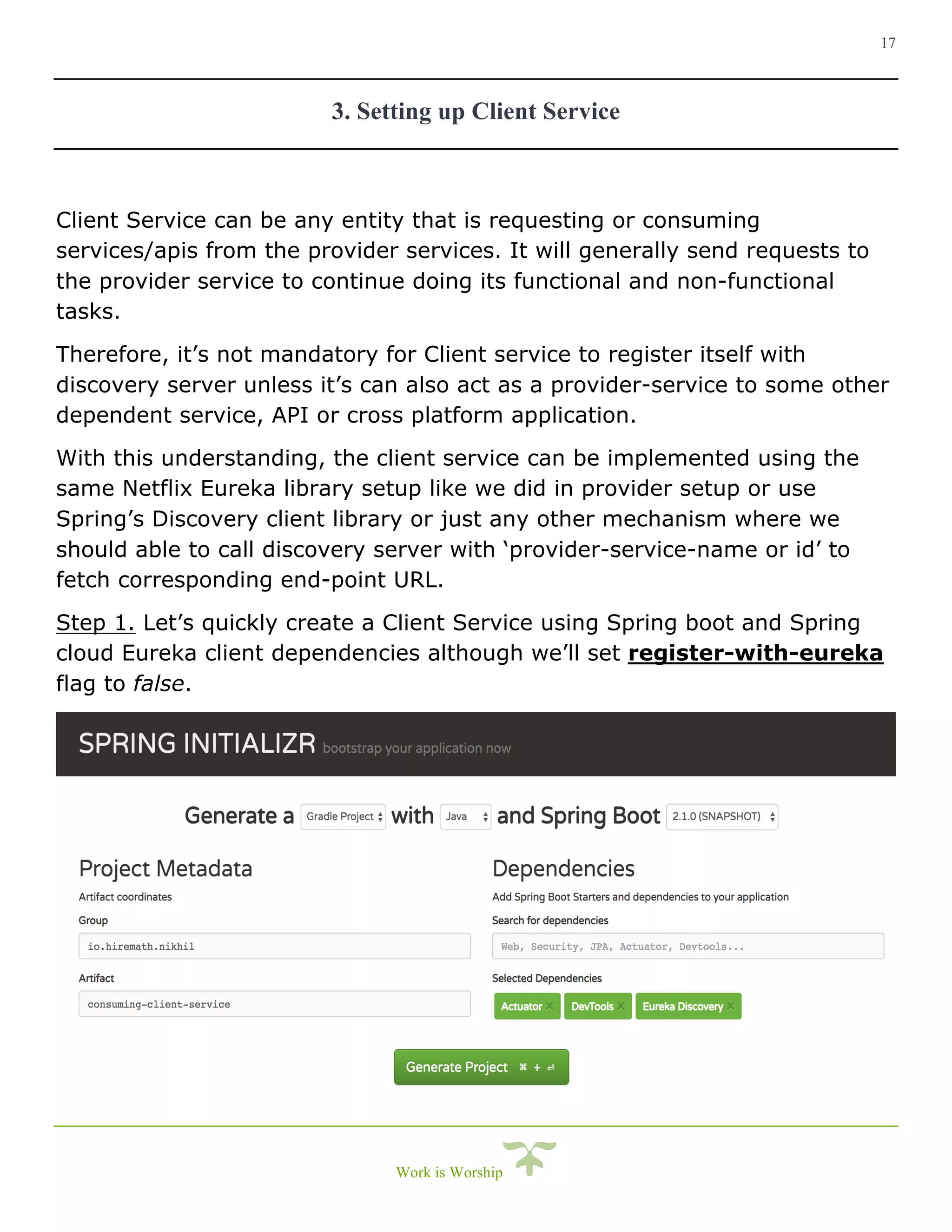
This document is a comprehensive guide on implementing service discovery using Spring Cloud, particularly focusing on Netflix Eureka. It outlines the importance of service discovery in microservices architecture, where clients can dynamically discover services without knowing their physical locations, thus easing the burden of URL management. The guide also provides practical steps for setting up both the discovery server and service instances, along with configuring a client service to utilize the discovery capabilities.