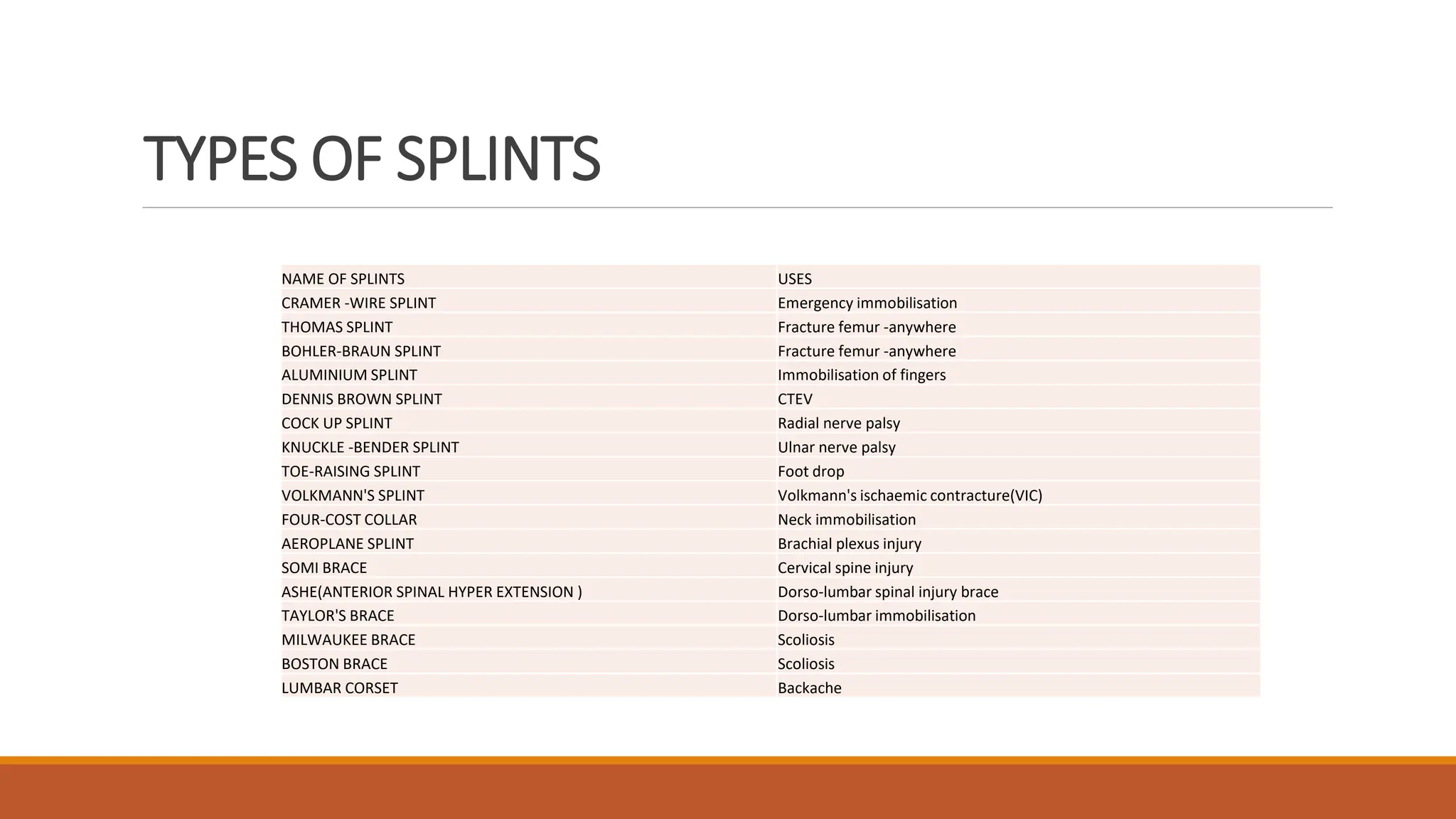
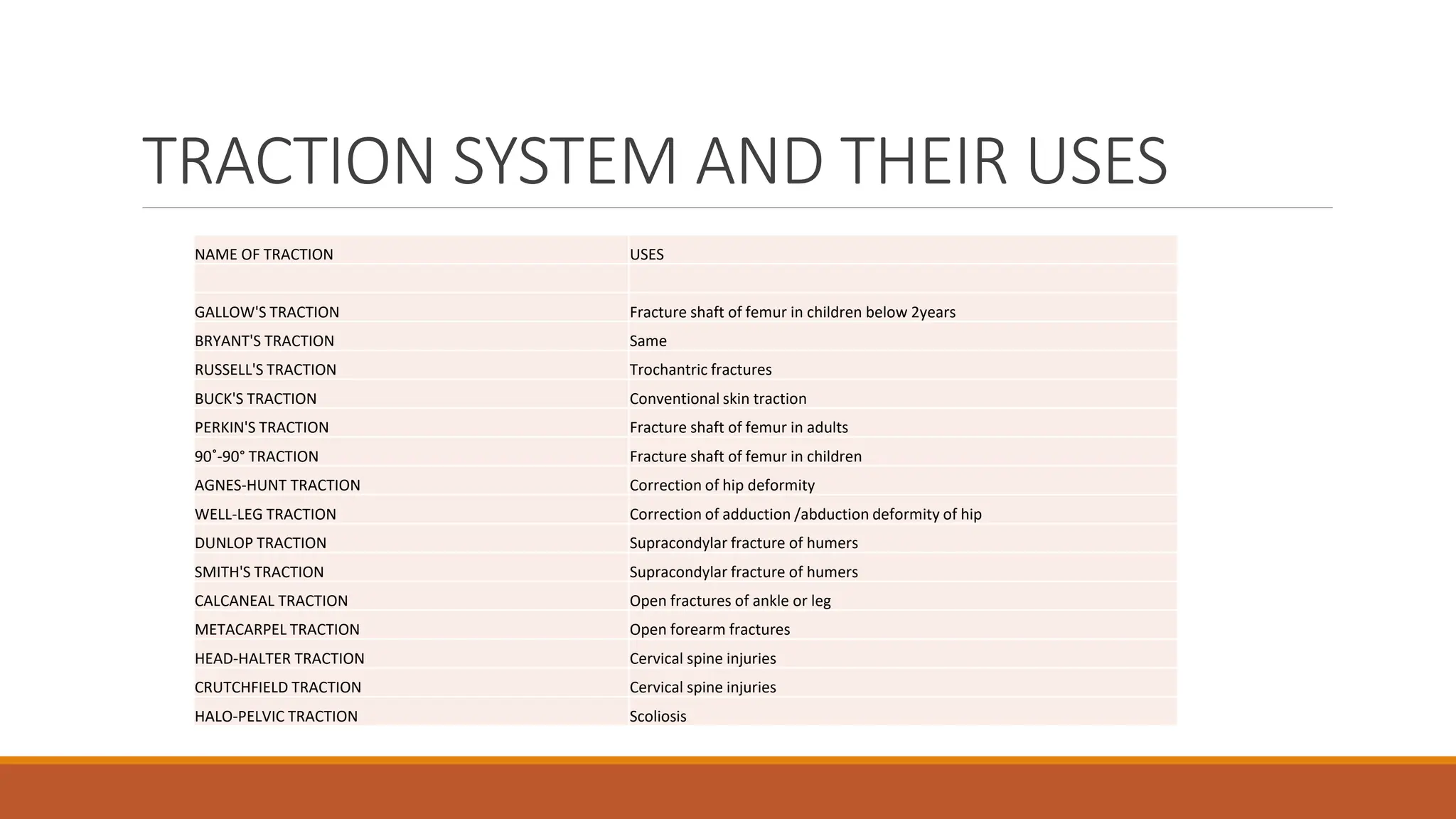
The document discusses splints and traction used in orthopedic practice, highlighting their purposes, types, and specific examples. It details various splints used for immobilizing fractures and other orthopedic conditions, as well as the two types of traction: fixed and sliding, with methods of application including skin and skeletal traction. The document also emphasizes the care of patients using splints and traction to ensure effectiveness and comfort.