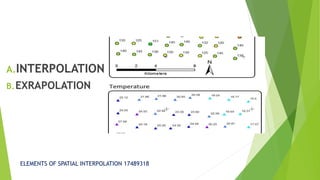
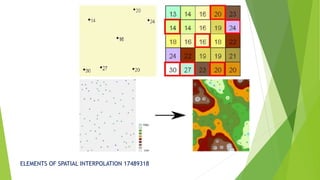
The document discusses spatial interpolation techniques. Spatial interpolation is the process of using points with known values to estimate values at other points, turning raw data into useful information by adding context and values. It can predict unknown values for geographic point data like elevation, rainfall, or chemical concentration. Common uses of spatial interpolation in GIS include calculating properties of a surface at given points, providing contours for graphical displays, and aiding in spatial decision making like terrain analysis and hydrology. Interpolation methods can be classified as global or local, exact or approximate, stochastic or deterministic, and abrupt or smooth.