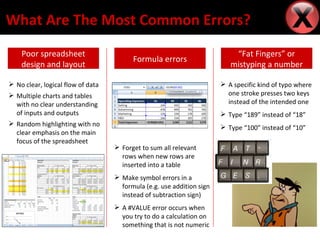
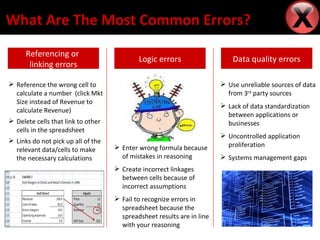
Professor Ray Panko conducted research on spreadsheet errors by auditing spreadsheets from various organizations. He found that while most spreadsheet errors occur in only a few percent of cells, these errors can be quite costly for organizations. Some common causes of spreadsheet errors include poor design, typos, formula errors, and lack of understanding of inputs and outputs. The most prevalent errors are referencing or linking errors, data quality issues, and logical flaws in reasoning. To prevent errors, organizations should train users, establish documentation and data standards, implement security measures, and check calculations.