The document discusses the 'Spider' system, a paraphrasing tool aimed at enhancing document editing and supporting machine translation pre-editing. It outlines the importance of paraphrases in natural language processing (NLP), pedagogical and professional contexts, and details Spider's development, features, and evaluation results. Future applications and research directions for the tool are also suggested, emphasizing its role in improving writing, translation, and linguistic quality assurance.


![IMPORTANCE OF PARAPHRASES IN NLP TASKS
Question Answering
[Ibrahim et al., 2003], [Paşca, 2003], [Duboué & Chu-Carroll, 2006]
Information Extraction and Text Mining
[Ibrahim et al., 2003], [Shinyama et al., 2002] [Shinyama & Sekine, 2003],
[Sekine, 2005] [Paşca, 2005], [Paşca & Dienes, 2005]
Summarization
[McKeown et al., 2002], [Barzilay, 2001, 2003], [Hirao et al., 2004] [Zhou et
al., 2006b]
Natural Language Generation
[Iordanskaja et al. 1991]
Plagiarism Detection
[Potthast et al., 2010], [Vila et al., 2010]
Machine Translation
[Zhou et al., 2006], [Callison-Burch et al., 2006a, 2006b, 2007 and 2008]
[Barreiro, 2008, 2009, 2011]
CICLing 2011 February 20-26, 2011
Anabela Barreiro Tokyo, Japan](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/spiderab-13007070343975-phpapp02/85/SPIDER-a-System-for-Paraphrasing-Applicability-in-Machine-Translation-Pre-Editing-Anabela-Barreiro-3-320.jpg)








![LINGUISTIC RESOURCES
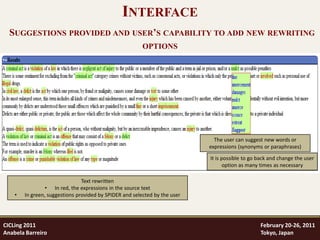
General language dictionary entries
impress,V+FLX=POLISH+SAL=PVPCpleasetype+PT=impressionar+DRV=NDRV01:BOOK+
VSUP=make+VSUP=cause+NPREP=on Morpho-syntactic
aesthetic,AFLX=NATURAL+SAL=AVstate+PT=aesthetically+DRV=AVDRV03 and semantic
relations
skepticism,N+FLX=BOOK+SAL=ABcause+PT=cepticismo+DRV=NAVDRV02
NDRV04 = <B>ion/Npred+Nom Rules to transform
morpho-syntactically
ADRV02 = <B>icable and semantically
AVDRV01 = <E>ly/ADV related words of
different parts of
AVDRV04 = <B>tically/ADV speech
Grammar to recognize adverbial compounds and
transform them into equivalent single adverbs
Contextual rules
Rules to improve precision
in specific contexts
[bring(vt)) N(charge; action)
> present(vt) N(idem)]
CICLing 2011 February 20-26, 2011
Anabela Barreiro Tokyo, Japan](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/spiderab-13007070343975-phpapp02/85/SPIDER-a-System-for-Paraphrasing-Applicability-in-Machine-Translation-Pre-Editing-Anabela-Barreiro-15-320.jpg)